
Reconstruction? - Cloudfront.net
... Reconstruction is the period of time (1865 – 1877), during which the U.S. began to rebuild following the Civil War. – Also, the process the federal gov. used to readmit defeated Confederate states back into the Union. ...
... Reconstruction is the period of time (1865 – 1877), during which the U.S. began to rebuild following the Civil War. – Also, the process the federal gov. used to readmit defeated Confederate states back into the Union. ...
Reconstruction Notes
... Tennessee - July 24, 1866 Arkansas - June 22, 1868 Florida - June 25, 1868 North Carolina - July 4, 1868 South Carolina - July 9, 1868 Louisiana - July 9, 1868 Alabama - July 13, 1868 Virginia - January 26, 1870 Mississippi - February 23, 1870 Texas - March 30, 1870 Georgia - July 15, 1870 ...
... Tennessee - July 24, 1866 Arkansas - June 22, 1868 Florida - June 25, 1868 North Carolina - July 4, 1868 South Carolina - July 9, 1868 Louisiana - July 9, 1868 Alabama - July 13, 1868 Virginia - January 26, 1870 Mississippi - February 23, 1870 Texas - March 30, 1870 Georgia - July 15, 1870 ...
Reconstruction PPT
... Give African American men the right to vote. Ratify the 14th and 15th amendments Eliminate the black codes Ironclad oath – which said that they had not voluntarily serve in the Confederate army. (many Southerners were not allowed to vote due to this) ...
... Give African American men the right to vote. Ratify the 14th and 15th amendments Eliminate the black codes Ironclad oath – which said that they had not voluntarily serve in the Confederate army. (many Southerners were not allowed to vote due to this) ...
Reconstruction Part I *With the end of the Civil War, the South was
... *When Congress re-convened on 4 December 1865 after a nine-month recess, the Republicans were shocked to see Southern Democrats back in town, many of whom were prominent former Confederates, including generals, cabinet officials, and even the former Vice-President, still under indictment for treason ...
... *When Congress re-convened on 4 December 1865 after a nine-month recess, the Republicans were shocked to see Southern Democrats back in town, many of whom were prominent former Confederates, including generals, cabinet officials, and even the former Vice-President, still under indictment for treason ...
Reconstruction Cornell Notes
... 23. What three amendments did the Radical Republicans add to the United States Constitution in order to help African-Americans? 24. Identify the Thirteenth Amendment. 25. Identify the Fourteenth Amendment. 26. Identify the Fifteenth Amendment. 27. How had the Civil War affected the Southern states? ...
... 23. What three amendments did the Radical Republicans add to the United States Constitution in order to help African-Americans? 24. Identify the Thirteenth Amendment. 25. Identify the Fourteenth Amendment. 26. Identify the Fifteenth Amendment. 27. How had the Civil War affected the Southern states? ...
Reconstruction Politics (1863/65
... • He was a Democrat & his Reconstruction plan was similar to Lincoln’s • Issued 13,000 pardons • Unconcerned with rights of former slaves • Impeached in 1868 ...
... • He was a Democrat & his Reconstruction plan was similar to Lincoln’s • Issued 13,000 pardons • Unconcerned with rights of former slaves • Impeached in 1868 ...
Reconstruction (1865
... Carpet-baggers — Northerners who come south to “profit of the misery of the south” -- buy up plantations. etc. ...
... Carpet-baggers — Northerners who come south to “profit of the misery of the south” -- buy up plantations. etc. ...
Introduction to Reconstruction
... for freedmen No military or political leader of the Confederacy would be allowed to hold state or federal office South would be occupied by federal troops and governed by army generals in order to maintain law and order Southern states must be punished for the death and destruction of the war Southe ...
... for freedmen No military or political leader of the Confederacy would be allowed to hold state or federal office South would be occupied by federal troops and governed by army generals in order to maintain law and order Southern states must be punished for the death and destruction of the war Southe ...
Southern Reconstruction
... Congress, not the president Since secession was against the law, Confederates ...
... Congress, not the president Since secession was against the law, Confederates ...
Reconstruction 1865-1877
... • 1865-13th- outlaw slavery• 1866--14th- Equality before the law-due process of rights. • Fight the Black Codes. • 1870--15th-right of citizens of the United States to vote shall not be denied or abridged by the United States or by any state on account of race, color, or previous condition of servit ...
