18.1 The Two Sides
... 6. It was the _________________ single day of fighting in the war. About ____________ died. 7. The great losses caused Lee to ____________, and for now, his northern invasion had failed. ...
... 6. It was the _________________ single day of fighting in the war. About ____________ died. 7. The great losses caused Lee to ____________, and for now, his northern invasion had failed. ...
The End of the Civil War
... conceived in liberty, and dedicated to the proposition that all men are created equal. Now we are engaged in a great civil war. . .testing whether that nation, or any nation so conceived and so dedicated. . . can long endure. We are met on a great battlefield of that war. We have come to dedicate a ...
... conceived in liberty, and dedicated to the proposition that all men are created equal. Now we are engaged in a great civil war. . .testing whether that nation, or any nation so conceived and so dedicated. . . can long endure. We are met on a great battlefield of that war. We have come to dedicate a ...
One of the most significant issues was the economic split between
... throughout the entire country. They considered the practice evil and contrary to the ideals of democracy. In addition to the conflict over slavery, many Southern states believed that the laws of the individual states should overrule the laws of the federal, or national, government. These Southerners ...
... throughout the entire country. They considered the practice evil and contrary to the ideals of democracy. In addition to the conflict over slavery, many Southern states believed that the laws of the individual states should overrule the laws of the federal, or national, government. These Southerners ...
Civil War Crossword Puzzle
... Kansas territory to called _____ _______ 9 the Union strategy to win the war was called the _____ plan 10 this eloquent speaker was an escaped slave 12 how many slaves were freed by the Emancipation Proclamation? 13 both the North and South used ______ (the draft) 15 Lincoln violated the constitutio ...
... Kansas territory to called _____ _______ 9 the Union strategy to win the war was called the _____ plan 10 this eloquent speaker was an escaped slave 12 how many slaves were freed by the Emancipation Proclamation? 13 both the North and South used ______ (the draft) 15 Lincoln violated the constitutio ...
Civil War Key Events
... Different Views on slavery Let the South leave Fighting a war of Invasion ...
... Different Views on slavery Let the South leave Fighting a war of Invasion ...
4.3 The North Takes Charge
... • Grant gave William Sherman command of the Mississippi; both generals believed in waging total war, where they wanted to destroy the South’s will to fight • Grant fought Lee in VA, while Sherman invaded GA and marched towards the sea, destroying everything in his path ...
... • Grant gave William Sherman command of the Mississippi; both generals believed in waging total war, where they wanted to destroy the South’s will to fight • Grant fought Lee in VA, while Sherman invaded GA and marched towards the sea, destroying everything in his path ...
S.O.L. 7 Review Sheet (Teacher Edition): Civil War and
... Southern states were illegitimate and the states had never really left the Union. He believed that Reconstruction was a matter of quickly restoring legitimate state governments that were loyal to the Union in the Southern states C.Lincoln also believed that once the war was over, to reunify the nati ...
... Southern states were illegitimate and the states had never really left the Union. He believed that Reconstruction was a matter of quickly restoring legitimate state governments that were loyal to the Union in the Southern states C.Lincoln also believed that once the war was over, to reunify the nati ...
Lincoln - drurban.info
... 1. Confiscation Acts (1861, 1862) – slaves would be freed if they fell into Union hands 2. Lincoln supported gradual emancipation and colonization 3. Emancipation would undermine Confederate diplomacy 4. Battle of Antietam served as springboard for Emancipation Proclamation ...
... 1. Confiscation Acts (1861, 1862) – slaves would be freed if they fell into Union hands 2. Lincoln supported gradual emancipation and colonization 3. Emancipation would undermine Confederate diplomacy 4. Battle of Antietam served as springboard for Emancipation Proclamation ...
Group One Period 7/8--1861 and Lincoln`s First Inaugural Address
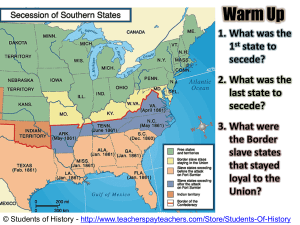
... •The climate in the seceded states was warmer which means more cotton which means more slaves •Seven states seceded after Lincoln’s election. Those were the lower Southern states •Four states secede after Fort Sumter. Those were the upper Southern states ...
... •The climate in the seceded states was warmer which means more cotton which means more slaves •Seven states seceded after Lincoln’s election. Those were the lower Southern states •Four states secede after Fort Sumter. Those were the upper Southern states ...
The United States Civil War
... Lincoln issues the Emancipation Proclamation, declaring all slaves in the Confederate states free and emphasizing their enlistment in the Union army • The war becomes a revolutionary struggle to abolish slavery ...
