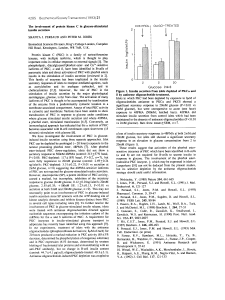
METABOLISM OF MONOSACCHARIDES AND DISACCHARIDES
... • For fructose to enter the pathways of intermediary metabolism, it must first be phosphorylated • This can be accomplished by either hexokinase or fructokinase (also called ketohexokinase). Hexokinase phosphorylates glucose in all cells of the body, and several additional hexoses can serve as subst ...
... • For fructose to enter the pathways of intermediary metabolism, it must first be phosphorylated • This can be accomplished by either hexokinase or fructokinase (also called ketohexokinase). Hexokinase phosphorylates glucose in all cells of the body, and several additional hexoses can serve as subst ...
Glycogen Metabolism-1 (Glycogenesis)
... To describe how glucose is converted into its storage form i.e. Glycogen ...
... To describe how glucose is converted into its storage form i.e. Glycogen ...
Endocrinology: A Molecular View
... Developed as part of the RCSB Collaborative Curriculum Development Program 2016 ...
... Developed as part of the RCSB Collaborative Curriculum Development Program 2016 ...
Document
... tissues and its conversion to glucose • In the liver, the glucose exported to blood circulation • In muscles, the glucose enters glycolysis for conversion to energy ...
... tissues and its conversion to glucose • In the liver, the glucose exported to blood circulation • In muscles, the glucose enters glycolysis for conversion to energy ...
Are Carbohydrates Healthy or Not? Fact Sheet
... Table sugar is actually made of two basic sugars, fructose and glucose, bonded together. When we consume table sugar, our digestive system breaks up the bonds and we absorb the fructose and glucose separately. Glucose is absorbed into the blood and carried for use by all our cells. Fructose is absor ...
... Table sugar is actually made of two basic sugars, fructose and glucose, bonded together. When we consume table sugar, our digestive system breaks up the bonds and we absorb the fructose and glucose separately. Glucose is absorbed into the blood and carried for use by all our cells. Fructose is absor ...
BCH_PRACTICAL_ASSIGNMENT__ADISA_1
... The Bowman's capsule surrounds each glomerulus, and collects the filtrate that the glomerulus forms. The filtrate contains waste products (e.g. urea), electrolytes (e.g. sodium, potassium, and chloride), amino acids, and glucose. The filtrate passes into the renal tubules of the kidney. In the first ...
... The Bowman's capsule surrounds each glomerulus, and collects the filtrate that the glomerulus forms. The filtrate contains waste products (e.g. urea), electrolytes (e.g. sodium, potassium, and chloride), amino acids, and glucose. The filtrate passes into the renal tubules of the kidney. In the first ...
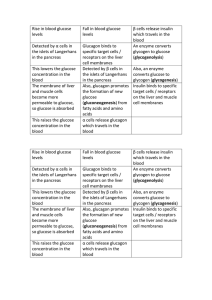
what is diabetes mellitus
... that produces hormones and an exocrine gland that produces digestive enzymes. It plays a strong role in metabolism in the body. Structures within the pancreas, known as Islets of Langerhans contain three different types of hormone secreting cells: Alpha Cells: secrete Glucagon Beta Cells: secrete In ...
... that produces hormones and an exocrine gland that produces digestive enzymes. It plays a strong role in metabolism in the body. Structures within the pancreas, known as Islets of Langerhans contain three different types of hormone secreting cells: Alpha Cells: secrete Glucagon Beta Cells: secrete In ...
Carbohydrate Metabolism 3
... 6- ↓↓ protein synthesis --> ↓↓ antibodies formation --> the patients liable for infections and poor wound healing. 7- A number of tissues don't require insulin for the entry of glucose into cells --> hence the intracellular glucose of the tissues attains a level similar to that of blood, then excess ...
... 6- ↓↓ protein synthesis --> ↓↓ antibodies formation --> the patients liable for infections and poor wound healing. 7- A number of tissues don't require insulin for the entry of glucose into cells --> hence the intracellular glucose of the tissues attains a level similar to that of blood, then excess ...