... • 1865-13th- outlaw slavery• 1866--14th- Equality before the law-due process of rights. • Fight the Black Codes. • 1870--15th-right of citizens of the United States to vote shall not be denied or abridged by the United States or by any state on account of race, color, or previous condition of servit ...
Reconstruction - Administration
... Congress immediately voted to impeach Johnson for violating Tenure of Office Act After promising to stop obstructing Republican policies, Johnson acquitted by 1 vote in Senate ...
... Congress immediately voted to impeach Johnson for violating Tenure of Office Act After promising to stop obstructing Republican policies, Johnson acquitted by 1 vote in Senate ...
Reconstruction PPT - stjohns
... Northerners address the issue of including Photograph of an enslaved family in South former slaves as Carolina taken in 1862 citizens in society? • What were some major challenges that former slaves faced? ...
... Northerners address the issue of including Photograph of an enslaved family in South former slaves as Carolina taken in 1862 citizens in society? • What were some major challenges that former slaves faced? ...
Reconstruction - St. Mary School
... Unlike Lincoln, the Radical Republicans wanted to punish the former leaders of the Confederacy . They passed the amendments known as the Reconstruction Amendments. Reconstruction Amendments. 13th Amendment --ended the practice of slavery in the United States. 14th Amendment was a response to Souther ...
... Unlike Lincoln, the Radical Republicans wanted to punish the former leaders of the Confederacy . They passed the amendments known as the Reconstruction Amendments. Reconstruction Amendments. 13th Amendment --ended the practice of slavery in the United States. 14th Amendment was a response to Souther ...
Reconstruction (1865-1876) - US History-
... February, 1866 President vetoed the Freedmen’s Bureau bill. March, 1866 Johnson vetoed the 1866 Civil Rights Act. Congress passed both bills over Johnson’s vetoes 1st in U. S. history!! ...
... February, 1866 President vetoed the Freedmen’s Bureau bill. March, 1866 Johnson vetoed the 1866 Civil Rights Act. Congress passed both bills over Johnson’s vetoes 1st in U. S. history!! ...
Slide 1
... officials. 6. Pres. Johnson attempts to fire Secretary of War Edwin Stanton, a Radical Republican interested in punishing the South. ...
... officials. 6. Pres. Johnson attempts to fire Secretary of War Edwin Stanton, a Radical Republican interested in punishing the South. ...
Reconstruction Era-1
... Southern governments refused to the 14th and 15th amendments and some white southerners used violence to prevent African Americans from voting. In response to this the Congress passed the Enforcement Act of 1870, giving the federal government more power to punish those who tried to prevent African A ...
... Southern governments refused to the 14th and 15th amendments and some white southerners used violence to prevent African Americans from voting. In response to this the Congress passed the Enforcement Act of 1870, giving the federal government more power to punish those who tried to prevent African A ...
Unit 6 CHAPTER 16: The Crises of Reconstruction 1865
... 11. __F__The Radical Republicans fell five votes short of the necessary 2/3rds majority needed to successfully impeach the president. Several Republicans sided with democrats opposed to conviction. 12. ____Ex-Confederate states were compelled to allow black men to vote as a prerequisite for readmiss ...
... 11. __F__The Radical Republicans fell five votes short of the necessary 2/3rds majority needed to successfully impeach the president. Several Republicans sided with democrats opposed to conviction. 12. ____Ex-Confederate states were compelled to allow black men to vote as a prerequisite for readmiss ...
Slide 1
... a federal reconstruction plan They used the Army to combat the effect of black codes and enforce new laws that guaranteed rights to African Americans in Southern states Federal reconstruction took the vote away from 10,000 to 15,000 white men who had been Confederate officials or soldiers ...
... a federal reconstruction plan They used the Army to combat the effect of black codes and enforce new laws that guaranteed rights to African Americans in Southern states Federal reconstruction took the vote away from 10,000 to 15,000 white men who had been Confederate officials or soldiers ...
Document
... *”Operates in favor of the colored and against the white race” c. Johnson Veto d. Congress overrides the presidential veto. 3. Reconstruction Act 1867 a. Johnson vetoed, veto overridden b. 10 Confederate States divided into 5 military districts *Police Power *Register new, loyal voters *New governme ...
... *”Operates in favor of the colored and against the white race” c. Johnson Veto d. Congress overrides the presidential veto. 3. Reconstruction Act 1867 a. Johnson vetoed, veto overridden b. 10 Confederate States divided into 5 military districts *Police Power *Register new, loyal voters *New governme ...
