Phase Relations in Active Filters
... Filter complexity is typically defined by the filter “order,” which is related to the number of energy storage elements (inductors and capacitors). The order of the filter transfer function’s denominator defines the attenuation rate as frequency increases. The asymptotic filter rolloff rate is –6n d ...
... Filter complexity is typically defined by the filter “order,” which is related to the number of energy storage elements (inductors and capacitors). The order of the filter transfer function’s denominator defines the attenuation rate as frequency increases. The asymptotic filter rolloff rate is –6n d ...
MAX3322E/MAX3323E ±15kV ESD-Protected, RS-232 Transceivers for Multidrop Applications General Description
... The MAX3322E/MAX3323E are RS-232 transceivers for multidrop applications (i.e., multiple-receiver operation). The devices are pin selectable between standard RS-232 operation with 5kΩ input resistance receivers or highinput-impedance receivers. Receivers of the MAX3322E/ MAX3323E remain active in bo ...
... The MAX3322E/MAX3323E are RS-232 transceivers for multidrop applications (i.e., multiple-receiver operation). The devices are pin selectable between standard RS-232 operation with 5kΩ input resistance receivers or highinput-impedance receivers. Receivers of the MAX3322E/ MAX3323E remain active in bo ...
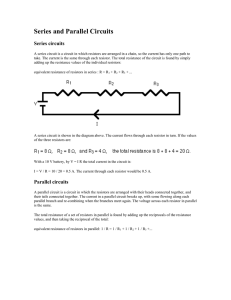
Series and Parallel Circuits
... you have two or more resistors in parallel, look for the one with the smallest resistance. The equivalent resistance will always be between the smallest resistance divided by the number of resistors, and the smallest resistance. Here's an example. You have three resistors in parallel, with values 6 ...
... you have two or more resistors in parallel, look for the one with the smallest resistance. The equivalent resistance will always be between the smallest resistance divided by the number of resistors, and the smallest resistance. Here's an example. You have three resistors in parallel, with values 6 ...
DC/AC Fundamentals: A Systems Approach
... •Band-pass and band-stop filters can be made from both series and parallel resonant circuits. •The bandwidth of a resonant filter is determined by the Q and the resonant frequency. •The output voltage at a critical frequency is 70.7% of the maximum. DC/AC Fundamentals: A Systems Approach Thomas L. F ...
... •Band-pass and band-stop filters can be made from both series and parallel resonant circuits. •The bandwidth of a resonant filter is determined by the Q and the resonant frequency. •The output voltage at a critical frequency is 70.7% of the maximum. DC/AC Fundamentals: A Systems Approach Thomas L. F ...
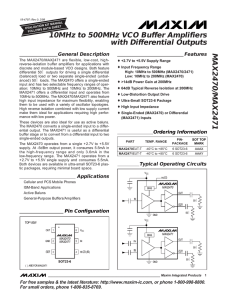
MAX4450/MAX4451 Ultra-Small, Low-Cost, 210MHz, Single-Supply Op Amps with Rail-to-Rail Outputs General Description
... • Don’t use wire-wrap boards; they are too inductive. • Don’t use IC sockets; they increase parasitic capacitance and inductance. • Use surface-mount instead of through-hole components for better high-frequency performance. • Use a PC board with at least two layers; it should be as free from voids a ...
... • Don’t use wire-wrap boards; they are too inductive. • Don’t use IC sockets; they increase parasitic capacitance and inductance. • Use surface-mount instead of through-hole components for better high-frequency performance. • Use a PC board with at least two layers; it should be as free from voids a ...
Aalborg Universitet inverters-based microgrid
... the MG voltage (VPCC), Z is the inductor impedance, E is the DGS capacitor voltage amplitude, V is the grid voltage amplitude and θ is the impedance angle. The droop method used to control the controllable DGS is based on two assumption, the first one is that the output impedance is purely inductive ...
... the MG voltage (VPCC), Z is the inductor impedance, E is the DGS capacitor voltage amplitude, V is the grid voltage amplitude and θ is the impedance angle. The droop method used to control the controllable DGS is based on two assumption, the first one is that the output impedance is purely inductive ...
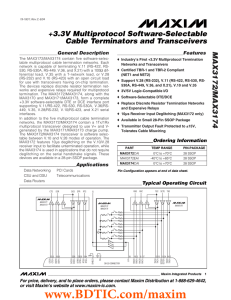
MAX3172/MAX3174 +3.3V Multiprotocol Software-Selectable Cable Terminators and Transceivers General Description
... and R_B with a 100Ω resistor). The receiver output enters a high-impedance state in no-cable mode, allowing this output line to be shared with other receivers (the receiver output has an internal pullup resistor to pull the output HIGH if not driven). Also, in no-cable mode, the transmitter output e ...
... and R_B with a 100Ω resistor). The receiver output enters a high-impedance state in no-cable mode, allowing this output line to be shared with other receivers (the receiver output has an internal pullup resistor to pull the output HIGH if not driven). Also, in no-cable mode, the transmitter output e ...
Zobel network

For the wave filter invented by Zobel and sometimes named after him see m-derived filters.Zobel networks are a type of filter section based on the image-impedance design principle. They are named after Otto Zobel of Bell Labs, who published a much-referenced paper on image filters in 1923. The distinguishing feature of Zobel networks is that the input impedance is fixed in the design independently of the transfer function. This characteristic is achieved at the expense of a much higher component count compared to other types of filter sections. The impedance would normally be specified to be constant and purely resistive. For this reason, they are also known as constant resistance networks. However, any impedance achievable with discrete components is possible.Zobel networks were formerly widely used in telecommunications to flatten and widen the frequency response of copper land lines, producing a higher-quality line from one originally intended for ordinary telephone use. However, as analogue technology has given way to digital, they are now little used.When used to cancel out the reactive portion of loudspeaker impedance, the design is sometimes called a Boucherot cell. In this case, only half the network is implemented as fixed components, the other half being the real and imaginary components of the loudspeaker impedance. This network is more akin to the power factor correction circuits used in electrical power distribution, hence the association with Boucherot's name.A common circuit form of Zobel networks is in the form of a bridged T. This term is often used to mean a Zobel network, sometimes incorrectly when the circuit implementation is, in fact, something other than a bridged T.Parts of this article or section rely on the reader's knowledge of the complex impedance representation of capacitors and inductors and on knowledge of the frequency domain representation of signals.↑