polarization of the allotropic hollow foms of carbon and its use in
... The effect of electron cumulation in hollow molecules (traps for electrons) can be applied to management in semiconductors: concentration of carriers of a charge, their thermal, electric properties and hardenings of materials with free electrons. The quantum properties of polarized resonators self-c ...
... The effect of electron cumulation in hollow molecules (traps for electrons) can be applied to management in semiconductors: concentration of carriers of a charge, their thermal, electric properties and hardenings of materials with free electrons. The quantum properties of polarized resonators self-c ...
The Quantum Atom (section 18)
... Bohr suggests: Electrons are only allowed to occupy certain orbits. They make quantum leaps between these orbits. When they do so, they emit or absorb single photons of light of energy E=hf. What are the allowed orbits? The ones with angular momentum in units of h/2π. WHY should this be? Bohr didn’t ...
... Bohr suggests: Electrons are only allowed to occupy certain orbits. They make quantum leaps between these orbits. When they do so, they emit or absorb single photons of light of energy E=hf. What are the allowed orbits? The ones with angular momentum in units of h/2π. WHY should this be? Bohr didn’t ...
Crash course on Quantum Mechanics
... By the basic existence and uniqueness theory of ordinary differential equations, the Newton’s equation has a unique solition for all times if the initial conditions x(0) = x, ẋ(0) = v at t = 0 are given. We need two initial conditions because the equation is of second order and for the same reason ...
... By the basic existence and uniqueness theory of ordinary differential equations, the Newton’s equation has a unique solition for all times if the initial conditions x(0) = x, ẋ(0) = v at t = 0 are given. We need two initial conditions because the equation is of second order and for the same reason ...
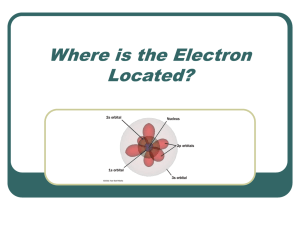
Where is the Electron Located?
... energy level occupied by an electron. Angular Momentum (l): Indicates the shape of the orbital (s,p,d,f,g) ...
... energy level occupied by an electron. Angular Momentum (l): Indicates the shape of the orbital (s,p,d,f,g) ...
Renormalization

In quantum field theory, the statistical mechanics of fields, and the theory of self-similar geometric structures, renormalization is any of a collection of techniques used to treat infinities arising in calculated quantities.Renormalization specifies relationships between parameters in the theory when the parameters describing large distance scales differ from the parameters describing small distances. Physically, the pileup of contributions from an infinity of scales involved in a problem may then result in infinities. When describing space and time as a continuum, certain statistical and quantum mechanical constructions are ill defined. To define them, this continuum limit, the removal of the ""construction scaffolding"" of lattices at various scales, has to be taken carefully, as detailed below.Renormalization was first developed in quantum electrodynamics (QED) to make sense of infinite integrals in perturbation theory. Initially viewed as a suspect provisional procedure even by some of its originators, renormalization eventually was embraced as an important and self-consistent actual mechanism of scale physics in several fields of physics and mathematics. Today, the point of view has shifted: on the basis of the breakthrough renormalization group insights of Kenneth Wilson, the focus is on variation of physical quantities across contiguous scales, while distant scales are related to each other through ""effective"" descriptions. All scales are linked in a broadly systematic way, and the actual physics pertinent to each is extracted with the suitable specific computational techniques appropriate for each.




![PROBLEM 1 [25 PTS] A system consists of N distinquishable](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/006063913_1-e1778e5c6114fd66466f556bb5f30c03-300x300.png)