Chapter 22: “The Ordeal of Reconstruction”
... Many Southerners regarded reconstruction as worse than the Civil War It destroyed their system of society The Republicans failed to improve the conditions of the South Conditions for blacks would remain difficult for at least another century until the Civil Rights Movement in the 1950’s & 60’s ...
... Many Southerners regarded reconstruction as worse than the Civil War It destroyed their system of society The Republicans failed to improve the conditions of the South Conditions for blacks would remain difficult for at least another century until the Civil Rights Movement in the 1950’s & 60’s ...
Reconstruction
... House and Senate and now had the power to override any presidential veto. They launched their own ideas for Reconstruction. ...
... House and Senate and now had the power to override any presidential veto. They launched their own ideas for Reconstruction. ...
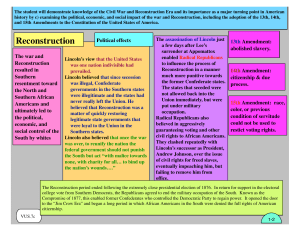
VUS.7c-1
... governments in the Southern states were illegitimate and the states had never really left the Union. He believed that Reconstruction was a matter of quickly restoring legitimate state governments that were loyal to the Union in the Southern states. Lincoln also believed that once the war was over, t ...
... governments in the Southern states were illegitimate and the states had never really left the Union. He believed that Reconstruction was a matter of quickly restoring legitimate state governments that were loyal to the Union in the Southern states. Lincoln also believed that once the war was over, t ...
Chapter 12 Study Guide
... 1. President Abraham Lincoln was assassinated by ___________________________________________. 2. In the 1876 presidential election, Republican Rutherford B. Hayes ran against Democratic candidate _____________________________________________________. 3. A former slave who became an abolitionist and ...
... 1. President Abraham Lincoln was assassinated by ___________________________________________. 2. In the 1876 presidential election, Republican Rutherford B. Hayes ran against Democratic candidate _____________________________________________________. 3. A former slave who became an abolitionist and ...
Reconstruction[1]
... Congress immediately voted to impeach Johnson for violating Tenure of Office Act After promising to stop obstructing Republican policies, Johnson acquitted by 1 vote in Senate ...
... Congress immediately voted to impeach Johnson for violating Tenure of Office Act After promising to stop obstructing Republican policies, Johnson acquitted by 1 vote in Senate ...
Model for Tuesday`s homework
... Classroom copy – put this BACK after you check your homework. a. 13th Amendment: banned slavery in the United States. This could mean that millions of former slaves now had the chance to own land, go to school, reunite with their families and live as free people. b. Legislators: the people who make ...
... Classroom copy – put this BACK after you check your homework. a. 13th Amendment: banned slavery in the United States. This could mean that millions of former slaves now had the chance to own land, go to school, reunite with their families and live as free people. b. Legislators: the people who make ...
Radical Republican

The Radical Republicans were a faction of American politicians within the Republican Party from about 1854 (before the American Civil War) until the end of Reconstruction in 1877. They called themselves ""Radicals"" and were opposed during the war by the Moderate Republicans (led by Abraham Lincoln), by the Conservative Republicans, and by the pro-slavery Democratic Party. After the war, the Radicals were opposed by self-styled ""conservatives"" (in the South) and ""liberals"" (in the North). Radicals strongly opposed slavery during the war and after the war distrusted ex-Confederates, demanding harsh policies for the former rebels, and emphasizing civil rights and voting rights for freedmen (recently freed slaves).During the war, Radical Republicans often opposed Lincoln in terms of selection of generals (especially his choice of Democrat George B. McClellan for top command) and his efforts to bring states back into the Union. The Radicals passed their own reconstruction plan through Congress in 1864, but Lincoln vetoed it and was putting his own policies in effect when he was assassinated in 1865. Radicals pushed for the uncompensated abolition of slavery, while Lincoln wanted to pay slave owners who were loyal to the Union. After the war, the Radicals demanded civil rights for freedmen, such as measures ensuring suffrage. They initiated the Reconstruction Acts, and limited political and voting rights for ex-Confederates. They bitterly fought President Andrew Johnson; they weakened his powers and attempted to remove him from office through impeachment, which failed by one vote. The Radicals were vigorously opposed by the Democratic Party and often by moderate and Liberal Republicans as well.





















![Reconstruction[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008644291_1-e6233bcb90b624220e71edb0c1f7b071-300x300.png)
