Numerical Methods for Computing Casimir
... scales (the most challenging situation for brute-force numerics). Nevertheless, many commonalities and guiding principles can be identified that seem to apply to a range of numerical techniques. Until a few years ago, Casimir forces and other EM fluctuation-induced interactions occupied an unusual p ...
... scales (the most challenging situation for brute-force numerics). Nevertheless, many commonalities and guiding principles can be identified that seem to apply to a range of numerical techniques. Until a few years ago, Casimir forces and other EM fluctuation-induced interactions occupied an unusual p ...
Using Support Vector Machines for Distributed Machine Learning
... variables. The quality of the learning machines in the distributed inference system can be summarized by R, which is a function of a given loss function L. Each type of learning problem can be associated with a particular loss function, L. Next, W depends on T , which is a time-related variable. Som ...
... variables. The quality of the learning machines in the distributed inference system can be summarized by R, which is a function of a given loss function L. Each type of learning problem can be associated with a particular loss function, L. Next, W depends on T , which is a time-related variable. Som ...
Long-Run Covariability
... even though the stochastic process generating the data may exhibit substantial persistence (Müller and Watson (forthcoming)). This allows large-sample inference about covariability parameters to be transformed into a finite-sample problem involving a handful of normal random variables and, while the ...
... even though the stochastic process generating the data may exhibit substantial persistence (Müller and Watson (forthcoming)). This allows large-sample inference about covariability parameters to be transformed into a finite-sample problem involving a handful of normal random variables and, while the ...
Estimation of income elasticities and their use in a CGE model for
... estimation of the income elasticities of the IAS leads to a seemingly unrelated regression model with identical explanatory variables, so that application of the method of ordinary least squares to each equation separately is efficient. In the empirical part of the paper we estimate the income elast ...
... estimation of the income elasticities of the IAS leads to a seemingly unrelated regression model with identical explanatory variables, so that application of the method of ordinary least squares to each equation separately is efficient. In the empirical part of the paper we estimate the income elast ...
Limitations of regression analysis
... yi , gives an overestimation, so OLS de…nes a bound around the true parameter. Measurement errors in yi : No bias problem, but potential for ...
... yi , gives an overestimation, so OLS de…nes a bound around the true parameter. Measurement errors in yi : No bias problem, but potential for ...
Journal of Applied Statistics Estimating utility functions using
... analysis with particular emphasis on the estimation of utility functions [1,6,7]. In addition, we explain how our work differs from the papers that use ME to estimate utility functions. As described in the previous subsection, the ME principle applies to estimation of probability distributions. Howe ...
... analysis with particular emphasis on the estimation of utility functions [1,6,7]. In addition, we explain how our work differs from the papers that use ME to estimate utility functions. As described in the previous subsection, the ME principle applies to estimation of probability distributions. Howe ...
Introduction to Econometrics - San Francisco State University
... of times that "heads" is observed. The possible values of X (called the support of X) are x 2 f0; 1; 2g. We can then calculate the probabilities P (X = 0), P (X = 1) and P (X = 2), in other words we can …nd the distribution of the random variable X. Exercise 5 Calculate the probabilty distribution o ...
... of times that "heads" is observed. The possible values of X (called the support of X) are x 2 f0; 1; 2g. We can then calculate the probabilities P (X = 0), P (X = 1) and P (X = 2), in other words we can …nd the distribution of the random variable X. Exercise 5 Calculate the probabilty distribution o ...
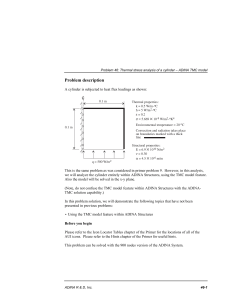
Thermal stress analysis of a cylinder – ADINA TMC model
... Problem description A cylinder is subjected to heat flux loadings as shown: C L ...
... Problem description A cylinder is subjected to heat flux loadings as shown: C L ...
Structural Econometric Modeling: Rationales and Examples from
... To understand the process of building a structural model, consider the example of a researcher who wishes to use household consumption, price and demographic data to estimate household demand for a particular good. The first step in building a structural model is to show that economic theory places ...
... To understand the process of building a structural model, consider the example of a researcher who wishes to use household consumption, price and demographic data to estimate household demand for a particular good. The first step in building a structural model is to show that economic theory places ...
Structure discovery in nonparametric regression through compositional kernel search Please share
... method for searching over this space of structures which mirrors the scientific discovery process. The learned structures can often decompose functions into interpretable components and enable long-range extrapolation on time-series datasets. Our structure search method outperforms many widely used ...
... method for searching over this space of structures which mirrors the scientific discovery process. The learned structures can often decompose functions into interpretable components and enable long-range extrapolation on time-series datasets. Our structure search method outperforms many widely used ...
On Label Dependence in Multi
... Fig. 2 shows the performance curves of the two methods as a function of α, where performance corresponds to the expected error rate given a random training set of size 50; two types of error are considered, the subset 0/1 loss (3) and the Hamming loss (4). As can be seen from these curves, unconditi ...
... Fig. 2 shows the performance curves of the two methods as a function of α, where performance corresponds to the expected error rate given a random training set of size 50; two types of error are considered, the subset 0/1 loss (3) and the Hamming loss (4). As can be seen from these curves, unconditi ...