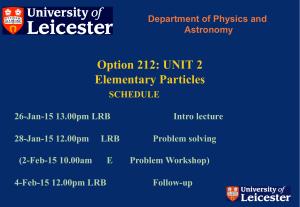
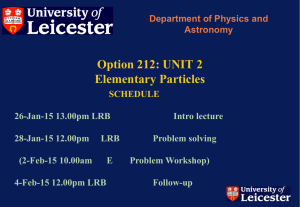
Sikkim NIC
... 26. A point charge q is rotated along a circle in the electric field generated by another point charge Q. The work done by the electric field on the rotating charge in one complete revolution is A. zero B. positive C. negative D. zero if the charge Q is at the center and nonzero otherwise. 27. 12 J ...
... 26. A point charge q is rotated along a circle in the electric field generated by another point charge Q. The work done by the electric field on the rotating charge in one complete revolution is A. zero B. positive C. negative D. zero if the charge Q is at the center and nonzero otherwise. 27. 12 J ...
The dangers of non-empirical confirmation
... alternative to string theory is loop quantum gravity, considered the “only game in town” by those who embrace it, under their set of assumptions. Any theory, physically correct or incorrect, has “no alternatives” under suitable assumptions; the problem is that these assumptions may be wrong. Here we ...
... alternative to string theory is loop quantum gravity, considered the “only game in town” by those who embrace it, under their set of assumptions. Any theory, physically correct or incorrect, has “no alternatives” under suitable assumptions; the problem is that these assumptions may be wrong. Here we ...
Quantum Mechanical Model
... Orbitals Orbitals are NOT circular orbits for electrons Orbitals are “areas of probability” for locating electrons A function of the coordinates (x, y, and z) of the electron’s position in 3-D space ...
... Orbitals Orbitals are NOT circular orbits for electrons Orbitals are “areas of probability” for locating electrons A function of the coordinates (x, y, and z) of the electron’s position in 3-D space ...
Oct 24 Agenda
... Most of the atom’s mass and all of it’s positive charge are contained in a small core called the nucleus. Most of the volume of the atom is empty space through which the tiny negatively charged electrons are randomly dispersed. There are equal numbers of positive and negative charged particles so at ...
... Most of the atom’s mass and all of it’s positive charge are contained in a small core called the nucleus. Most of the volume of the atom is empty space through which the tiny negatively charged electrons are randomly dispersed. There are equal numbers of positive and negative charged particles so at ...
PPT
... show interference only if they get to the same place. The (x,y,z,t) coordinates must all be the same. The wave function representing MANY particles is a function of ALL their coordinates, so if there are two lumps of this wave function evolving in time, they show interference only if ALL the coordin ...
... show interference only if they get to the same place. The (x,y,z,t) coordinates must all be the same. The wave function representing MANY particles is a function of ALL their coordinates, so if there are two lumps of this wave function evolving in time, they show interference only if ALL the coordin ...
univERsity oF copEnhAGEn
... formulation of bosonic string theory [3] and the integration over these geometries was approximated by a summation over triangulations constructed from equilateral triangles with link lengths at , where at again was a UV cutoff. However, the results were identical to the hypercubic lattice results. ...
... formulation of bosonic string theory [3] and the integration over these geometries was approximated by a summation over triangulations constructed from equilateral triangles with link lengths at , where at again was a UV cutoff. However, the results were identical to the hypercubic lattice results. ...
evaluating your performance
... to -v, where v is the velocity of the rock, and neglect the buoyant force exerted by air. Which of the following is correct? (A) The acceleration of the rock is always equal to I. (B) The acceleration of the rock is equal to g only at the top of the flight. (C) The acceleration of the rock is always ...
... to -v, where v is the velocity of the rock, and neglect the buoyant force exerted by air. Which of the following is correct? (A) The acceleration of the rock is always equal to I. (B) The acceleration of the rock is equal to g only at the top of the flight. (C) The acceleration of the rock is always ...
Renormalization

In quantum field theory, the statistical mechanics of fields, and the theory of self-similar geometric structures, renormalization is any of a collection of techniques used to treat infinities arising in calculated quantities.Renormalization specifies relationships between parameters in the theory when the parameters describing large distance scales differ from the parameters describing small distances. Physically, the pileup of contributions from an infinity of scales involved in a problem may then result in infinities. When describing space and time as a continuum, certain statistical and quantum mechanical constructions are ill defined. To define them, this continuum limit, the removal of the ""construction scaffolding"" of lattices at various scales, has to be taken carefully, as detailed below.Renormalization was first developed in quantum electrodynamics (QED) to make sense of infinite integrals in perturbation theory. Initially viewed as a suspect provisional procedure even by some of its originators, renormalization eventually was embraced as an important and self-consistent actual mechanism of scale physics in several fields of physics and mathematics. Today, the point of view has shifted: on the basis of the breakthrough renormalization group insights of Kenneth Wilson, the focus is on variation of physical quantities across contiguous scales, while distant scales are related to each other through ""effective"" descriptions. All scales are linked in a broadly systematic way, and the actual physics pertinent to each is extracted with the suitable specific computational techniques appropriate for each.