Early Chick and Poultry Mortality
... Recently reference has been made to the possible role of low levels of blood glucose in triggering some of the non specific early mortality problems noted with chicks and poults . A recent article by Dr. W.E. Donaldson provides further interesting information on the importance of maintaining blood g ...
... Recently reference has been made to the possible role of low levels of blood glucose in triggering some of the non specific early mortality problems noted with chicks and poults . A recent article by Dr. W.E. Donaldson provides further interesting information on the importance of maintaining blood g ...
NME2.32 - Insulin and Glucagon
... o The three primary targets for insulin action are the liver, muscle and adipose tissue There are significantly more receptors in the body than are needed for maximum response o Insulin itself down-regulates the number of receptors in tissues it affects reducing sensitivity o The same maximum respon ...
... o The three primary targets for insulin action are the liver, muscle and adipose tissue There are significantly more receptors in the body than are needed for maximum response o Insulin itself down-regulates the number of receptors in tissues it affects reducing sensitivity o The same maximum respon ...
CARBOHYDRATES
... - Can bind to a H+ ion when the H+ concentration increases - Can release a H+ ion when the H+ concentration decreases Maintains homeostasis ...
... - Can bind to a H+ ion when the H+ concentration increases - Can release a H+ ion when the H+ concentration decreases Maintains homeostasis ...
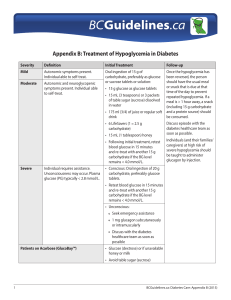
Appendix B: Treatment of Hypoglycemia in Diabetes
... been reversed, the person should have the usual meal or snack that is due at that time of the day to prevent repeated hypoglycemia. If a meal is > 1 hour away, a snack (including 15 g carbohydrate and a protein source) should be consumed. ...
... been reversed, the person should have the usual meal or snack that is due at that time of the day to prevent repeated hypoglycemia. If a meal is > 1 hour away, a snack (including 15 g carbohydrate and a protein source) should be consumed. ...
diabetic ketoacidosis
... • Complications of Type I diabetes • Due to decreased insulin intake • Marked by: high blood glucose metabolic acidosis coma ...
... • Complications of Type I diabetes • Due to decreased insulin intake • Marked by: high blood glucose metabolic acidosis coma ...
Glucose M9Y Glucose M9Y medium, used to cultivate E. coli, is a
... supplemented with yeast extract. It is based on M9 salts6 with a pH of 6.9±0.2 and employs glucose as the carbon source. Alternative carbon sources may be substituted. Buffering is provided by a sodium-potassium phosphate system. Ammonium chloride provides a nitrogen source. Yeast extract is added t ...
... supplemented with yeast extract. It is based on M9 salts6 with a pH of 6.9±0.2 and employs glucose as the carbon source. Alternative carbon sources may be substituted. Buffering is provided by a sodium-potassium phosphate system. Ammonium chloride provides a nitrogen source. Yeast extract is added t ...
What is diabetes?
... When food is digested, the protein is broken down into amino acids; the fat is broken down into fatty acids; and the carbohydrate is broken down into glucose. It is easy to see, then, that most of the glucose (sugar) in your blood comes from the carbohydrate in foods. ...
... When food is digested, the protein is broken down into amino acids; the fat is broken down into fatty acids; and the carbohydrate is broken down into glucose. It is easy to see, then, that most of the glucose (sugar) in your blood comes from the carbohydrate in foods. ...
Homo sapiens glucokinase (hexokinase 4) (GCK), transcript variant 1
... HXKP; MODY2; ATP:D-hexose 6-phosphotransferase; OTTHUMP00000024521; OTTHUMP00000159308; glucokinase; hexokinase D, pancreatic isozyme; glucokinase (hexokinase 4) LocusID: 2645 ...
... HXKP; MODY2; ATP:D-hexose 6-phosphotransferase; OTTHUMP00000024521; OTTHUMP00000159308; glucokinase; hexokinase D, pancreatic isozyme; glucokinase (hexokinase 4) LocusID: 2645 ...