Lincoln & the Union Command & handout
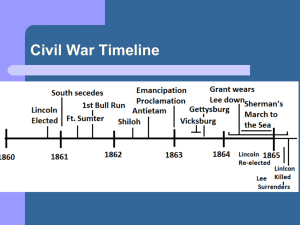
... As Lee moved North, Lincoln replaced Hooker with George Meade After a chance engagement in Gettysburg only days after taking command, Meade rushed his army into defensive position in the hills around the town Meade’s army beat Lee at Gettysburg in what many people consider the turning point of th ...
... As Lee moved North, Lincoln replaced Hooker with George Meade After a chance engagement in Gettysburg only days after taking command, Meade rushed his army into defensive position in the hills around the town Meade’s army beat Lee at Gettysburg in what many people consider the turning point of th ...
Reconstruction
... Andrew Johnson, who succeeded Lincoln carried on his plan • Lincoln’s plan was very lenient and was intended to make it easy for the South to rejoin the Union. The plan would: 1. offer a general amnesty (forgiveness) to all Southerners who took an oath of loyalty and accepted the end of slavery 2. r ...
... Andrew Johnson, who succeeded Lincoln carried on his plan • Lincoln’s plan was very lenient and was intended to make it easy for the South to rejoin the Union. The plan would: 1. offer a general amnesty (forgiveness) to all Southerners who took an oath of loyalty and accepted the end of slavery 2. r ...
File
... Benjamin Montgomery was a former slave who became a landowner, however most other slaves were unable to till (farm) their own land. What did these slaves do for work? ...
... Benjamin Montgomery was a former slave who became a landowner, however most other slaves were unable to till (farm) their own land. What did these slaves do for work? ...
Bull Run - Central Magnet School
... for launching Emancipation Proclamation • By midsummer 1862, Border States safely in fold and Lincoln ready to move – Lincoln decided to wait for outcome of Lee's invasion – Antietam served as needed emancipation springboard – Lincoln issued preliminary Emancipation Proclamation on September 23, 186 ...
... for launching Emancipation Proclamation • By midsummer 1862, Border States safely in fold and Lincoln ready to move – Lincoln decided to wait for outcome of Lee's invasion – Antietam served as needed emancipation springboard – Lincoln issued preliminary Emancipation Proclamation on September 23, 186 ...
Period 5 1844-1877 - Marblehead High School
... • THE BIG IDEA: As the nation expanded and its population grew, regional tensions, especially over slavery, led to a civil war—the course and aftermath of which transformed American society. • Key Concept 5.1: The United States became more connected with the world as it pursued an expansionist forei ...
... • THE BIG IDEA: As the nation expanded and its population grew, regional tensions, especially over slavery, led to a civil war—the course and aftermath of which transformed American society. • Key Concept 5.1: The United States became more connected with the world as it pursued an expansionist forei ...
10 Days - Antietam
... Union was losing because it looked like a desperate move. They told him to wait until they had a victory. Do you agree with the cabinet’s opinion? Why or why not? ...
... Union was losing because it looked like a desperate move. They told him to wait until they had a victory. Do you agree with the cabinet’s opinion? Why or why not? ...
Unit 4
... Describe the three main groups of white people in the South's social structure, what percentages they were of the total southern population and how each group felt about the practice of slavery. ...
... Describe the three main groups of white people in the South's social structure, what percentages they were of the total southern population and how each group felt about the practice of slavery. ...
Civil War Lesson Plan Differences Between the North and the South
... 4) Discuss conflicting opinions of Abraham Lincoln during the war. Ask students: Did most Northerners and Southerners feel the same way about the President? What was the Emancipation Proclamation? How did it affect peoples' feelings towards Lincoln? How did it change the war? Help students understan ...
... 4) Discuss conflicting opinions of Abraham Lincoln during the war. Ask students: Did most Northerners and Southerners feel the same way about the President? What was the Emancipation Proclamation? How did it affect peoples' feelings towards Lincoln? How did it change the war? Help students understan ...
Reconstruction1strevised choice
... • Started his acting career in 1855 and by 1860 was making $20,000 a year…. • many called him "the handsomest man in America“ and he had an easy charm about him that attracted women…. • In 1859 Booth was an eyewitness to the execution of John Brown and stood near the scaffold with other armed men to ...
... • Started his acting career in 1855 and by 1860 was making $20,000 a year…. • many called him "the handsomest man in America“ and he had an easy charm about him that attracted women…. • In 1859 Booth was an eyewitness to the execution of John Brown and stood near the scaffold with other armed men to ...
APUSH-CH19-20-practice - apush
... E) two North American nations would have weaker economies than one. B) war would weaken the United States' power in the Western Hemisphere. ...
... E) two North American nations would have weaker economies than one. B) war would weaken the United States' power in the Western Hemisphere. ...
chapter 15 section 1 - Northside Middle School
... loyalty to U.S. to regain right to vote 1..People from Confederacy couldn’t hold public office without Congress’ approval 2. Cancelled public debt held by ...
... loyalty to U.S. to regain right to vote 1..People from Confederacy couldn’t hold public office without Congress’ approval 2. Cancelled public debt held by ...
Politics and Society in Indiana During the Civil War Indiana was a
... tied to the one great issue of military conflict. Republicans enacted other legislation, including the Homestead Act (1862) to facilitate settlement in the West, the Morrill Land Grant Act (1862) that supported agricultural colleges, a higher tariff on manufactured goods, and measures to help build ...
