Introduction to PYTHON
... • Python is a software package called an interpreter. • When you write a Python program, the Python interpreter reads your program and carries out the instructions it contains. • The main difference from a compiler is that the standard implementations of Python compile (i.e., translate) source code ...
... • Python is a software package called an interpreter. • When you write a Python program, the Python interpreter reads your program and carries out the instructions it contains. • The main difference from a compiler is that the standard implementations of Python compile (i.e., translate) source code ...
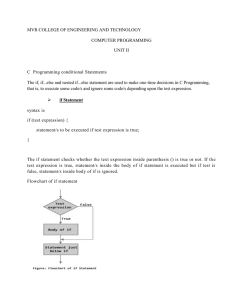
C Programming conditional Statements
... In this program, the user is asked to enter the value of n. Suppose you entered 19 then, count is initialized to 1 at first. Then, the test expression in the for loop,i.e., (count<= n) becomes true. So, the code in the body of for loop is executed which makes sum to 1. Then, the expression ++count i ...
... In this program, the user is asked to enter the value of n. Suppose you entered 19 then, count is initialized to 1 at first. Then, the test expression in the for loop,i.e., (count<= n) becomes true. So, the code in the body of for loop is executed which makes sum to 1. Then, the expression ++count i ...
Lecture 11 Notes
... several reasons. The main one being that programs are easier to read and reason about. Some scripting languages such as Perl still use dynamic scoping. Also, some versions of Common Lisp support both static and dynamic scoping. Note that dynamic binding has some advantages. For example, it can be us ...
... several reasons. The main one being that programs are easier to read and reason about. Some scripting languages such as Perl still use dynamic scoping. Also, some versions of Common Lisp support both static and dynamic scoping. Note that dynamic binding has some advantages. For example, it can be us ...
Lisp, Then and Now
... Lisp is a kind of math implemented as a programming language, just as Prolog is a kind of logic implemented as a programming language You don’t need to understand lambda calculus to use Lisp ...
... Lisp is a kind of math implemented as a programming language, just as Prolog is a kind of logic implemented as a programming language You don’t need to understand lambda calculus to use Lisp ...
lisp_47542238
... The two most important kinds of objects in LISP for you to know about are atoms and lists. Atoms are represented as sequences of characters of reasonable length. Such as :34 or join. Lists are recursively constructed from atoms Such as: (a john 34 c3po). The interpreter treats any list as containing ...
... The two most important kinds of objects in LISP for you to know about are atoms and lists. Atoms are represented as sequences of characters of reasonable length. Such as :34 or join. Lists are recursively constructed from atoms Such as: (a john 34 c3po). The interpreter treats any list as containing ...