CN-0273 (Rev.B)
... The next step is to analyze the common-mode voltage restrictions. The common-mode voltage at the input to the ADA4817-2 must fall between −VS to +VS − 1.8 V, or −5 V to +2.2 V for ±5 V supplies. The output swing of the ADA4817-2 is limited to ±3.5 V when operating on ±5 V supplies (refer to the ADA4 ...
... The next step is to analyze the common-mode voltage restrictions. The common-mode voltage at the input to the ADA4817-2 must fall between −VS to +VS − 1.8 V, or −5 V to +2.2 V for ±5 V supplies. The output swing of the ADA4817-2 is limited to ±3.5 V when operating on ±5 V supplies (refer to the ADA4 ...
Building a CIM Network Model
... Voltage or phase angle @ High Step (RMA1) Voltage or phase angle @ Low Step (RMI1) ...
... Voltage or phase angle @ High Step (RMA1) Voltage or phase angle @ Low Step (RMI1) ...
Analyse series ac circuits
... Because this triangle no longer represents the voltages, no arrowheads are used. Each side now represents the electrical properties of: Z = impedance R = resistance XL = inductive reactance This figure is known as the impedance triangle, and it allows us to calculate any one of the sides, knowing th ...
... Because this triangle no longer represents the voltages, no arrowheads are used. Each side now represents the electrical properties of: Z = impedance R = resistance XL = inductive reactance This figure is known as the impedance triangle, and it allows us to calculate any one of the sides, knowing th ...
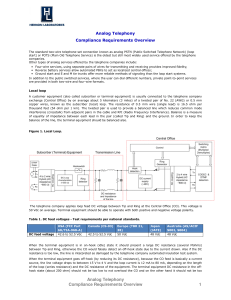
Analog Telephony Overview
... The total harmonic distortion (THD) of the telephone sending and receiving electro-acoustic paths should not exceed 7% (and 10% for higher level signals). An ideal transmission path would output a single continuous wave (CW) signal of the same frequency as the stimulus CW signal applied to the input ...
... The total harmonic distortion (THD) of the telephone sending and receiving electro-acoustic paths should not exceed 7% (and 10% for higher level signals). An ideal transmission path would output a single continuous wave (CW) signal of the same frequency as the stimulus CW signal applied to the input ...
RF2472 2.4GHz LOW NOISE AMPLIFIER WITH ENABLE Features
... examples. The 10nH inductor in the bias line is part of an output impedance matching circuit. At higher frequencies, the impedance of the matching circuit, alone, would become highly inductive. The large reactive termination of the output port could cause the circuit to oscillate at a high frequency ...
... examples. The 10nH inductor in the bias line is part of an output impedance matching circuit. At higher frequencies, the impedance of the matching circuit, alone, would become highly inductive. The large reactive termination of the output port could cause the circuit to oscillate at a high frequency ...
香港考試局
... A series circuit consisting of a pure inductor L, a pure capacitor C and a pure resistor R is connected across an a.c. supply. The variations with applied frequency f of the resistance R, the reactance XC of the capacitor, the reactance XL of the inductor and the impedance Z of the circuit are repre ...
... A series circuit consisting of a pure inductor L, a pure capacitor C and a pure resistor R is connected across an a.c. supply. The variations with applied frequency f of the resistance R, the reactance XC of the capacitor, the reactance XL of the inductor and the impedance Z of the circuit are repre ...
lab sheet - Faculty of Engineering
... noise power that is not within its bandwidth. Since the noise power within the bandwidth is very small, a high signal-to-noise ratio at the output can be attained. Enable transformer coupling and impedance transformation – Sometimes the load can be coupled to the amplifier through mutual inductance. ...
... noise power that is not within its bandwidth. Since the noise power within the bandwidth is very small, a high signal-to-noise ratio at the output can be attained. Enable transformer coupling and impedance transformation – Sometimes the load can be coupled to the amplifier through mutual inductance. ...
Zobel network

For the wave filter invented by Zobel and sometimes named after him see m-derived filters.Zobel networks are a type of filter section based on the image-impedance design principle. They are named after Otto Zobel of Bell Labs, who published a much-referenced paper on image filters in 1923. The distinguishing feature of Zobel networks is that the input impedance is fixed in the design independently of the transfer function. This characteristic is achieved at the expense of a much higher component count compared to other types of filter sections. The impedance would normally be specified to be constant and purely resistive. For this reason, they are also known as constant resistance networks. However, any impedance achievable with discrete components is possible.Zobel networks were formerly widely used in telecommunications to flatten and widen the frequency response of copper land lines, producing a higher-quality line from one originally intended for ordinary telephone use. However, as analogue technology has given way to digital, they are now little used.When used to cancel out the reactive portion of loudspeaker impedance, the design is sometimes called a Boucherot cell. In this case, only half the network is implemented as fixed components, the other half being the real and imaginary components of the loudspeaker impedance. This network is more akin to the power factor correction circuits used in electrical power distribution, hence the association with Boucherot's name.A common circuit form of Zobel networks is in the form of a bridged T. This term is often used to mean a Zobel network, sometimes incorrectly when the circuit implementation is, in fact, something other than a bridged T.Parts of this article or section rely on the reader's knowledge of the complex impedance representation of capacitors and inductors and on knowledge of the frequency domain representation of signals.↑