... Lincoln issues the Emancipation Proclamation, declaring all slaves in the Confederate states free and emphasizing their enlistment in the Union army • The war becomes a revolutionary struggle to abolish slavery ...
CHAPTER 10, 11, 12 2017 STUDY GUIDE
... The Confederate victory at Bull Run made the South think they had won the war It also made the North realize that they had underestimated their opponent ...
... The Confederate victory at Bull Run made the South think they had won the war It also made the North realize that they had underestimated their opponent ...
File
... Lincoln bluntly and tactfully replied thanking Seward and reminding him he was President. Seward offered to resign, Lincoln refused, Seward becomes Lincoln’s biggest supporter. ...
... Lincoln bluntly and tactfully replied thanking Seward and reminding him he was President. Seward offered to resign, Lincoln refused, Seward becomes Lincoln’s biggest supporter. ...
Monday, Nov
... Explain how the firing on Fort Sumter and Lincoln's call for troops galvanized both sides for war: Context: By the time Abraham Lincoln took office in March of 1861, seven southern states had already seceded. In his inaugural address he said there would be “no conflict unless the South provoked it.” ...
... Explain how the firing on Fort Sumter and Lincoln's call for troops galvanized both sides for war: Context: By the time Abraham Lincoln took office in March of 1861, seven southern states had already seceded. In his inaugural address he said there would be “no conflict unless the South provoked it.” ...
Summary: Civil War Begins
... president. Lincoln wanted unity and peace but it was too late. Confederates attacked Fort Sumter on April 12, 1861. Lincoln called for men to fight the rebellion. The Civil War began. ...
... president. Lincoln wanted unity and peace but it was too late. Confederates attacked Fort Sumter on April 12, 1861. Lincoln called for men to fight the rebellion. The Civil War began. ...
Civil War Timeline2012
... Andrew _________________ becomes president; plans to follow Lincoln’s lenient plan for reconciliation Reconstruction refers to the _________________ after the Civil War when the southern states would be readmitted to the U.S. Some northerners (known as ________________ Republicans) believed that ...
... Andrew _________________ becomes president; plans to follow Lincoln’s lenient plan for reconciliation Reconstruction refers to the _________________ after the Civil War when the southern states would be readmitted to the U.S. Some northerners (known as ________________ Republicans) believed that ...
Forming a New Nation
... 1. The balance in the Senate a. free v. slave states 2. The Compromise of 1850 a. CA Statehood b. Fugitive Slave Act c. Stowe’s Uncle Tom’s Cabin 3. The Kansas-Nebraska Act a. Stephen A. Douglas b. popular sovereignty c. Kansas-Nebraska Act passes d. Republican Party created ...
... 1. The balance in the Senate a. free v. slave states 2. The Compromise of 1850 a. CA Statehood b. Fugitive Slave Act c. Stowe’s Uncle Tom’s Cabin 3. The Kansas-Nebraska Act a. Stephen A. Douglas b. popular sovereignty c. Kansas-Nebraska Act passes d. Republican Party created ...
Summary: Lincoln`s Election
... Douglas. They debated so people could hear their ideas. Douglas wanted popular sovereignty for territories. He did not think slavery was wrong. Lincoln said slavery was evil, but he did not support abolition. Lincoln lost, but the debates made him famous. Many southerners thought he wanted to abolis ...
... Douglas. They debated so people could hear their ideas. Douglas wanted popular sovereignty for territories. He did not think slavery was wrong. Lincoln said slavery was evil, but he did not support abolition. Lincoln lost, but the debates made him famous. Many southerners thought he wanted to abolis ...
Hampton Roads Conference

The Hampton Roads Conference was a peace conference held between the United States and the Confederate States on February 3, 1865, aboard the steamboat River Queen in Hampton Roads, Virginia, to discuss terms to end the American Civil War. President Abraham Lincoln and Secretary of State William H. Seward, representing the Union, met with three commissioners from the Confederacy: Vice President Alexander H. Stephens, Senator Robert M. T. Hunter, and Assistant Secretary of War John A. Campbell.The representatives discussed a possible alliance against France, the possible terms of surrender, the question of whether slavery might persist after the war, and the question of whether the South would be compensated for property lost through emancipation. Lincoln and Seward reportedly offered some possibilities for compromise on the issue of slavery. The only concrete agreement reached was over prisoner-of-war exchanges.The Confederate commissioners immediately returned to Richmond at the conclusion of the conference. Confederate President Jefferson Davis announced that the North would not compromise. Lincoln drafted an amnesty agreement based on terms discussed at the Conference, but met with opposition from his Cabinet. John Campbell continued to advocate for a peace agreement and met again with Lincoln after the fall of Richmond on April 2. The war continued until April 9, 1865.