File - the Analysis of Electrical Engineering ELEC 291
... Draw the circuit with calculated values. ...
... Draw the circuit with calculated values. ...
High Definition Stereo Headphone Amplifier Ear+ Purist HD Ear+ HD
... From signal source (e.g. CD player) ...
... From signal source (e.g. CD player) ...
07LAB4 - Guelph Physics
... In summary, we have seen that, if the open loop gain of the amplifier is large, we can have an amplifier circuit whose gain depends only on the ratio of passive components and whose input impedance is equal to Z1. ...
... In summary, we have seen that, if the open loop gain of the amplifier is large, we can have an amplifier circuit whose gain depends only on the ratio of passive components and whose input impedance is equal to Z1. ...
A New Definition of Characteristic Impedance
... evaluating lines of two different lengths (e.g., 1 and 2/). A necessary condition for a unique result is that the port discontinuity ...
... evaluating lines of two different lengths (e.g., 1 and 2/). A necessary condition for a unique result is that the port discontinuity ...
Impedance Spectroscopy, Strength and Limitations
... and relaxation processes) that contribute to the frequency dispersion. Using just a simple equivalent circuit may yield visually an acceptable fit in the impedance or admittance representation, or even a seemingly excellent fit in a Bode representation. Proper analysis, however, can yield more infor ...
... and relaxation processes) that contribute to the frequency dispersion. Using just a simple equivalent circuit may yield visually an acceptable fit in the impedance or admittance representation, or even a seemingly excellent fit in a Bode representation. Proper analysis, however, can yield more infor ...
AP Quiz #24 Circuits
... The current in the circuit is 2 amperes when the resistance in the circuit is adjusted to 10 ohms. Under these conditions the motor lifts a l-kilogram mass vertically at a constant speed of 2 meters per second. a. Determine the electrical power that is i. dissipated in the resistor ...
... The current in the circuit is 2 amperes when the resistance in the circuit is adjusted to 10 ohms. Under these conditions the motor lifts a l-kilogram mass vertically at a constant speed of 2 meters per second. a. Determine the electrical power that is i. dissipated in the resistor ...
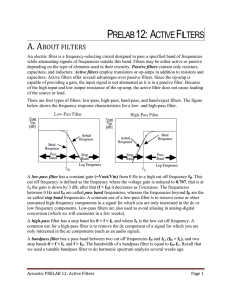
PRELAB 12: ACTIVE FILTERS
... A low-pass filter has a constant gain (=Vout/Vin) from 0 Hz to a high cut off frequency fH. This cut off frequency is defined as the frequency where the voltage gain is reduced to 0.707, that is at fH the gain is down by 3 dB; after that (f > fH) it decreases as f increases. The frequencies between ...
... A low-pass filter has a constant gain (=Vout/Vin) from 0 Hz to a high cut off frequency fH. This cut off frequency is defined as the frequency where the voltage gain is reduced to 0.707, that is at fH the gain is down by 3 dB; after that (f > fH) it decreases as f increases. The frequencies between ...
Introduction Simulation Methodology.
... Once the load line has been designed, it is time for large signal simulation. The input matching section is designed in a similar manner as the output section with the exception that since the return loss can be measured during simulation, it is much easier to either manually tune or automatically o ...
... Once the load line has been designed, it is time for large signal simulation. The input matching section is designed in a similar manner as the output section with the exception that since the return loss can be measured during simulation, it is much easier to either manually tune or automatically o ...
Chapter 1 0 - RC Circuits
... • The phase angle () of a series RC circuit varies inversely with frequency • For each parallel RC circuit, there is an equivalent series circuit for any given frequency • The impedance of a circuit can be determined by measuring the applied voltage and the total current and then applying Ohm’s law ...
... • The phase angle () of a series RC circuit varies inversely with frequency • For each parallel RC circuit, there is an equivalent series circuit for any given frequency • The impedance of a circuit can be determined by measuring the applied voltage and the total current and then applying Ohm’s law ...
Zobel network

For the wave filter invented by Zobel and sometimes named after him see m-derived filters.Zobel networks are a type of filter section based on the image-impedance design principle. They are named after Otto Zobel of Bell Labs, who published a much-referenced paper on image filters in 1923. The distinguishing feature of Zobel networks is that the input impedance is fixed in the design independently of the transfer function. This characteristic is achieved at the expense of a much higher component count compared to other types of filter sections. The impedance would normally be specified to be constant and purely resistive. For this reason, they are also known as constant resistance networks. However, any impedance achievable with discrete components is possible.Zobel networks were formerly widely used in telecommunications to flatten and widen the frequency response of copper land lines, producing a higher-quality line from one originally intended for ordinary telephone use. However, as analogue technology has given way to digital, they are now little used.When used to cancel out the reactive portion of loudspeaker impedance, the design is sometimes called a Boucherot cell. In this case, only half the network is implemented as fixed components, the other half being the real and imaginary components of the loudspeaker impedance. This network is more akin to the power factor correction circuits used in electrical power distribution, hence the association with Boucherot's name.A common circuit form of Zobel networks is in the form of a bridged T. This term is often used to mean a Zobel network, sometimes incorrectly when the circuit implementation is, in fact, something other than a bridged T.Parts of this article or section rely on the reader's knowledge of the complex impedance representation of capacitors and inductors and on knowledge of the frequency domain representation of signals.↑