Note Cards 601. Stephen A. Douglas A moderate, who introduced
... that slavery was justified when compared to the cannibalistic approach of capitalism. Tried to justify slavery. 619. Hinton Helper, The Impending Crisis of the South Hinton Helper of North Carolina spoke for poor, non-slave-owing Whites in his 1857 book, which as a violent attack on slavery. It was ...
... that slavery was justified when compared to the cannibalistic approach of capitalism. Tried to justify slavery. 619. Hinton Helper, The Impending Crisis of the South Hinton Helper of North Carolina spoke for poor, non-slave-owing Whites in his 1857 book, which as a violent attack on slavery. It was ...
secession and the civil war
... • 200,000 African American Union troops • Many others labor in Northern war effort • Lincoln pushes further for black rights ...
... • 200,000 African American Union troops • Many others labor in Northern war effort • Lincoln pushes further for black rights ...
The American Civil War
... of food and disease. Union camps often retaliated for perceived maltreatment of Union soldiers by the CSA ...
... of food and disease. Union camps often retaliated for perceived maltreatment of Union soldiers by the CSA ...
The Civil War
... 1861 – The 1st major battle of the war takes place at Bull Run on July 21st 1863 – The Battle of Gettysburg ends the Confederate drive into the North – Abraham Lincoln issues the Emancipation Proclamation 1864 – General U.S. Grant becomes commander of the Union Army 1865, April 9 – General Lee surre ...
... 1861 – The 1st major battle of the war takes place at Bull Run on July 21st 1863 – The Battle of Gettysburg ends the Confederate drive into the North – Abraham Lincoln issues the Emancipation Proclamation 1864 – General U.S. Grant becomes commander of the Union Army 1865, April 9 – General Lee surre ...
File - Team Sigma
... Union forces turn back Lee’s first invasion of the North. The loss discouraged foreign support of the Confederate States. Bloodiest day of fighting. ...
... Union forces turn back Lee’s first invasion of the North. The loss discouraged foreign support of the Confederate States. Bloodiest day of fighting. ...
Name - Central CUSD 4
... T 4. The Battle of Bull Run showed both sides that their soldiers needed more training. Q 5. The commander of the Union armies in 1861 was a cautious person and his name was George McClellan. T 6. The battle between the ironclads the Monitor and the Merrimack resulted in the building of many more ir ...
... T 4. The Battle of Bull Run showed both sides that their soldiers needed more training. Q 5. The commander of the Union armies in 1861 was a cautious person and his name was George McClellan. T 6. The battle between the ironclads the Monitor and the Merrimack resulted in the building of many more ir ...
civil war gazette ii - Cajon Valley Union School District
... captured the Confederate capital The first step of the plan to surround the Confederacy by sea worked as the North had a superior navy and ship building factories. The ironclads proved beneficial to both sides, but the Confederates could not break the Union blockade, and was refused help from Europe ...
... captured the Confederate capital The first step of the plan to surround the Confederacy by sea worked as the North had a superior navy and ship building factories. The ironclads proved beneficial to both sides, but the Confederates could not break the Union blockade, and was refused help from Europe ...
Units 8-9-10 Jeopardy - Westward Expansion, Civil War
... 1. Slaves are not citizens 2. Congress can’t limit slavery ...
... 1. Slaves are not citizens 2. Congress can’t limit slavery ...
File unit 7 vocabulary word wall
... 1865, and more generally the emancipation of African-American slaves throughout the Confederate South. Celebrated on June 19 and recognized as a state holiday or special day of observance in most states. ...
... 1865, and more generally the emancipation of African-American slaves throughout the Confederate South. Celebrated on June 19 and recognized as a state holiday or special day of observance in most states. ...
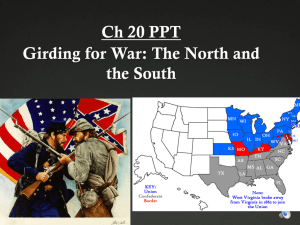
Girding for War: The North and the South, 1861-1865
... as volunteers became scarce, money was offered to them in return for service; still, there were many deserters. • The South had to resort to a draft nearly a year before the North, and it also had its privileges for the rich—those who owned or oversaw 20 slaves or more were exempt from the ...
... as volunteers became scarce, money was offered to them in return for service; still, there were many deserters. • The South had to resort to a draft nearly a year before the North, and it also had its privileges for the rich—those who owned or oversaw 20 slaves or more were exempt from the ...
Slide 1
... • State constitution could only be voted on by white males who swore never to held arms against the ...
... • State constitution could only be voted on by white males who swore never to held arms against the ...
