Ch. 32
... 1) What is Ohm’s Law. Give the equation. 2) How does current flow in AC circuit. Does current flow in a closed or open circuit. 3) What are series and parallel circuit. 4) Is current constant in a series circuit. How do you measure total resistance in a series circuit. If you increase the number of ...
... 1) What is Ohm’s Law. Give the equation. 2) How does current flow in AC circuit. Does current flow in a closed or open circuit. 3) What are series and parallel circuit. 4) Is current constant in a series circuit. How do you measure total resistance in a series circuit. If you increase the number of ...
What does the “PASSIVE” device mean
... for high voltage and high frequency applications (low power losses needed), as charge accumulators thanks to big specific capacity, as variable capacitors for tuned RF applications, for filtering in AC/DC converters, in power sources. ...
... for high voltage and high frequency applications (low power losses needed), as charge accumulators thanks to big specific capacity, as variable capacitors for tuned RF applications, for filtering in AC/DC converters, in power sources. ...
1 - India Study Channel
... (The coil is made of copper wire of cross-sectional area 10-5 m2 and the free electron density in copper is given to be about 1029m-3) 17. A person with a normal near point(25cm) using a compound microscope with objective of focal length 8.0mm and an eye-piece of focal length 25cm can bring an objec ...
... (The coil is made of copper wire of cross-sectional area 10-5 m2 and the free electron density in copper is given to be about 1029m-3) 17. A person with a normal near point(25cm) using a compound microscope with objective of focal length 8.0mm and an eye-piece of focal length 25cm can bring an objec ...
P3.4.5.1 - LD Didactic
... In this experiment the transformer is used to isolate two AC circuits electrically. There is no conductive connection between the primary and the secondary coils; both coils are coupled by the magnetic field. Therefore an earth free voltage source is available on the secondary side whose outputs can ...
... In this experiment the transformer is used to isolate two AC circuits electrically. There is no conductive connection between the primary and the secondary coils; both coils are coupled by the magnetic field. Therefore an earth free voltage source is available on the secondary side whose outputs can ...
EE101 Elements of Electrical Engineering
... Unit 2. A.C. circuits: Common signals and there waveform, RMS and Average value, form factor and peak factor of sinusoidal wave, Impedance of series and parallel circuits, Phasor diagram, Power, Power factor, Power Triangle, Resonance and Q-factor, Superposition, Thevenin’s and Norton’s Maximum Powe ...
... Unit 2. A.C. circuits: Common signals and there waveform, RMS and Average value, form factor and peak factor of sinusoidal wave, Impedance of series and parallel circuits, Phasor diagram, Power, Power factor, Power Triangle, Resonance and Q-factor, Superposition, Thevenin’s and Norton’s Maximum Powe ...
S17-ViceChairReport
... Duality Derived Transformer Models for Low-Frequency Electromagnetic Transients –Part I: Topological Models Equivalent Winding Capacitance Network for Transformer Transient Analysis based on Standard Test Data Hybrid Electromagnetic Unified Power Flow Controller: A Novel Flexible and Effective Appro ...
... Duality Derived Transformer Models for Low-Frequency Electromagnetic Transients –Part I: Topological Models Equivalent Winding Capacitance Network for Transformer Transient Analysis based on Standard Test Data Hybrid Electromagnetic Unified Power Flow Controller: A Novel Flexible and Effective Appro ...
Solutions
... The area control error (ACE) for an electric balancing authority can never be negative because transmission lines always have real power losses. ...
... The area control error (ACE) for an electric balancing authority can never be negative because transmission lines always have real power losses. ...
What`s on an Electric Power Pole?
... What’s on an Electric Power Pole? This is an illustration of basic equipment found on a typical distribution pole and can vary by location. ...
... What’s on an Electric Power Pole? This is an illustration of basic equipment found on a typical distribution pole and can vary by location. ...
Audio Power Amplifier Operation with Transformer Load
... before the zero crossing, perhaps a quarter cycle, might compensate just as the initial fraction of a cycle produced by the function generator seems to. Another alternative is to make the transition from zero to maximum output in more than one step, allowing the magnetizing current to stabilize each ...
... before the zero crossing, perhaps a quarter cycle, might compensate just as the initial fraction of a cycle produced by the function generator seems to. Another alternative is to make the transition from zero to maximum output in more than one step, allowing the magnetizing current to stabilize each ...
A Class D AM Transmitter for 75 Meters
... voltage. Typical RF power devices generally operate from supply voltages in the range of 13.8Vdc to 50Vdc with few exceptions. The modulation impedance is calculated by simple ohms law, Vdd/Idd. For the case of a typical linear 1kW RF module operating from 50Vdc this works out to 1.66 ohms. Such a l ...
... voltage. Typical RF power devices generally operate from supply voltages in the range of 13.8Vdc to 50Vdc with few exceptions. The modulation impedance is calculated by simple ohms law, Vdd/Idd. For the case of a typical linear 1kW RF module operating from 50Vdc this works out to 1.66 ohms. Such a l ...
