Logit, Probit and Tobit: Models for Categorical and Limited
... • How to interpret the coefficients : In both models, If b > 0 Î p increases as X increases If b < 0 Î p decreases as X increases – As mentioned above, b cannot be interpreted as a simple slope as in ordinary regression. Because the rate at which the curve ascends or descends changes according to th ...
... • How to interpret the coefficients : In both models, If b > 0 Î p increases as X increases If b < 0 Î p decreases as X increases – As mentioned above, b cannot be interpreted as a simple slope as in ordinary regression. Because the rate at which the curve ascends or descends changes according to th ...
Capturing the Laws of (Data) Nature
... a local dataset. Any command the user performs on this object is forwarded to the data management system. We propose to leverage this method for model fitting as well. Together with the aforementioned integration of statistical environments into data management systems, this can create a win-win sit ...
... a local dataset. Any command the user performs on this object is forwarded to the data management system. We propose to leverage this method for model fitting as well. Together with the aforementioned integration of statistical environments into data management systems, this can create a win-win sit ...
How to perform a one-way ANOVA using Minitab
... Label one column to hold the yields (‘Yield’) and another (‘Catalyst’) to hold the labels that will indicate which group each yield belongs to. Enter all the percentage yields into the relevant column and put suitable labels into the other column. The worksheet should then look like this: ...
... Label one column to hold the yields (‘Yield’) and another (‘Catalyst’) to hold the labels that will indicate which group each yield belongs to. Enter all the percentage yields into the relevant column and put suitable labels into the other column. The worksheet should then look like this: ...
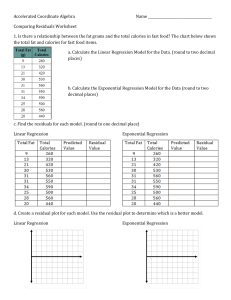
Maths-S1
... Know that the PMCC of coded data is the same as for the original data Interpret the value of the PMCC as a measure of correlation Know the least squares regression line equation y = a + bx Look up and use the equations for a and b to find the least squares regression line Use coding and substitution ...
... Know that the PMCC of coded data is the same as for the original data Interpret the value of the PMCC as a measure of correlation Know the least squares regression line equation y = a + bx Look up and use the equations for a and b to find the least squares regression line Use coding and substitution ...
What is Statistics? Introduction Bayesian Methods in Mplus
... parameters Likelihood function – relates all variables into a full probability model Posterior Distribution – after using data to update the prior information about unknown parameters ...
... parameters Likelihood function – relates all variables into a full probability model Posterior Distribution – after using data to update the prior information about unknown parameters ...
Multiple Regression Analysis Using ANCOVA in University Model
... A. Multiple Regression Multiple regression is an extension of simple regression from one to several quantitative explanatory variables. It involves more than one independent variable and the curves obtained are not only used to make predictions rather for the purposes of optimization. The structural ...
... A. Multiple Regression Multiple regression is an extension of simple regression from one to several quantitative explanatory variables. It involves more than one independent variable and the curves obtained are not only used to make predictions rather for the purposes of optimization. The structural ...
Mining massive Data Sets from web
... percentage of connections between two pages), and the confidence (the percentage of connections between two pages with respect to all the visits to the first page). A more specific analysis of the associations between pages is often performed by studying sequences of visited pages. The pattern of visit ...
... percentage of connections between two pages), and the confidence (the percentage of connections between two pages with respect to all the visits to the first page). A more specific analysis of the associations between pages is often performed by studying sequences of visited pages. The pattern of visit ...
Homework 3 - Yisong Yue
... (a) (3 points) Please calculate the entropy at each split point (as well as at the root). (b) (3 points) Calculate the information gain at each split. (c) (2 points) Draw the tree. (d) (5 points) Using the same data set above, train your decision tree using Gini index as splitting criteria. Since th ...
... (a) (3 points) Please calculate the entropy at each split point (as well as at the root). (b) (3 points) Calculate the information gain at each split. (c) (2 points) Draw the tree. (d) (5 points) Using the same data set above, train your decision tree using Gini index as splitting criteria. Since th ...
Linear Models
... K is the total number of variables The category left out becomes the “base” category It’s value is contained in the intercept Model is Y = ai + bj + …+ e or ...
... K is the total number of variables The category left out becomes the “base” category It’s value is contained in the intercept Model is Y = ai + bj + …+ e or ...
Age group
... Explain what is meant by transforming data. Discuss the advantages of transforming nonlinear data. Tell where y=log(x) fits into the heirarchy of power transformations. Explain the ladder of power transformations. Explain how linear growth differs from exponential growth. Identify real-life situatio ...
... Explain what is meant by transforming data. Discuss the advantages of transforming nonlinear data. Tell where y=log(x) fits into the heirarchy of power transformations. Explain the ladder of power transformations. Explain how linear growth differs from exponential growth. Identify real-life situatio ...