Evolutionary Computing, or “What Would a Computer Do?”
... Dr. David Fogel of Natural Selection, Inc. says that when considering computer performance, one standard was always “what would a human do?” and that games of skill have often played a role in this evaluation. Older AI systems were based on codified rules that emulated human behaviour. Today, Fogel ...
... Dr. David Fogel of Natural Selection, Inc. says that when considering computer performance, one standard was always “what would a human do?” and that games of skill have often played a role in this evaluation. Older AI systems were based on codified rules that emulated human behaviour. Today, Fogel ...
Document
... Artificial Intelligence and law is a subfield of AI mainly concerned with applications of AI to legal informatics problems and original research of those problems Information retrieval related to law (manual, ...
... Artificial Intelligence and law is a subfield of AI mainly concerned with applications of AI to legal informatics problems and original research of those problems Information retrieval related to law (manual, ...
COGS 515 Artificial Intelligence for Cognitive Science Spring 2014
... COGS 515 Artificial Intelligence for Cognitive Science Spring 2014-‐2015 ...
... COGS 515 Artificial Intelligence for Cognitive Science Spring 2014-‐2015 ...
CentimentWhitePaperMachineEthics.pase.comments
... Nuclear experimentation by governments was rampant until the nuclear non-proliferation treaty. In this event real world laws finally began to catch up with the technology, by which point it was too late, thousands of people had died, from the weapons themselves and the side effects of a lack of unde ...
... Nuclear experimentation by governments was rampant until the nuclear non-proliferation treaty. In this event real world laws finally began to catch up with the technology, by which point it was too late, thousands of people had died, from the weapons themselves and the side effects of a lack of unde ...
Lecture Notes
... • 1943: McCulloch & Pitts: Boolean circuit of the brain • 1950: Turing’s “Computing machinery and intelligence” • 1950s: Early AI Programs including Samuel’s checkers, Newell and Simon’s Logic Theorist ...
... • 1943: McCulloch & Pitts: Boolean circuit of the brain • 1950: Turing’s “Computing machinery and intelligence” • 1950s: Early AI Programs including Samuel’s checkers, Newell and Simon’s Logic Theorist ...
Introduction to Artificial Intelligence
... ▫ It encompasses the knowledge of how to solve problems efficiently and effectively, how to plan steps in solving a complex problem, how to improve performance, and so ...
... ▫ It encompasses the knowledge of how to solve problems efficiently and effectively, how to plan steps in solving a complex problem, how to improve performance, and so ...
Belief-optimal Reasoning for Cyber-physical Systems
... • Act vs. think, human-like vs. rational ...
... • Act vs. think, human-like vs. rational ...
Preface Diane J. Cook and Narayanan C Krishnan Parisa Rashidi Marjorie Skubic
... the need for the development of patient-centric technologies that promote safe independent living. These patient-centric technologies need to address various aging related physical and cognitive health problems such as heart disease, diabetes, deterioration of physical function, falling, wandering, ...
... the need for the development of patient-centric technologies that promote safe independent living. These patient-centric technologies need to address various aging related physical and cognitive health problems such as heart disease, diabetes, deterioration of physical function, falling, wandering, ...
Convergent or Divergent Superintelligence
... Reasons to think general intelligence is hard • No free lunch theorems • The Bias-Variance dilemma – Specific bias vs. slow learning rate ...
... Reasons to think general intelligence is hard • No free lunch theorems • The Bias-Variance dilemma – Specific bias vs. slow learning rate ...
notes - Computer Science
... The goal of AI is to build intelligent systems. This raises the question: what do we mean by ‘intelligent system’ ? We’ll come to that shortly. Before that, we might ask: why would we want to build intelligent systems? There is a scientific reason and an engineering reason: • AI may help us to under ...
... The goal of AI is to build intelligent systems. This raises the question: what do we mean by ‘intelligent system’ ? We’ll come to that shortly. Before that, we might ask: why would we want to build intelligent systems? There is a scientific reason and an engineering reason: • AI may help us to under ...
Artificial Intelligence
... vast knowledge bases of facts in the languages now used for expressing knowledge. ...
... vast knowledge bases of facts in the languages now used for expressing knowledge. ...
ppt - DePaul University
... problematic concept conjunction of two difficult terms artificial “not natural” ...
... problematic concept conjunction of two difficult terms artificial “not natural” ...
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
... AI is the artificial intelligence of robot. This is created to help robots think for themselves. All robots use this technology no matter how small it may be. There are 4 generations in robots and they areFirst-Generation Universal Robots: Lizard-scale intelligence Second-Generation Universal Robots ...
... AI is the artificial intelligence of robot. This is created to help robots think for themselves. All robots use this technology no matter how small it may be. There are 4 generations in robots and they areFirst-Generation Universal Robots: Lizard-scale intelligence Second-Generation Universal Robots ...
