Introducing Power Supplies And Plasma Systems
... other; the current through a capacitor leads the voltage, while the current through an inductor lags the voltage. In both cases, the voltage and current are “out of phase” with each other (see the discussion of maximum power delivery on page 9). A capacitive impedance can be canceled out by an induc ...
... other; the current through a capacitor leads the voltage, while the current through an inductor lags the voltage. In both cases, the voltage and current are “out of phase” with each other (see the discussion of maximum power delivery on page 9). A capacitive impedance can be canceled out by an induc ...
gain and output impedance of JFET stages
... voltage source (VCVS) and voltage-controlled current source (VCCS) are suitable models for the JFET device, because the controlled source can be transformed accordingly using the Thévenin and Norton theorems of circuit analysis. Figure 2 indicates the VCVS and VCCS small-signal models for a general ...
... voltage source (VCVS) and voltage-controlled current source (VCCS) are suitable models for the JFET device, because the controlled source can be transformed accordingly using the Thévenin and Norton theorems of circuit analysis. Figure 2 indicates the VCVS and VCCS small-signal models for a general ...
IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE) e-ISSN: 2278-1676,p-ISSN: 2320-3331,
... Keywords: Conducted emission, Composite filter, electromagnetic compatibility, lumped elements, and power line filter. ...
... Keywords: Conducted emission, Composite filter, electromagnetic compatibility, lumped elements, and power line filter. ...
results of the optinos project – deficits and unsureness in test
... disturbance source of the inverter can deliver its short circuit current which can be measured alternatively with a current probe on a single inverter line or as voltage drop above the network impedance using the RF output port of the AMN. The network has quite low impedances even at 50Hz or 60Hz be ...
... disturbance source of the inverter can deliver its short circuit current which can be measured alternatively with a current probe on a single inverter line or as voltage drop above the network impedance using the RF output port of the AMN. The network has quite low impedances even at 50Hz or 60Hz be ...
Amateur Extra Licensing Class
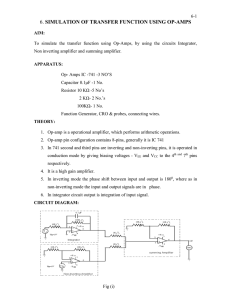
... The gain of an op amp is the function of the input resistor and the feed back resistor. Gain in calculated by dividing the input resistor RI value into the feedback resistor RF. In figure E7-4 if the input resistor,R1, is 10,000 ohms and the feedback resistor ,RF, 1s 1,000,000 ohms the gain would be ...
... The gain of an op amp is the function of the input resistor and the feed back resistor. Gain in calculated by dividing the input resistor RI value into the feedback resistor RF. In figure E7-4 if the input resistor,R1, is 10,000 ohms and the feedback resistor ,RF, 1s 1,000,000 ohms the gain would be ...
STEVAL-TDR019V1
... Information in this document is provided solely in connection with ST products. STMicroelectronics NV and its subsidiaries (“ST”) reserve the right to make changes, corrections, modifications or improvements, to this document, and the products and services described herein at any time, without notic ...
... Information in this document is provided solely in connection with ST products. STMicroelectronics NV and its subsidiaries (“ST”) reserve the right to make changes, corrections, modifications or improvements, to this document, and the products and services described herein at any time, without notic ...
Zobel network

For the wave filter invented by Zobel and sometimes named after him see m-derived filters.Zobel networks are a type of filter section based on the image-impedance design principle. They are named after Otto Zobel of Bell Labs, who published a much-referenced paper on image filters in 1923. The distinguishing feature of Zobel networks is that the input impedance is fixed in the design independently of the transfer function. This characteristic is achieved at the expense of a much higher component count compared to other types of filter sections. The impedance would normally be specified to be constant and purely resistive. For this reason, they are also known as constant resistance networks. However, any impedance achievable with discrete components is possible.Zobel networks were formerly widely used in telecommunications to flatten and widen the frequency response of copper land lines, producing a higher-quality line from one originally intended for ordinary telephone use. However, as analogue technology has given way to digital, they are now little used.When used to cancel out the reactive portion of loudspeaker impedance, the design is sometimes called a Boucherot cell. In this case, only half the network is implemented as fixed components, the other half being the real and imaginary components of the loudspeaker impedance. This network is more akin to the power factor correction circuits used in electrical power distribution, hence the association with Boucherot's name.A common circuit form of Zobel networks is in the form of a bridged T. This term is often used to mean a Zobel network, sometimes incorrectly when the circuit implementation is, in fact, something other than a bridged T.Parts of this article or section rely on the reader's knowledge of the complex impedance representation of capacitors and inductors and on knowledge of the frequency domain representation of signals.↑
![Touch Current Basics.ppt [Compatibility Mode]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/007899503_2-89947630ac5049138593ad1d5ba74dfa-300x300.png)