doc - The Crowned Anarchist Literature and Science Fiction
... internal structure, in which case one speaks of relativistic continuum mechanics. This article is concerned only with relativistic point-particle mechanics. It is also assumed that quantum mechanical effects are unimportant, otherwise relativistic quantum mechanics or relativistic quantum field theo ...
... internal structure, in which case one speaks of relativistic continuum mechanics. This article is concerned only with relativistic point-particle mechanics. It is also assumed that quantum mechanical effects are unimportant, otherwise relativistic quantum mechanics or relativistic quantum field theo ...
Unit 2 – Electrons and Periodic Behavior Cartoon courtesy of
... orientation of the electron’s orbital with respect to the three axes in space (x,y,z). Have to split up p, d, f orbitals. ...
... orientation of the electron’s orbital with respect to the three axes in space (x,y,z). Have to split up p, d, f orbitals. ...
Coherent transport through a quantum dot in a strong magnetic field *
... Whereas in the q"1 case the propagator has poles at all integer multiples of the noninteracting level spacing *e, in the interacting case the first q!1 poles (above the Fermi energy) are removed. This effect, which can be regarded as a remnant of the Coulomb blockade for particles with short-range i ...
... Whereas in the q"1 case the propagator has poles at all integer multiples of the noninteracting level spacing *e, in the interacting case the first q!1 poles (above the Fermi energy) are removed. This effect, which can be regarded as a remnant of the Coulomb blockade for particles with short-range i ...
Exercises #1 - Berkeley City College
... 3. the magnetic quantum number ml describes the orientation of the orbitals in space with respect to the x-, y-, and z- coordinates. Within each sublevel, ml is allowed values from -l through 0 to +l. For example, if l = 0, ml = 0; if l = 1, ml = -1, 0, or +1; if l = 2, ml = -2, -1, 0, +1, and +2, a ...
... 3. the magnetic quantum number ml describes the orientation of the orbitals in space with respect to the x-, y-, and z- coordinates. Within each sublevel, ml is allowed values from -l through 0 to +l. For example, if l = 0, ml = 0; if l = 1, ml = -1, 0, or +1; if l = 2, ml = -2, -1, 0, +1, and +2, a ...
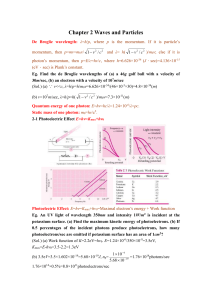
Chapter 2 Waves and Particles De Broglie wavelength: λ=h/p, where
... Eg. An UV light of wavelength 350nm and intensity 1W/m2 is incident at the potassium surface. (a) Find the maximum kinetic energy of photoelectrons. (b) If 0.5 percentages of the incident photons produce photoelectrons, how many photoelectrons/sec are emitted if potassium surface has an area of 1cm2 ...
... Eg. An UV light of wavelength 350nm and intensity 1W/m2 is incident at the potassium surface. (a) Find the maximum kinetic energy of photoelectrons. (b) If 0.5 percentages of the incident photons produce photoelectrons, how many photoelectrons/sec are emitted if potassium surface has an area of 1cm2 ...
electric fields
... was to come up with a standard constant for the elementary charge. The data that he used to find the value of the elementary charge is considered to be some of the most accurate and meticulously obtained experimental data ever recorded. SET-UP A fine mist of oil was sprayed from an atomizer. Most of ...
... was to come up with a standard constant for the elementary charge. The data that he used to find the value of the elementary charge is considered to be some of the most accurate and meticulously obtained experimental data ever recorded. SET-UP A fine mist of oil was sprayed from an atomizer. Most of ...
Renormalization

In quantum field theory, the statistical mechanics of fields, and the theory of self-similar geometric structures, renormalization is any of a collection of techniques used to treat infinities arising in calculated quantities.Renormalization specifies relationships between parameters in the theory when the parameters describing large distance scales differ from the parameters describing small distances. Physically, the pileup of contributions from an infinity of scales involved in a problem may then result in infinities. When describing space and time as a continuum, certain statistical and quantum mechanical constructions are ill defined. To define them, this continuum limit, the removal of the ""construction scaffolding"" of lattices at various scales, has to be taken carefully, as detailed below.Renormalization was first developed in quantum electrodynamics (QED) to make sense of infinite integrals in perturbation theory. Initially viewed as a suspect provisional procedure even by some of its originators, renormalization eventually was embraced as an important and self-consistent actual mechanism of scale physics in several fields of physics and mathematics. Today, the point of view has shifted: on the basis of the breakthrough renormalization group insights of Kenneth Wilson, the focus is on variation of physical quantities across contiguous scales, while distant scales are related to each other through ""effective"" descriptions. All scales are linked in a broadly systematic way, and the actual physics pertinent to each is extracted with the suitable specific computational techniques appropriate for each.