Electrical Formulas
... secondary. This applied voltage divided by the rated primary voltage (times 100) is the impedance of the transformer. Example: For a 480 Volt rated primary, if 9.6 volts causes secondary full load current to flow through the shorted secondary, the transformer impedance is 9.6/480 = .02 = 2%Z. * Note ...
... secondary. This applied voltage divided by the rated primary voltage (times 100) is the impedance of the transformer. Example: For a 480 Volt rated primary, if 9.6 volts causes secondary full load current to flow through the shorted secondary, the transformer impedance is 9.6/480 = .02 = 2%Z. * Note ...
bodeplot
... Remember – you’ll load in actual data from your experiment! Next I’ll construct the data points that correspond to a second order system with the transfer function used in the Case 1 example. I’ll do that in two steps: first calculating the magnitude of the denominator, then taking the reciprocal. Y ...
... Remember – you’ll load in actual data from your experiment! Next I’ll construct the data points that correspond to a second order system with the transfer function used in the Case 1 example. I’ll do that in two steps: first calculating the magnitude of the denominator, then taking the reciprocal. Y ...
TPA2001D2 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... settings, smaller packaging, and fewer external components. The most significant advancement with this device is its modulation scheme that allows the amplifier to operate without the output filter. Eliminating the output filter saves the user approximately 30% in system cost and 75% in PCB area. Th ...
... settings, smaller packaging, and fewer external components. The most significant advancement with this device is its modulation scheme that allows the amplifier to operate without the output filter. Eliminating the output filter saves the user approximately 30% in system cost and 75% in PCB area. Th ...
Uses and Limitations of Micro-Synchrophasor
... PMUs, which enable extremely precise measurement of voltages and currents, are a mature technology widely used throughout high-voltage transmission applications. They have not yet been utilized in lower-voltage, distribution-level operations, though, in part because electric failures and power outag ...
... PMUs, which enable extremely precise measurement of voltages and currents, are a mature technology widely used throughout high-voltage transmission applications. They have not yet been utilized in lower-voltage, distribution-level operations, though, in part because electric failures and power outag ...
Simulating FPGA Power Integrity Using S-Parameter Models
... Decoupling capacitors are often characterized by vendors by means of three parameters: R (resistance), L (inductance), and C (capacitance). The C parameter is the decap's intrinsic capacitance; the L is its intrinsic inductance; and the R is the ESR of the decoupling capacitor. When this simple RLC ...
... Decoupling capacitors are often characterized by vendors by means of three parameters: R (resistance), L (inductance), and C (capacitance). The C parameter is the decap's intrinsic capacitance; the L is its intrinsic inductance; and the R is the ESR of the decoupling capacitor. When this simple RLC ...
2. experimental
... Subharmonic sequences were generated by gradual increase of driving current keeping the selected driving frequency constant (45 < f < 55 Hz). The sequences appear at particular discrete values of I0, and the process recorded in air is shown in Fig. 4. The resonant mode (f=45 Hz) is clearly visible i ...
... Subharmonic sequences were generated by gradual increase of driving current keeping the selected driving frequency constant (45 < f < 55 Hz). The sequences appear at particular discrete values of I0, and the process recorded in air is shown in Fig. 4. The resonant mode (f=45 Hz) is clearly visible i ...
AN-679 APPLICATION NOTE
... (also know as the Nyquist frequency), i.e., 450 kHz, are imaged or folded back down below 225 kHz (arrows labeled as Image Frequencies). This will happen with all ADCs no matter what the archi tecture. In the example shown, it can be seen that only frequencies near the sampling frequency, i.e., 450 ...
... (also know as the Nyquist frequency), i.e., 450 kHz, are imaged or folded back down below 225 kHz (arrows labeled as Image Frequencies). This will happen with all ADCs no matter what the archi tecture. In the example shown, it can be seen that only frequencies near the sampling frequency, i.e., 450 ...
Lecture 4: RLC series circuit: V
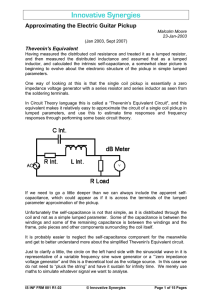
... Ideally, the frequency response is flat over 20-20,000 Hz, and rolls off sharply at frequencies below 20 Hz and above 20,000 Hz. ...
... Ideally, the frequency response is flat over 20-20,000 Hz, and rolls off sharply at frequencies below 20 Hz and above 20,000 Hz. ...
Lecture 4: RLC series circuit: V
... Ideally, the frequency response is flat over 20-20,000 Hz, and rolls off sharply at frequencies below 20 Hz and above 20,000 Hz. ...
... Ideally, the frequency response is flat over 20-20,000 Hz, and rolls off sharply at frequencies below 20 Hz and above 20,000 Hz. ...
Zobel network

For the wave filter invented by Zobel and sometimes named after him see m-derived filters.Zobel networks are a type of filter section based on the image-impedance design principle. They are named after Otto Zobel of Bell Labs, who published a much-referenced paper on image filters in 1923. The distinguishing feature of Zobel networks is that the input impedance is fixed in the design independently of the transfer function. This characteristic is achieved at the expense of a much higher component count compared to other types of filter sections. The impedance would normally be specified to be constant and purely resistive. For this reason, they are also known as constant resistance networks. However, any impedance achievable with discrete components is possible.Zobel networks were formerly widely used in telecommunications to flatten and widen the frequency response of copper land lines, producing a higher-quality line from one originally intended for ordinary telephone use. However, as analogue technology has given way to digital, they are now little used.When used to cancel out the reactive portion of loudspeaker impedance, the design is sometimes called a Boucherot cell. In this case, only half the network is implemented as fixed components, the other half being the real and imaginary components of the loudspeaker impedance. This network is more akin to the power factor correction circuits used in electrical power distribution, hence the association with Boucherot's name.A common circuit form of Zobel networks is in the form of a bridged T. This term is often used to mean a Zobel network, sometimes incorrectly when the circuit implementation is, in fact, something other than a bridged T.Parts of this article or section rely on the reader's knowledge of the complex impedance representation of capacitors and inductors and on knowledge of the frequency domain representation of signals.↑