Brief History - Rogelio Davila
... Warren McCulloch and Walter Pitts [1943] theorized about the relationships between simple computing elements and biological neurons. They show that it was possible to compute any computable function by networks of logical gates. Alan Turing publishes “Computer Machinery and Intelligence” where he pr ...
... Warren McCulloch and Walter Pitts [1943] theorized about the relationships between simple computing elements and biological neurons. They show that it was possible to compute any computable function by networks of logical gates. Alan Turing publishes “Computer Machinery and Intelligence” where he pr ...
Document
... – An expert system is a software designed to replicate the decision-making process of a human expert, within a narrow topic. At the heart of every expert system is a knowledge base representing ideas from the specific field of expertise – A knowledge-based system derives knowledge from experts as we ...
... – An expert system is a software designed to replicate the decision-making process of a human expert, within a narrow topic. At the heart of every expert system is a knowledge base representing ideas from the specific field of expertise – A knowledge-based system derives knowledge from experts as we ...
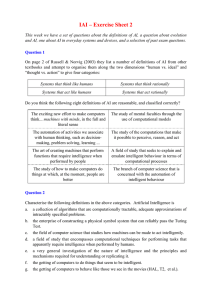
IAI – Exercise Sheet 2
... On page 2 of Russell & Norvig (2003) they list a number of definitions of AI from other textbooks and attempt to organise them along the two dimensions “human vs. ideal” and “thought vs. action” to give four categories: Systems that think like humans ...
... On page 2 of Russell & Norvig (2003) they list a number of definitions of AI from other textbooks and attempt to organise them along the two dimensions “human vs. ideal” and “thought vs. action” to give four categories: Systems that think like humans ...
Artificial Intelligence: Introduction
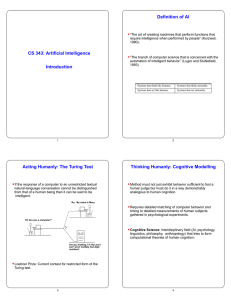
... Too general a problem – unsolved in the general case Intelligence takes many forms, which are not necessarily best tested this way Is it actually intelligent? (Chinese room) ...
... Too general a problem – unsolved in the general case Intelligence takes many forms, which are not necessarily best tested this way Is it actually intelligent? (Chinese room) ...
AI-01
... [Russel, 2003] S. Russell and P. Norvig Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach Prentice Hall, 2003, Second Edition [Patterson, 1990] D. W. Patterson, “Introduction to Artificial Intelligence and Expert Systems”, Prentice-Hall Inc., Englewood Cliffs, N.J, USA, ...
... [Russel, 2003] S. Russell and P. Norvig Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach Prentice Hall, 2003, Second Edition [Patterson, 1990] D. W. Patterson, “Introduction to Artificial Intelligence and Expert Systems”, Prentice-Hall Inc., Englewood Cliffs, N.J, USA, ...
- RehanCodes
... successfully in English (or some other human language) Knowledge representation to store information provided before or during the interrogation; Automated reasoning to use the stored information to answer questions and to draw new conclusions Machine learning to adapt to new circumstances and ...
... successfully in English (or some other human language) Knowledge representation to store information provided before or during the interrogation; Automated reasoning to use the stored information to answer questions and to draw new conclusions Machine learning to adapt to new circumstances and ...
Introduction to Artificial Intelligence
... •If the response of a computer to an unrestricted textual natural-language conversation cannot be distinguished from that of a human being then it can be said to be intelligent. ...
... •If the response of a computer to an unrestricted textual natural-language conversation cannot be distinguished from that of a human being then it can be said to be intelligent. ...
www.mcs.uvawise.edu
... the material properties of extension and motion, and that it follows the laws of physics. The mind (or soul), on the other hand, was described as a nonmaterial entity that lacks extension and motion, and does not follow the laws of physics. Descartes argued that only humans have minds, and that the ...
... the material properties of extension and motion, and that it follows the laws of physics. The mind (or soul), on the other hand, was described as a nonmaterial entity that lacks extension and motion, and does not follow the laws of physics. Descartes argued that only humans have minds, and that the ...
Intro to Business Intelligence
... applications and technologies for gathering, providing access to, and analyzing data for the purpose of helping enterprise users make better business decisions. • The term implies having a comprehensive knowledge of all of the factors that affect your business. Wikipedia ...
... applications and technologies for gathering, providing access to, and analyzing data for the purpose of helping enterprise users make better business decisions. • The term implies having a comprehensive knowledge of all of the factors that affect your business. Wikipedia ...
Slide 1
... machines someday because our brains themselves are machines! • One problem is that we know very little about how the brain actually works • Even though we do not understand how the brain performs many mental skills, we can still work toward making machines that do the same or similar things • Artifi ...
... machines someday because our brains themselves are machines! • One problem is that we know very little about how the brain actually works • Even though we do not understand how the brain performs many mental skills, we can still work toward making machines that do the same or similar things • Artifi ...