Ùتاب اÙÙغة اÙØ¥ÙجÙÙزÙØ©
... But, planes land here every two minutes. 2Each can only be used in front of a singular noun. Each person who benefits form our charity gets a minimum of fifty grammes of rice a day. 3Other is an adjective, pronoun, and noun. (a) In other circumstances we could discuss this matter without bitterness, ...
... But, planes land here every two minutes. 2Each can only be used in front of a singular noun. Each person who benefits form our charity gets a minimum of fifty grammes of rice a day. 3Other is an adjective, pronoun, and noun. (a) In other circumstances we could discuss this matter without bitterness, ...
passive i - English6th2009
... Ron decorates the street every year. = Active. (I know that Ron decorates the street every ...
... Ron decorates the street every year. = Active. (I know that Ron decorates the street every ...
Differentiating eventivity and dynamicity: the Aktionsart of
... prototypical event characteristics with other properties that are generally associated to states. As we will see, this causes trouble both from an empirical and a theoretical perspective. In the empirical side, there is no doubt that we want to be able to properly characterise classes of predicates ...
... prototypical event characteristics with other properties that are generally associated to states. As we will see, this causes trouble both from an empirical and a theoretical perspective. In the empirical side, there is no doubt that we want to be able to properly characterise classes of predicates ...
AP Spanish Study Sheet: Gustar and Gustar-like Verbs
... like." Well, not exactly. In Spanish, instead of talking about what "you like", you say what "pleases you." The meaning is basically the same; it's just expressed differently, with the verb gustar (to be pleasing). This activity will explain the grammatically correct use of gustar and other verbs th ...
... like." Well, not exactly. In Spanish, instead of talking about what "you like", you say what "pleases you." The meaning is basically the same; it's just expressed differently, with the verb gustar (to be pleasing). This activity will explain the grammatically correct use of gustar and other verbs th ...
Realidades 1 Gramática C-1A a C-5A
... Tú, usted, ustedes, and vosotros(as) all mean “you.” . Use tú with family, friends, people your age or younger, and anyone you call by his or her first name. . Use usted with adults you address with a title, such as señor, señora, profesor(a), etc. Usted is usually written as Ud. . In Latin America, ...
... Tú, usted, ustedes, and vosotros(as) all mean “you.” . Use tú with family, friends, people your age or younger, and anyone you call by his or her first name. . Use usted with adults you address with a title, such as señor, señora, profesor(a), etc. Usted is usually written as Ud. . In Latin America, ...
Present progressive
... In English The present perfect indicative is used to say what has or has not happened in a period of time up to the present. It is formed with the present tense of the verb to have and the past participle of the main verb: (I, you) have, (he, she, it) has, (we, you, they) have + past participle. Isa ...
... In English The present perfect indicative is used to say what has or has not happened in a period of time up to the present. It is formed with the present tense of the verb to have and the past participle of the main verb: (I, you) have, (he, she, it) has, (we, you, they) have + past participle. Isa ...
Grammar In Context Book #2, 5th edition
... • A kitten costs fifty dollars. • It takes two months to train a dog. ...
... • A kitten costs fifty dollars. • It takes two months to train a dog. ...
Constructional Licensing in Morphology and Syntax
... These words ending in the suffix -s have the function of possessor. The only nouns that can be used with this kind of possessor marker are proper names, nouns that can be used as forms of address, like vader father’, moeder ‘mother’ and dominee ‘reverend’, that is, words functioning as proper names, ...
... These words ending in the suffix -s have the function of possessor. The only nouns that can be used with this kind of possessor marker are proper names, nouns that can be used as forms of address, like vader father’, moeder ‘mother’ and dominee ‘reverend’, that is, words functioning as proper names, ...
arnprior district high school
... be creative! Choose unique places to travel, fun things to do, interesting people to meet, etc. ...
... be creative! Choose unique places to travel, fun things to do, interesting people to meet, etc. ...
Verbs, Adverbs, Prepositions, Conjunctions, Interjections
... anything about what the action is; it tell you about the time of the action. When you identify the verb of the sentence, you give both the helping verb & the main verb. For example, if I asked you what the verb in the first sentence is, you’d say, “has eaten.” ...
... anything about what the action is; it tell you about the time of the action. When you identify the verb of the sentence, you give both the helping verb & the main verb. For example, if I asked you what the verb in the first sentence is, you’d say, “has eaten.” ...
Verbs, Adverbs, Prepositions, Conjunctions, Interjections
... anything about what the action is; it tell you about the time of the action. When you identify the verb of the sentence, you give both the helping verb & the main verb. For example, if I asked you what the verb in the first sentence is, you’d say, “has eaten.” ...
