Electronic Commerce
... Artificial Intelligence is the study of how to make computers do things at which, at the moment, people are better. ...
... Artificial Intelligence is the study of how to make computers do things at which, at the moment, people are better. ...
Artificial Intelligence
... What is artificial intelligence? It is the science and engineering of making intelligent machines, especially intelligent computer programs. It is related to the similar task of using computers to understand human intelligence, but AI does not have to confine itself to methods that are biologically ...
... What is artificial intelligence? It is the science and engineering of making intelligent machines, especially intelligent computer programs. It is related to the similar task of using computers to understand human intelligence, but AI does not have to confine itself to methods that are biologically ...
Some major differences between expert systems and other systems:
... whereas most AI systems must work with symbolic inp ut. Perhaps most important, human reasoning is able to make use at all times of a wide context of experience and bring that to bear on individual problems; in contrast, AI systems typically gain their power by having a very narrow focus. ...
... whereas most AI systems must work with symbolic inp ut. Perhaps most important, human reasoning is able to make use at all times of a wide context of experience and bring that to bear on individual problems; in contrast, AI systems typically gain their power by having a very narrow focus. ...
ai-course-outline
... Artificial Intelligence – A Modern Approach (2nd edition) By Stuart Russell & Peter Norvig References: Course Objectives: Obtain an overview of artificial intelligence (AI) principles and approaches. Develop a basic understanding of the building blocks of AI as presented in terms of intelligent agen ...
... Artificial Intelligence – A Modern Approach (2nd edition) By Stuart Russell & Peter Norvig References: Course Objectives: Obtain an overview of artificial intelligence (AI) principles and approaches. Develop a basic understanding of the building blocks of AI as presented in terms of intelligent agen ...
Whatever happened to machines that think?
... intelligence on a platter. The late 1960s and early 1970s saw feverish speculation about the impact intelligent machines might have on the world and the advantages they would bring to whoever developed them. The computer HAL in Stanley Kubrick's classic 1968 movie 2001: A space odyssey summed up the ...
... intelligence on a platter. The late 1960s and early 1970s saw feverish speculation about the impact intelligent machines might have on the world and the advantages they would bring to whoever developed them. The computer HAL in Stanley Kubrick's classic 1968 movie 2001: A space odyssey summed up the ...
Brief History of Artificial Intelligence - OCW
... The Stanford Cart, built by Hans Moravec, becomes the first computercontrolled, autonomous vehicle when it successfully traverses a chair-filled room and circumnavigates the Stanford AI Lab. Drew McDermott & Jon Doyle at MIT, and John McCarthy at Stanford begin publishing work on non-monotonic logic ...
... The Stanford Cart, built by Hans Moravec, becomes the first computercontrolled, autonomous vehicle when it successfully traverses a chair-filled room and circumnavigates the Stanford AI Lab. Drew McDermott & Jon Doyle at MIT, and John McCarthy at Stanford begin publishing work on non-monotonic logic ...
The Shape of Things to Come or How Things Will Shape the Way
... How does Taz figure out where it is? • Has a map in its memory. • Measures how far it travels to get a rough idea of where it is at on the map. • Uses its laser and sonar readings to recognize places on its map to get an exact ...
... How does Taz figure out where it is? • Has a map in its memory. • Measures how far it travels to get a rough idea of where it is at on the map. • Uses its laser and sonar readings to recognize places on its map to get an exact ...
Artificial Intelligence
... with my work. You can think of it kind of like Jarvis in Iron Man. I’ll start teaching it to understand my voice to control everything in our home … I’ll teach it to let friends in by looking at their faces when they ring the doorbell ... I’ll teach it to let me know if anything is going on in Max’s ...
... with my work. You can think of it kind of like Jarvis in Iron Man. I’ll start teaching it to understand my voice to control everything in our home … I’ll teach it to let friends in by looking at their faces when they ring the doorbell ... I’ll teach it to let me know if anything is going on in Max’s ...
The History of Artificial Intelligence
... Today: Computer as Artist Two paintings done by Harold Cohen’s Aaron program: ...
... Today: Computer as Artist Two paintings done by Harold Cohen’s Aaron program: ...
Vorlesung Grundlagen der Künstlichen Intelligenz
... the Dartmouth Conference, the first conference devoted to the subject. Demonstration of the first running AI program, the Logic Theorist (LT) written by Allen Newell, J.C. Shaw and Herbert Simon ...
... the Dartmouth Conference, the first conference devoted to the subject. Demonstration of the first running AI program, the Logic Theorist (LT) written by Allen Newell, J.C. Shaw and Herbert Simon ...
Course Syllabus - Dr. Randy Ribler
... reasoning. Additional topics may include game theory, planning, understanding, natural language processing, machine learning, neural networks, genetic algorithms, expert systems, and real-time systems. Students develop competence in a language widely used for A.I. programming, typically LISP or Prol ...
... reasoning. Additional topics may include game theory, planning, understanding, natural language processing, machine learning, neural networks, genetic algorithms, expert systems, and real-time systems. Students develop competence in a language widely used for A.I. programming, typically LISP or Prol ...
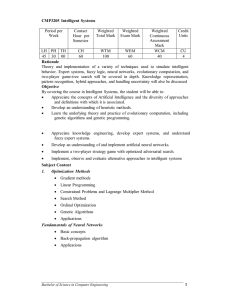
CMP3205 Intelligent Systems
... Theory and implementation of a variety of techniques used to simulate intelligent behavior. Expert systems, fuzzy logic, neural networks, evolutionary computation, and two-player game-tree search will be covered in depth. Knowledge representation, pattern recognition, hybrid approaches, and handling ...
