Transformer modeling basics
... Not using per unit » Need to include turns ratio » Divide leakage L, winding R between windings Transformers ...
... Not using per unit » Need to include turns ratio » Divide leakage L, winding R between windings Transformers ...
311i2datasheets
... Step-Up Transformers Primary Voltage (V) 400/415/Other? Secondary Voltage (kV) 3.3/6.6/11/22/Other? Frequency and Number of Phases (P) ...
... Step-Up Transformers Primary Voltage (V) 400/415/Other? Secondary Voltage (kV) 3.3/6.6/11/22/Other? Frequency and Number of Phases (P) ...
Chapter 4 Additional Problems
... X4.15 Three 100 kVA, 12,470:7200 V, 60 Hz, two-winding transformers are to be connected to provide 300 kVA, 7200/4160 V service to an industrial customer from the three-phase 7200 V distribution mains. (a) Determine the connection arrangement for this transformer bank. (b) For balanced operation, wi ...
... X4.15 Three 100 kVA, 12,470:7200 V, 60 Hz, two-winding transformers are to be connected to provide 300 kVA, 7200/4160 V service to an industrial customer from the three-phase 7200 V distribution mains. (a) Determine the connection arrangement for this transformer bank. (b) For balanced operation, wi ...
Potential Transformer Definition
... stepping down the system voltage to a safe value which can be fed to low ratings meters and relays. Commercially available relays and meters used for protection and metering, are designed for low voltage. This is a simplest form of potential transformer definition. Voltage Transformer or Potential T ...
... stepping down the system voltage to a safe value which can be fed to low ratings meters and relays. Commercially available relays and meters used for protection and metering, are designed for low voltage. This is a simplest form of potential transformer definition. Voltage Transformer or Potential T ...
Transformers plays a crucial role in the power
... cable with brass copper terminals or vise-versa. Cable supports and clips should be provided in such a way that the cable should not create unnecessary load on the bushing terminals. It has been seen in few occasions that the L.V cables are hanging against the terminal bushings without any support, ...
... cable with brass copper terminals or vise-versa. Cable supports and clips should be provided in such a way that the cable should not create unnecessary load on the bushing terminals. It has been seen in few occasions that the L.V cables are hanging against the terminal bushings without any support, ...
Unit-8Lecture 52 TESTING OF CABLES Cables are very important
... Transformers are tested for overvoltages by exciting the secondary of the transformer from a high frequency a.c. source (100 to 400 Hz) to about twice the rated voltage. This reduces the core saturation and also limits the charging current necessary in large power transformers. The insulation withst ...
... Transformers are tested for overvoltages by exciting the secondary of the transformer from a high frequency a.c. source (100 to 400 Hz) to about twice the rated voltage. This reduces the core saturation and also limits the charging current necessary in large power transformers. The insulation withst ...
Maintaining a Constant DC Power Supply
... Energy dissipated in an electrical or electronic circuit or device per unit of time is known as the electrical power (electrical power is usually measured in watts). Electrical energy supplied by a current to an appliance enables it to do work witch could provide some other form of energy. The diffi ...
... Energy dissipated in an electrical or electronic circuit or device per unit of time is known as the electrical power (electrical power is usually measured in watts). Electrical energy supplied by a current to an appliance enables it to do work witch could provide some other form of energy. The diffi ...
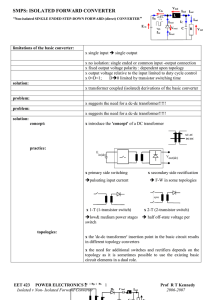
SMPS: ISOLATED FORWARD CONVERTER "Non
... x single input single output x no isolation: single ended or common input -output connection x fixed output voltage polarity : dependent upon topology x output voltage relative to the input limited to duty cycle control x 0
... x single input single output x no isolation: single ended or common input -output connection x fixed output voltage polarity : dependent upon topology x output voltage relative to the input limited to duty cycle control x 0
Document
... Impedance Reflection with Transformers Transformers can be used to match loads (impedances). This means that if we look at the apparent impedance seen at the primary side of a transformer (Z’) we will see the impedance at the secondary side divided by the turns ratio squared. ...
... Impedance Reflection with Transformers Transformers can be used to match loads (impedances). This means that if we look at the apparent impedance seen at the primary side of a transformer (Z’) we will see the impedance at the secondary side divided by the turns ratio squared. ...
Typical Current Transformer
... Due to this type of arrangement, the current transformer is often referred too as a “series transformer” as the primary winding, which never has more than a very few turns, is in series with the current carrying conductor. The secondary winding may have a large number of coil turns wound on a lamina ...