... tied to the one great issue of military conflict. Republicans enacted other legislation, including the Homestead Act (1862) to facilitate settlement in the West, the Morrill Land Grant Act (1862) that supported agricultural colleges, a higher tariff on manufactured goods, and measures to help build ...
Teacher: Date: Subject:
... stimulated by 1. They feared being for which of the following _____________________ expect the house to fall; 1. the elimination of drafted into the reasons? _ A. Increasing but I do expect it will taxes on defense Northern army. A. Great Britain refused to sectionalism B. cease to be divided. It wi ...
... stimulated by 1. They feared being for which of the following _____________________ expect the house to fall; 1. the elimination of drafted into the reasons? _ A. Increasing but I do expect it will taxes on defense Northern army. A. Great Britain refused to sectionalism B. cease to be divided. It wi ...
Reconstruction Comes to Georgia
... 1. What was the Freedman’s Bureau, and what role did it play during Reconstruction? A government agency established in 1865 to help both freed slaves and poor whites cope with their everyday problems by offering them clothing, food, and other necessities. They later focused on providing education an ...
... 1. What was the Freedman’s Bureau, and what role did it play during Reconstruction? A government agency established in 1865 to help both freed slaves and poor whites cope with their everyday problems by offering them clothing, food, and other necessities. They later focused on providing education an ...
Reconstruction
... secession was illegal, Confederate governments in the Southern states were illegitimate (not legal governments) and the states had never really left the Union. As a result, Lincoln believed that Reconstruction in the Southern states was a matter of quickly restoring legitimate state governments that ...
... secession was illegal, Confederate governments in the Southern states were illegitimate (not legal governments) and the states had never really left the Union. As a result, Lincoln believed that Reconstruction in the Southern states was a matter of quickly restoring legitimate state governments that ...
Practice Terms Test 4,5,6
... 52. Loyalty to the interests of one's own region or section of the country, rather than to the country as a whole. 53. Someone that calls for the ending of slavery. 54. Admitted California to the Union as a free state, put no federal restrictions on slavery for Utah or New Mexico, and passed Fugitiv ...
... 52. Loyalty to the interests of one's own region or section of the country, rather than to the country as a whole. 53. Someone that calls for the ending of slavery. 54. Admitted California to the Union as a free state, put no federal restrictions on slavery for Utah or New Mexico, and passed Fugitiv ...
Reconstruction 1863-1877
... state government, and elect a constitutional convention to write a new state constitution which recognized Emancipation • These newly Reconstructed states would then be eligible to be fully admitted to the Union and to send representatives to Congress ...
... state government, and elect a constitutional convention to write a new state constitution which recognized Emancipation • These newly Reconstructed states would then be eligible to be fully admitted to the Union and to send representatives to Congress ...
File - Ms. Albu`s Class Site
... President Johnson was born to impoverished parents in North Carolina, orphaned at an early age, and moved to Tennessee. Self-educated, he rose through the political ranks to be a congressman, a governor of Tennessee, and a United States senator. At the outbreak of the Civil War, Johnson was the only ...
... President Johnson was born to impoverished parents in North Carolina, orphaned at an early age, and moved to Tennessee. Self-educated, he rose through the political ranks to be a congressman, a governor of Tennessee, and a United States senator. At the outbreak of the Civil War, Johnson was the only ...
Slide 1
... 8. How did the South’s principle of states’ rights undermine the Confederate war effort? A. The South had few mines to provide natural resources that the Confederate war effort required. B. Each state worked in its own interest, preventing the coordination of efforts. C. Each state decided for itse ...
... 8. How did the South’s principle of states’ rights undermine the Confederate war effort? A. The South had few mines to provide natural resources that the Confederate war effort required. B. Each state worked in its own interest, preventing the coordination of efforts. C. Each state decided for itse ...
7 - Immaculateheartacademy.org
... An ugly dose of anti-foreignism or “nativism” was injected into the campaign, even though slavery extension loomed largest. The recent influx of immigrants from Ireland and Germany had alarmed “nativists,” as many old-stock Protestants were called. They organized the American party, known also as th ...
... An ugly dose of anti-foreignism or “nativism” was injected into the campaign, even though slavery extension loomed largest. The recent influx of immigrants from Ireland and Germany had alarmed “nativists,” as many old-stock Protestants were called. They organized the American party, known also as th ...
Hampton Roads Conference

The Hampton Roads Conference was a peace conference held between the United States and the Confederate States on February 3, 1865, aboard the steamboat River Queen in Hampton Roads, Virginia, to discuss terms to end the American Civil War. President Abraham Lincoln and Secretary of State William H. Seward, representing the Union, met with three commissioners from the Confederacy: Vice President Alexander H. Stephens, Senator Robert M. T. Hunter, and Assistant Secretary of War John A. Campbell.The representatives discussed a possible alliance against France, the possible terms of surrender, the question of whether slavery might persist after the war, and the question of whether the South would be compensated for property lost through emancipation. Lincoln and Seward reportedly offered some possibilities for compromise on the issue of slavery. The only concrete agreement reached was over prisoner-of-war exchanges.The Confederate commissioners immediately returned to Richmond at the conclusion of the conference. Confederate President Jefferson Davis announced that the North would not compromise. Lincoln drafted an amnesty agreement based on terms discussed at the Conference, but met with opposition from his Cabinet. John Campbell continued to advocate for a peace agreement and met again with Lincoln after the fall of Richmond on April 2. The war continued until April 9, 1865.