CWHomeFront1
... •Lincoln resorted to extreme measures to quash protest. •The Union had to exercise a firm hand with slave states that did not secede to keep their loyalty. •Lincoln put Kentucky under martial law to secure it. •Also Lincoln suspended the writ of habeas corpus, the right to be charged with a crime ...
... •Lincoln resorted to extreme measures to quash protest. •The Union had to exercise a firm hand with slave states that did not secede to keep their loyalty. •Lincoln put Kentucky under martial law to secure it. •Also Lincoln suspended the writ of habeas corpus, the right to be charged with a crime ...
The Civil War
... shell – to fire explosive objects at something; rockets, grenades, etc. sovereignty – independent authority claimed by a state or community President Abraham Lincoln called for 75,000 volunteers to serve as soldiers in a campaign against the South. The term of enlistment was only 90 days—most northe ...
... shell – to fire explosive objects at something; rockets, grenades, etc. sovereignty – independent authority claimed by a state or community President Abraham Lincoln called for 75,000 volunteers to serve as soldiers in a campaign against the South. The term of enlistment was only 90 days—most northe ...
President`s ppt 2
... United States, and subject to the jurisdiction thereof, are citizens of the United States and of the State wherein they reside. No State shall make or enforce any law which shall abridge the privileges or immunities of citizens of the United States; nor shall any State deprive any person of life, li ...
... United States, and subject to the jurisdiction thereof, are citizens of the United States and of the State wherein they reside. No State shall make or enforce any law which shall abridge the privileges or immunities of citizens of the United States; nor shall any State deprive any person of life, li ...
Civil War Study Guide
... 2. Describe the early Civil War battles. First Battle of Bull Run-first major battle in the war-Confederacy victory Battle of Antietam-1862, important victory for Union 3. How did military technology change the way that war was fought? allowed them to kill/wound more enemies because the weapons were ...
... 2. Describe the early Civil War battles. First Battle of Bull Run-first major battle in the war-Confederacy victory Battle of Antietam-1862, important victory for Union 3. How did military technology change the way that war was fought? allowed them to kill/wound more enemies because the weapons were ...
s 10% Plan
... – Should they be pardoned or punished? 2. Now that black southerners were free would they have equal rights? – If so, How would these rights be protected? ...
... – Should they be pardoned or punished? 2. Now that black southerners were free would they have equal rights? – If so, How would these rights be protected? ...
The Civil War - SchoolWorld an Edline Solution
... opening the Northern territory to slavery. Both sides begin sending settlers into the areas in an effort to influence the future of these areas. 1855 – As Kansas prepares for elections thousands of Border Ruffians from Missouri (slave) enter the territory in an effort to influence the election. Th ...
... opening the Northern territory to slavery. Both sides begin sending settlers into the areas in an effort to influence the future of these areas. 1855 – As Kansas prepares for elections thousands of Border Ruffians from Missouri (slave) enter the territory in an effort to influence the election. Th ...
North and South
... Maryland, Delaware, W. Virginia – these had slaves At onset of war, Lincoln declared: he wasn’t fighting to free Blacks, but to save the Union. Maryland: Lincoln declared martial law - sent in Union troops to W. Virginia and Missouri. “Indian Territory” – Most of the 5 Civilized tribes (some owned s ...
... Maryland, Delaware, W. Virginia – these had slaves At onset of war, Lincoln declared: he wasn’t fighting to free Blacks, but to save the Union. Maryland: Lincoln declared martial law - sent in Union troops to W. Virginia and Missouri. “Indian Territory” – Most of the 5 Civilized tribes (some owned s ...
The American Civil War
... Southerners felt their economic, property, and other rights were threatened ...
... Southerners felt their economic, property, and other rights were threatened ...
Hampton Roads Conference

The Hampton Roads Conference was a peace conference held between the United States and the Confederate States on February 3, 1865, aboard the steamboat River Queen in Hampton Roads, Virginia, to discuss terms to end the American Civil War. President Abraham Lincoln and Secretary of State William H. Seward, representing the Union, met with three commissioners from the Confederacy: Vice President Alexander H. Stephens, Senator Robert M. T. Hunter, and Assistant Secretary of War John A. Campbell.The representatives discussed a possible alliance against France, the possible terms of surrender, the question of whether slavery might persist after the war, and the question of whether the South would be compensated for property lost through emancipation. Lincoln and Seward reportedly offered some possibilities for compromise on the issue of slavery. The only concrete agreement reached was over prisoner-of-war exchanges.The Confederate commissioners immediately returned to Richmond at the conclusion of the conference. Confederate President Jefferson Davis announced that the North would not compromise. Lincoln drafted an amnesty agreement based on terms discussed at the Conference, but met with opposition from his Cabinet. John Campbell continued to advocate for a peace agreement and met again with Lincoln after the fall of Richmond on April 2. The war continued until April 9, 1865.