Data Management for Decision Support
... • Associations- These techniques identify affinity among the collection reflected in the examined records. These affinities are often referred to as rules. Foe example, 60% of all record that contain A & B also contain C & D. Product affinity in Market basket analysis • Sequencing- Identifies patter ...
... • Associations- These techniques identify affinity among the collection reflected in the examined records. These affinities are often referred to as rules. Foe example, 60% of all record that contain A & B also contain C & D. Product affinity in Market basket analysis • Sequencing- Identifies patter ...
Week 2
... widths of groups are not all the same –Normed groupings grouped by proportions of cases e.g., percentiles, quartiles, median-splits [a special form of non-uniform grouping] ...
... widths of groups are not all the same –Normed groupings grouped by proportions of cases e.g., percentiles, quartiles, median-splits [a special form of non-uniform grouping] ...
Accelerating Sparse Canonical Correlation Analysis for Large Brain
... Application to accelerate enhanced SCCA models as well as other bimultivariate statistical models for analyzing brain imaging genetics data. ...
... Application to accelerate enhanced SCCA models as well as other bimultivariate statistical models for analyzing brain imaging genetics data. ...
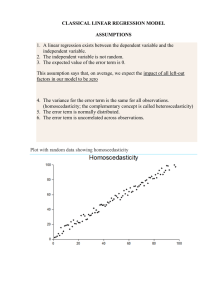
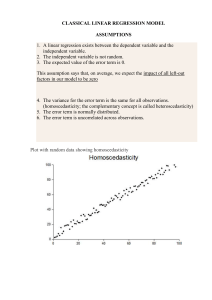
CLASSICAL LINEAR REGRESSION MODEL ASSUMPTIONS 1. A
... 4. The variance for the error term is the same for all observations. (homoscedasticity; the complementary concept is called heteroscedasticity) 5. The error term is normally distributed. 6. The error term is uncorrelated across observations. ...
... 4. The variance for the error term is the same for all observations. (homoscedasticity; the complementary concept is called heteroscedasticity) 5. The error term is normally distributed. 6. The error term is uncorrelated across observations. ...
Technical Problem Solving 2015 regional v2 key
... 9. Name 3 factors that physically impact heating rates in these situations that have not been factored in to our lab experiment. * chemical changes during the cooking process * changes in density ...
... 9. Name 3 factors that physically impact heating rates in these situations that have not been factored in to our lab experiment. * chemical changes during the cooking process * changes in density ...
Syllabus - Georgia Tech ISyE
... Use statistical tests and confidence intervals to assess mathematical uncertainty in statistical decisions Select proper statistical techniques for statistical decision making based on the type of data available Use statistical software to conduct data analyses and interpret output Draw sound statis ...
... Use statistical tests and confidence intervals to assess mathematical uncertainty in statistical decisions Select proper statistical techniques for statistical decision making based on the type of data available Use statistical software to conduct data analyses and interpret output Draw sound statis ...
Defining Learning
... In practice this is specific to the domain and the amount of data available. The larger and more complex our hypothesis set ℋ is, the more data we need. The closer (or more confident) we want to be in our predictions, the more data we need. ...
... In practice this is specific to the domain and the amount of data available. The larger and more complex our hypothesis set ℋ is, the more data we need. The closer (or more confident) we want to be in our predictions, the more data we need. ...
2.7
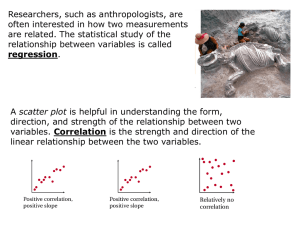
... Researchers, such as anthropologists, are often interested in how two measurements are related. The statistical study of the relationship between variables is called regression. ...
... Researchers, such as anthropologists, are often interested in how two measurements are related. The statistical study of the relationship between variables is called regression. ...
Lab 5
... and hit OK. The goodness of fit R2 =0.96 and the elasticity of assets to sales is 0.78 and significant. Under View, look at actual, fitted, residual:graph. The fit looks pretty good over the 50 observations. Of course for the industries with only one firm there are no degrees of freedom. Note that t ...
... and hit OK. The goodness of fit R2 =0.96 and the elasticity of assets to sales is 0.78 and significant. Under View, look at actual, fitted, residual:graph. The fit looks pretty good over the 50 observations. Of course for the industries with only one firm there are no degrees of freedom. Note that t ...
Muskingum Valley ESC Standards-Based Mathematics Course of
... (Gr.11#5) Use technology to find the Least Square Regression Line, the regression coefficient and the correlation coefficient for bivariate data with a linear trend, and interpret each of these statistics in the context of the problem situation. (Gr.11#6) Use technology to compute the standard devia ...
... (Gr.11#5) Use technology to find the Least Square Regression Line, the regression coefficient and the correlation coefficient for bivariate data with a linear trend, and interpret each of these statistics in the context of the problem situation. (Gr.11#6) Use technology to compute the standard devia ...