... Theory and implementation of a variety of techniques used to simulate intelligent behavior. Expert systems, fuzzy logic, neural networks, evolutionary computation, and two-player game-tree search will be covered in depth. Knowledge representation, pattern recognition, hybrid approaches, and handling ...
biology
... Renowned for her description and associated notes on Charles Babbage's Analytical Engine which was never built, but Ada's notes are widely recognized as containing the first ever computer program. “The Analytical Engine has no pretensions whatever to originate anything. It can do whatever we know ho ...
... Renowned for her description and associated notes on Charles Babbage's Analytical Engine which was never built, but Ada's notes are widely recognized as containing the first ever computer program. “The Analytical Engine has no pretensions whatever to originate anything. It can do whatever we know ho ...
Introduction
... • “Will emotions be explicitly programmed into a machine? No. That is ridiculous. Any direct simulation of emotions cannot approach the complexity of human emotions, which arise indirectly from the organization of our minds. Programs or machines will acquire emotions in the same way: as by-products ...
... • “Will emotions be explicitly programmed into a machine? No. That is ridiculous. Any direct simulation of emotions cannot approach the complexity of human emotions, which arise indirectly from the organization of our minds. Programs or machines will acquire emotions in the same way: as by-products ...
Lec1-AIIntro - Donald Bren School of Information and Computer
... AI Prehistory • Philosophy – logic, methods of reasoning – mind as physical system – foundations of learning, language, rationality ...
... AI Prehistory • Philosophy – logic, methods of reasoning – mind as physical system – foundations of learning, language, rationality ...
What is AI?
... Chinese Room Argument “The reason that no computer program can ever be a mind is simply that a computer program is only syntactical, and minds are more than syntactical. Minds are semantical, they have content.” - John Searle ...
... Chinese Room Argument “The reason that no computer program can ever be a mind is simply that a computer program is only syntactical, and minds are more than syntactical. Minds are semantical, they have content.” - John Searle ...
Soft Computing - 123seminarsonly.com
... Conventional AI manipulates symbols on the assumption that human intelligence behavior can be stored in symbolically structured knowledge bases: this is known as: “ The physical symbol system hypothesis” Focuses on attempt to mimic human intelligent behavior by expressing it in language forms or s ...
... Conventional AI manipulates symbols on the assumption that human intelligence behavior can be stored in symbolically structured knowledge bases: this is known as: “ The physical symbol system hypothesis” Focuses on attempt to mimic human intelligent behavior by expressing it in language forms or s ...
lecture01 - University of Virginia
... History of AI Read the complete story in text • Alan Turing (1950) did much to define the problems and techniques • John McCarthy helped coordinate the players (1956) • Alan Newell and Herbert Simon (1956) did much to demonstrate first solutions • Marvin Minsky (student of von Neumann) built a neur ...
... History of AI Read the complete story in text • Alan Turing (1950) did much to define the problems and techniques • John McCarthy helped coordinate the players (1956) • Alan Newell and Herbert Simon (1956) did much to demonstrate first solutions • Marvin Minsky (student of von Neumann) built a neur ...
Presentation – John Mc. Carthy
... Computing Machinery and Intelligence - Alan Turing • Turing Test – Define Intelligence as: • Actions that are indistinguishable from known intelligent beings, i.e. humans • Side steps philosophical arguments ...
... Computing Machinery and Intelligence - Alan Turing • Turing Test – Define Intelligence as: • Actions that are indistinguishable from known intelligent beings, i.e. humans • Side steps philosophical arguments ...
Special session Automation 2017
... continuously adapt to, data without being explicitly programmed for that kind of data and to move from one problem domain to another with very few changes to their algorithmic core. Finally, Machine Intelligence systems gather from machine learning, but additionally posses the ability to perceive an ...
... continuously adapt to, data without being explicitly programmed for that kind of data and to move from one problem domain to another with very few changes to their algorithmic core. Finally, Machine Intelligence systems gather from machine learning, but additionally posses the ability to perceive an ...
Introduction to Artificial Intelligence – Unit 1 What is AI? Course 67842
... Acting humanly: Turing Test Turing (1950) “Computing machinery and intelligence”: “Can machines think?” “Can machines ...
... Acting humanly: Turing Test Turing (1950) “Computing machinery and intelligence”: “Can machines think?” “Can machines ...
Document
... and initiated the field of logic. The development of formal logic in the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries, provided a precise notation for statements about all kinds of things in the world and the relations between them. By 1965, programs existed that could, given enough time and memory ...
... and initiated the field of logic. The development of formal logic in the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries, provided a precise notation for statements about all kinds of things in the world and the relations between them. By 1965, programs existed that could, given enough time and memory ...
Lecture 2 Slides - UBC Department of Computer Science
... Not from last time AI assumes that what the brain does may be thought of at some level as some form of computation The assumption above is probably valid A physical symbol system has the necessary and sufficient means for intelligent behavior (The Physical Symbol System Hypothesis) These assumption ...
... Not from last time AI assumes that what the brain does may be thought of at some level as some form of computation The assumption above is probably valid A physical symbol system has the necessary and sufficient means for intelligent behavior (The Physical Symbol System Hypothesis) These assumption ...
Hans W. Guesgen - Massey University
... mutually restricting variables. During this period he held a one-year post-doctoral fellowship at the International Computer Science Institute in Berkeley, California, where his research focus changed to spatial and temporal reasoning. His work in this area includes pioneering research in qualitativ ...
... mutually restricting variables. During this period he held a one-year post-doctoral fellowship at the International Computer Science Institute in Berkeley, California, where his research focus changed to spatial and temporal reasoning. His work in this area includes pioneering research in qualitativ ...