... Due to this type of arrangement, the current transformer is often referred too as a “series transformer” as the primary winding, which never has more than a very few turns, is in series with the current carrying conductor. The secondary winding may have a large number of coil turns wound on a lamina ...
Transformers
... supply. It is just a piece of iron with some wire wrapped around it. The secondary side works using electromagnetic induction. To make a current flow, a magnetic field needs to be changing perpendicular to the coil. When there is an alternating current in the primary side, the direction of the magne ...
... supply. It is just a piece of iron with some wire wrapped around it. The secondary side works using electromagnetic induction. To make a current flow, a magnetic field needs to be changing perpendicular to the coil. When there is an alternating current in the primary side, the direction of the magne ...
Red Writing: information about the content of the policy
... Secondary short circuit current a) P1 winding b) P2 winding c) M winding Recommended maximum rating of fuses protecting the voltage transformer secondary windings ...
... Secondary short circuit current a) P1 winding b) P2 winding c) M winding Recommended maximum rating of fuses protecting the voltage transformer secondary windings ...
Basic electrical engineering
... Kirchhoff’s Laws – Formation of network equations by mesh current method – Matrix representation – Solution of network equations by matrix method – Star delta conversion. Magnetic circuits – mmf, field strength, flux density, reluctance, permeability – comparison of electric and magnetic circuits – ...
... Kirchhoff’s Laws – Formation of network equations by mesh current method – Matrix representation – Solution of network equations by matrix method – Star delta conversion. Magnetic circuits – mmf, field strength, flux density, reluctance, permeability – comparison of electric and magnetic circuits – ...
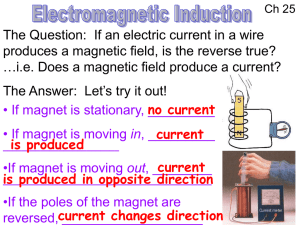
Magnetic Flux and Faraday`s Law of Induction
... The transformer is very efficient at doing what is does do to the lack of moving parts (hence very little friction). It is indispensible when transporting electrical energy over long distances. A transformer has two coils, primary or input coil, and secondary or output coil wrapped around laminated ...
... The transformer is very efficient at doing what is does do to the lack of moving parts (hence very little friction). It is indispensible when transporting electrical energy over long distances. A transformer has two coils, primary or input coil, and secondary or output coil wrapped around laminated ...
Document
... _____ 5. What device converts mechanical energy into electrical energy? a. electric motor c. electromagnetic motor b. electric generator d. magnetic motor _____ 6. When electric current changes direction it is called a(n) a. generated current. c. alternating current. b. electromagnetic current. d. r ...
... _____ 5. What device converts mechanical energy into electrical energy? a. electric motor c. electromagnetic motor b. electric generator d. magnetic motor _____ 6. When electric current changes direction it is called a(n) a. generated current. c. alternating current. b. electromagnetic current. d. r ...
Transformer Fully Explained By faisal qaswar
... Transformers for use at power or audio frequencies typically have cores made of high permeability silicon steel. The steel has a permeability many times that of free space, and the core thus serves to greatly reduce the magnetising current, and confine the flux to a path which closely couples the ...
... Transformers for use at power or audio frequencies typically have cores made of high permeability silicon steel. The steel has a permeability many times that of free space, and the core thus serves to greatly reduce the magnetising current, and confine the flux to a path which closely couples the ...
datasheet - PFIFFNER Instrument Transformers Ltd
... in high-voltage substations within the 245 –550 kV range. They transfer high voltage and high current into standardised, equivalent values for meters, measuring and protection devices. The voltage transformer component is located in the top of the pressure-resistant head housing and the current tran ...
... in high-voltage substations within the 245 –550 kV range. They transfer high voltage and high current into standardised, equivalent values for meters, measuring and protection devices. The voltage transformer component is located in the top of the pressure-resistant head housing and the current tran ...
Transformer

A transformer is an electrical device that transfers electrical energy between two or more circuits through electromagnetic induction. Commonly, transformers are used to increase or decrease the voltages of alternating current in electric power applications.A varying current in the transformer's primary winding creates a varying magnetic flux in the transformer core and a varying magnetic field impinging on the transformer's secondary winding. This varying magnetic field at the secondary winding induces a varying electromotive force (EMF) or voltage in the secondary winding. Making use of Faraday's Law in conjunction with high magnetic permeability core properties, transformers can thus be designed to efficiently change AC voltages from one voltage level to another within power networks.Since the invention of the first constant potential transformer in 1885, transformers have become essential for the transmission, distribution, and utilization of alternating current electrical energy. A wide range of transformer designs are encountered in electronic and electric power applications. Transformers range in size from RF transformers less than a cubic centimeter in volume to units interconnecting the power grid weighing hundreds of tons.