What pMRI Scientists Want
... In essence, MRI is a process by which the nuclear insides of a test subject are turned into tiny magnets. A separate signal then perturbs these magnets which, upon removal of the perturbation, return to their starting position. During this process of relaxation a time varying magnetic flux is genera ...
... In essence, MRI is a process by which the nuclear insides of a test subject are turned into tiny magnets. A separate signal then perturbs these magnets which, upon removal of the perturbation, return to their starting position. During this process of relaxation a time varying magnetic flux is genera ...
Ideal Transformer.
... Obtain components are connected in parallel The open circuit test is conducted by applying rated voltage at rated frequency to one of the windings, with the other windings open circuited. The input power and current are measured. For reasons of safety and convenience, the measurements are ma ...
... Obtain components are connected in parallel The open circuit test is conducted by applying rated voltage at rated frequency to one of the windings, with the other windings open circuited. The input power and current are measured. For reasons of safety and convenience, the measurements are ma ...
Why is a transformer needed?
... A transformer is a passive electrical device designed to convert alternating current from one voltage to another by magnetic induction. It can be designed to "step up" or "step down" voltages and works on the magnetic induction principle. A transformer has no moving parts and is a completely static ...
... A transformer is a passive electrical device designed to convert alternating current from one voltage to another by magnetic induction. It can be designed to "step up" or "step down" voltages and works on the magnetic induction principle. A transformer has no moving parts and is a completely static ...
SMJE 2103 Electiral Power System
... (a) If the power system is exactly as described above in Figure (a), what will the voltage at the load be? What will the transmission line losses be? (b) Suppose a 1:10 step-up transformer is placed at the generator end of the transmission line and a 10:1 step-down transformer is placed at the load ...
... (a) If the power system is exactly as described above in Figure (a), what will the voltage at the load be? What will the transmission line losses be? (b) Suppose a 1:10 step-up transformer is placed at the generator end of the transmission line and a 10:1 step-down transformer is placed at the load ...
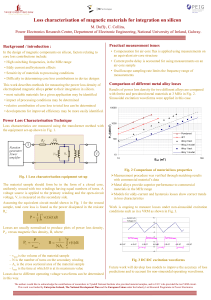
Loss characterization of magnetic materials for integration on silicon
... • Sensitivity of materials to processing conditions • Difficulty in determining core loss contributions in device designs This work describes methods for measuring the power loss density of electroplated magnetic alloys prior to their integration in silicon. • most suitable materials for a given app ...
... • Sensitivity of materials to processing conditions • Difficulty in determining core loss contributions in device designs This work describes methods for measuring the power loss density of electroplated magnetic alloys prior to their integration in silicon. • most suitable materials for a given app ...
ENERGY CONVERSION ONE
... • Solidly grounding the neutrals of windings specially primary winding, this connection provide a path for 3rd harmonic current flow, produced and do not let build up of large 3rd voltages . Also provides a return path for any current imbalances in load • Adding a third winding (tertiary) connected ...
... • Solidly grounding the neutrals of windings specially primary winding, this connection provide a path for 3rd harmonic current flow, produced and do not let build up of large 3rd voltages . Also provides a return path for any current imbalances in load • Adding a third winding (tertiary) connected ...
rt41LURES IN THREE-PHASE STATOR WINDINGS
... insulation in all phases of the stator winding typically is caused by load demands exceeding the rating of the motor. NOTE: Under-voltage and over-voltage (exceeding NEMA standards) will result in the same type of insulation deterioration. ...
... insulation in all phases of the stator winding typically is caused by load demands exceeding the rating of the motor. NOTE: Under-voltage and over-voltage (exceeding NEMA standards) will result in the same type of insulation deterioration. ...
Exam 3 Practice
... reactance of j1.0 ohms per phase. Assume the armature resistance (Ra) is zero. The field current is set to produce a terminal voltage of 480V (line–line) at full load. At full load the machine supplies 60 amps at 1.0 power factor. a)(1) Sketch the per phase equivalent circuit showing the field and a ...
... reactance of j1.0 ohms per phase. Assume the armature resistance (Ra) is zero. The field current is set to produce a terminal voltage of 480V (line–line) at full load. At full load the machine supplies 60 amps at 1.0 power factor. a)(1) Sketch the per phase equivalent circuit showing the field and a ...
Transformer

A transformer is an electrical device that transfers electrical energy between two or more circuits through electromagnetic induction. Commonly, transformers are used to increase or decrease the voltages of alternating current in electric power applications.A varying current in the transformer's primary winding creates a varying magnetic flux in the transformer core and a varying magnetic field impinging on the transformer's secondary winding. This varying magnetic field at the secondary winding induces a varying electromotive force (EMF) or voltage in the secondary winding. Making use of Faraday's Law in conjunction with high magnetic permeability core properties, transformers can thus be designed to efficiently change AC voltages from one voltage level to another within power networks.Since the invention of the first constant potential transformer in 1885, transformers have become essential for the transmission, distribution, and utilization of alternating current electrical energy. A wide range of transformer designs are encountered in electronic and electric power applications. Transformers range in size from RF transformers less than a cubic centimeter in volume to units interconnecting the power grid weighing hundreds of tons.