The North Tries to Compromise - LOUISVILLE
... southern states would rejoin the Union if the North returned all runaway enslaved people • Senator John Crittenden of Kentucky offered a compromise suggesting that the Constitution be changed to allow slavery in all new territories – Also suggested that any state north of 36 degrees 30 minutes north ...
... southern states would rejoin the Union if the North returned all runaway enslaved people • Senator John Crittenden of Kentucky offered a compromise suggesting that the Constitution be changed to allow slavery in all new territories – Also suggested that any state north of 36 degrees 30 minutes north ...
Civil War Jeopardy.jpc
... Name two advantages the North had during the war and two disadvantages they faced heading into the war. ...
... Name two advantages the North had during the war and two disadvantages they faced heading into the war. ...
Lincoln & Secession
... Scott Decision made slavery legal every where. • Douglas’ response is known as the Freeport Doctrine. – If states do not want slavery, then they should make laws against it. • Lost support of Southern Democrats. ...
... Scott Decision made slavery legal every where. • Douglas’ response is known as the Freeport Doctrine. – If states do not want slavery, then they should make laws against it. • Lost support of Southern Democrats. ...
The American Civil War 1861
... Lincoln hoped to prevent a war. “We are not enemies, but friends,” Lincoln told Southerners after taking the oath of office. “We must not be enemies.” But time was running out. ...
... Lincoln hoped to prevent a war. “We are not enemies, but friends,” Lincoln told Southerners after taking the oath of office. “We must not be enemies.” But time was running out. ...
File
... Court ruled that slaves were property and no restrictions could be placed on slavery Lincoln emerged as a national political force in his debates with Senator Douglas Brown’s radical abolitionist tactics and raid on a federal arsenal enraged the South Lincoln elected president in this four-way race ...
... Court ruled that slaves were property and no restrictions could be placed on slavery Lincoln emerged as a national political force in his debates with Senator Douglas Brown’s radical abolitionist tactics and raid on a federal arsenal enraged the South Lincoln elected president in this four-way race ...
US History review power point
... “A house divided against itself cannot stand…” The Fight to Preserve the Union ...
... “A house divided against itself cannot stand…” The Fight to Preserve the Union ...
Secession and the Start of the Civil War Chapter 10 Section 4
... The Confederate States of America • The south drafted a new constitution modeled after the US Constitution, but with 2 key differences: ...
... The Confederate States of America • The south drafted a new constitution modeled after the US Constitution, but with 2 key differences: ...
Grading of a sample essay
... At the root of all of the problems was the slavery. The abolishment was considered one of the most influential and south. The American Revolution had been fought to validate the idea that all men were created equal, but slavery was legal in all of the thirteen colonies. Eventually its existence came ...
... At the root of all of the problems was the slavery. The abolishment was considered one of the most influential and south. The American Revolution had been fought to validate the idea that all men were created equal, but slavery was legal in all of the thirteen colonies. Eventually its existence came ...
The Emancipation Proclamation
... • The Confederacy was than able to make their way into Maryland • The Confederacy was poised to continue North and potentially win the war ...
... • The Confederacy was than able to make their way into Maryland • The Confederacy was poised to continue North and potentially win the war ...
THE HISTORY OF THE UNITED STATES 1492-1877
... • Emancipation Proclamation: • Lincoln’s aim: keeping the Union together with or without slavery • Issued on 9-22-1862 • “As of January 1, 1863 all slaves in Confederate states or areas still under active rebellion would be thenceforward and forever free” • Reasons: • Military: elimination of potent ...
... • Emancipation Proclamation: • Lincoln’s aim: keeping the Union together with or without slavery • Issued on 9-22-1862 • “As of January 1, 1863 all slaves in Confederate states or areas still under active rebellion would be thenceforward and forever free” • Reasons: • Military: elimination of potent ...
Slide 1 - TheFoxHole
... Lincoln Douglass Debate Douglas supported popular sovereignty Lincoln did think it was right for the majority to deny the minority of rights Lincoln didn’t support the spread of slavery but didn’t think the federal government had the power to get rid of it. He felt slavery would eventually die out ...
... Lincoln Douglass Debate Douglas supported popular sovereignty Lincoln did think it was right for the majority to deny the minority of rights Lincoln didn’t support the spread of slavery but didn’t think the federal government had the power to get rid of it. He felt slavery would eventually die out ...
