poster
... spread out over time. Therefore, the electron acts as a wave and will go through both slits and interfere with itself. This is why a distinct interference pattern will show up on the screen after shooting out electrons for a period of time.” Sample “Realist” Response “We just can't know EXACTLY wher ...
... spread out over time. Therefore, the electron acts as a wave and will go through both slits and interfere with itself. This is why a distinct interference pattern will show up on the screen after shooting out electrons for a period of time.” Sample “Realist” Response “We just can't know EXACTLY wher ...
Introduction to Superconductivity Theory - GDR Mico
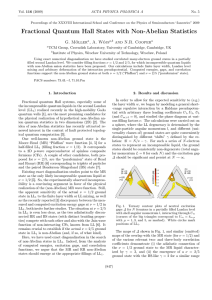
... The electrons in a metal interact with one another with a short range repulsive potential (screened Coulomb). The phenomenological theory for metals was developed by L. Landau in 1956 (Landau Fermi liquid theory). This system of interacting electrons is adiabatically connected to a system of free el ...
... The electrons in a metal interact with one another with a short range repulsive potential (screened Coulomb). The phenomenological theory for metals was developed by L. Landau in 1956 (Landau Fermi liquid theory). This system of interacting electrons is adiabatically connected to a system of free el ...
IMFUFA- Roskilde Universitetscenter- postbox 260
... series is divergent. Formally, we can put z=-1, whereby the infinite sum becomes the previously mentioned sum of all positive integers, and we can assign it a value given by the analytical continuation of the zetafunction to z=-1. In this way we get at the renormalized value ζ(-1) = -1/124 , i.e., n ...
... series is divergent. Formally, we can put z=-1, whereby the infinite sum becomes the previously mentioned sum of all positive integers, and we can assign it a value given by the analytical continuation of the zetafunction to z=-1. In this way we get at the renormalized value ζ(-1) = -1/124 , i.e., n ...
272 prac3
... 4. A charged particle is moving in a uniform, constant magnetic field. Which of the following statements concerning the magnetic force exerted on the particle is false? (a) it does no work on the particle (b) it increases the speed of the particle (c) it changes the velocity of the particle (d) it c ...
... 4. A charged particle is moving in a uniform, constant magnetic field. Which of the following statements concerning the magnetic force exerted on the particle is false? (a) it does no work on the particle (b) it increases the speed of the particle (c) it changes the velocity of the particle (d) it c ...
phys1444-fall11
... – The free electrons in the box would redistribute themselves along the surface so that the field lines would not penetrate into the metal. ...
... – The free electrons in the box would redistribute themselves along the surface so that the field lines would not penetrate into the metal. ...
Chapter 6: Electronic Structure of Atoms
... of Johann Balmer who first developed an equation by which their frequencies could be calculated. Electron transitions ending in n = 1 and n = 3 are called the Lyman and the Paschen series, respectively. ...
... of Johann Balmer who first developed an equation by which their frequencies could be calculated. Electron transitions ending in n = 1 and n = 3 are called the Lyman and the Paschen series, respectively. ...
Renormalization

In quantum field theory, the statistical mechanics of fields, and the theory of self-similar geometric structures, renormalization is any of a collection of techniques used to treat infinities arising in calculated quantities.Renormalization specifies relationships between parameters in the theory when the parameters describing large distance scales differ from the parameters describing small distances. Physically, the pileup of contributions from an infinity of scales involved in a problem may then result in infinities. When describing space and time as a continuum, certain statistical and quantum mechanical constructions are ill defined. To define them, this continuum limit, the removal of the ""construction scaffolding"" of lattices at various scales, has to be taken carefully, as detailed below.Renormalization was first developed in quantum electrodynamics (QED) to make sense of infinite integrals in perturbation theory. Initially viewed as a suspect provisional procedure even by some of its originators, renormalization eventually was embraced as an important and self-consistent actual mechanism of scale physics in several fields of physics and mathematics. Today, the point of view has shifted: on the basis of the breakthrough renormalization group insights of Kenneth Wilson, the focus is on variation of physical quantities across contiguous scales, while distant scales are related to each other through ""effective"" descriptions. All scales are linked in a broadly systematic way, and the actual physics pertinent to each is extracted with the suitable specific computational techniques appropriate for each.