Aim: What was the nation`s plan for rebuilding the Union
... Lincoln’s Plan (Ten Percent Plan) – Lincoln wanted to reunite the nation as quickly and painless as possible. He offered amnesty, official pardon, for all illegal acts supporting the rebellion. In order to receive amnesty, southerners had to do two things: 1) swear an oath of loyalty to the United S ...
... Lincoln’s Plan (Ten Percent Plan) – Lincoln wanted to reunite the nation as quickly and painless as possible. He offered amnesty, official pardon, for all illegal acts supporting the rebellion. In order to receive amnesty, southerners had to do two things: 1) swear an oath of loyalty to the United S ...
The Election of 1860
... Mississippi, and Texas also seceded. • Formed the nation the Confederate States of America • Jefferson Davis became their president. ...
... Mississippi, and Texas also seceded. • Formed the nation the Confederate States of America • Jefferson Davis became their president. ...
Battles Xs and Os
... This is known as the bloodiest single-day battle on American soil. After this battle, the purpose for the war shifted from preserving the Union to freeing the slaves. ...
... This is known as the bloodiest single-day battle on American soil. After this battle, the purpose for the war shifted from preserving the Union to freeing the slaves. ...
Civil War Review - Social Studies With A Smile
... Many southern whites thought that ____________________ was necessary for the South’s economy. The Confederacy fought to maintain its __________________. Some Northerners fought because they hated slavery. Most Northerners wanted to preserve the ________________. Each side had certain strengths. The ...
... Many southern whites thought that ____________________ was necessary for the South’s economy. The Confederacy fought to maintain its __________________. Some Northerners fought because they hated slavery. Most Northerners wanted to preserve the ________________. Each side had certain strengths. The ...
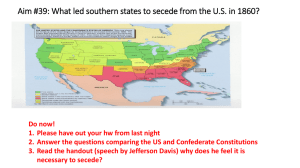
Aim #39: What led southern states to secede
... d. President Buchanan did little to prevent southern secession 1. Believed Constitution didn’t give him authority to stop secession with force 2. Many of his advisors were prosouthern e. Lincoln’s Inaugural f. Ft. Sumter (April 12, 1861) 1. Was fired upon by Southern troops, considered start of Civi ...
... d. President Buchanan did little to prevent southern secession 1. Believed Constitution didn’t give him authority to stop secession with force 2. Many of his advisors were prosouthern e. Lincoln’s Inaugural f. Ft. Sumter (April 12, 1861) 1. Was fired upon by Southern troops, considered start of Civi ...
16.3-A Call to Freedom 16.4-Life During the Civil War
... • They dug trenches for the Confederates protection in battles ...
... • They dug trenches for the Confederates protection in battles ...
PresentationExpress - Cathedral High School
... committee to discuss with Lincoln a possible end to the war. Congress had just proposed the Thirteenth Amendment outlawing slavery but the Confederate peace delegation could not accept it. ...
... committee to discuss with Lincoln a possible end to the war. Congress had just proposed the Thirteenth Amendment outlawing slavery but the Confederate peace delegation could not accept it. ...
A Nation Divided Against Itself
... seceded, the other Lower South States followed • Created a new nation: • The Confederate States of America (the Confederacy) ...
... seceded, the other Lower South States followed • Created a new nation: • The Confederate States of America (the Confederacy) ...
Hampton Roads Conference

The Hampton Roads Conference was a peace conference held between the United States and the Confederate States on February 3, 1865, aboard the steamboat River Queen in Hampton Roads, Virginia, to discuss terms to end the American Civil War. President Abraham Lincoln and Secretary of State William H. Seward, representing the Union, met with three commissioners from the Confederacy: Vice President Alexander H. Stephens, Senator Robert M. T. Hunter, and Assistant Secretary of War John A. Campbell.The representatives discussed a possible alliance against France, the possible terms of surrender, the question of whether slavery might persist after the war, and the question of whether the South would be compensated for property lost through emancipation. Lincoln and Seward reportedly offered some possibilities for compromise on the issue of slavery. The only concrete agreement reached was over prisoner-of-war exchanges.The Confederate commissioners immediately returned to Richmond at the conclusion of the conference. Confederate President Jefferson Davis announced that the North would not compromise. Lincoln drafted an amnesty agreement based on terms discussed at the Conference, but met with opposition from his Cabinet. John Campbell continued to advocate for a peace agreement and met again with Lincoln after the fall of Richmond on April 2. The war continued until April 9, 1865.