... anything about what the action is; it tell you about the time of the action. When you identify the verb of the sentence, you give both the helping verb & the main verb. For example, if I asked you what the verb in the first sentence is, you’d say, “has eaten.” ...
"it" AS A FORMAL OBJECT
... The sentence thus has two objects: the formal object it and a notional object, which is a clause. The formal object it may be either a direct object (I take it that everything is O.K.) , or an indirect non-recipient object (She objected to it that her husband should go and fetch them from the statio ...
... The sentence thus has two objects: the formal object it and a notional object, which is a clause. The formal object it may be either a direct object (I take it that everything is O.K.) , or an indirect non-recipient object (She objected to it that her husband should go and fetch them from the statio ...
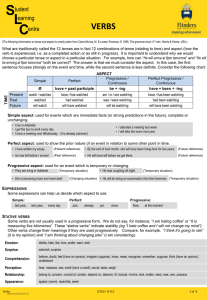
Verbs - Flinders University
... (The following information on tense and aspect is mostly taken from Celce-Murcia, M & Larsen-Freeman, D 1999, The grammar book, 2nd edn, Heinle & Heinle, USA.) ...
... (The following information on tense and aspect is mostly taken from Celce-Murcia, M & Larsen-Freeman, D 1999, The grammar book, 2nd edn, Heinle & Heinle, USA.) ...
Mini Lesson - WordPress.com
... I guesses that I don't need that though. Now you is just somebody that I used to know. Now and then I thinks of all the times you screwed me over. Part of me believing it were always something that I'd done. But I doesn't want to live that way, reading into every word you say. You said that you coul ...
... I guesses that I don't need that though. Now you is just somebody that I used to know. Now and then I thinks of all the times you screwed me over. Part of me believing it were always something that I'd done. But I doesn't want to live that way, reading into every word you say. You said that you coul ...
Understanding Verb Forms
... Give the correct form (past, past participle, or present participle) of the verb in italics, as indicated in parentheses. 1. The dancers are (perform) on stage. (present participle) 2. We (watch) a folk dance an hour ago. (past) 3. We are (learn) dances from different countries. (present participle) ...
... Give the correct form (past, past participle, or present participle) of the verb in italics, as indicated in parentheses. 1. The dancers are (perform) on stage. (present participle) 2. We (watch) a folk dance an hour ago. (past) 3. We are (learn) dances from different countries. (present participle) ...
Lay - Cloudfront.net
... Give the correct form (past, past participle, or present participle) of the verb in italics, as indicated in parentheses. 1. The dancers are (perform) on stage. (present participle) 2. We (watch) a folk dance an hour ago. (past) 3. We are (learn) dances from different countries. (present participle) ...
... Give the correct form (past, past participle, or present participle) of the verb in italics, as indicated in parentheses. 1. The dancers are (perform) on stage. (present participle) 2. We (watch) a folk dance an hour ago. (past) 3. We are (learn) dances from different countries. (present participle) ...
Document
... Sometimes adjectives become substantivized. In this case they have the functions of nouns in the sentence and are always preceded by the definite article. They can be partially substantivized (i.e. acquiring only some of the morphological characteristics of nouns) or fully substantivized (i.e. can b ...
... Sometimes adjectives become substantivized. In this case they have the functions of nouns in the sentence and are always preceded by the definite article. They can be partially substantivized (i.e. acquiring only some of the morphological characteristics of nouns) or fully substantivized (i.e. can b ...
Week 2
... L.8.1 b: Form and use verbs in the active and passive voice. L.8.1 c: Form and use verbs in the indicative, imperative, interrogative, conditional, and subjunctive mood. L.8.1 d: Recognize and correct inappropriate shifts in verb voice or mood. L. 8.2: Demonstrate command of the conventions of stand ...
... L.8.1 b: Form and use verbs in the active and passive voice. L.8.1 c: Form and use verbs in the indicative, imperative, interrogative, conditional, and subjunctive mood. L.8.1 d: Recognize and correct inappropriate shifts in verb voice or mood. L. 8.2: Demonstrate command of the conventions of stand ...
6 Understanding Verb Forms
... Give the correct form (past, past participle, or present participle) of the verb in italics, as indicated in parentheses. 1. The dancers are (perform) on stage. (present participle) 2. We (watch) a folk dance an hour ago. (past) 3. We are (learn) dances from different countries. (present participle) ...
... Give the correct form (past, past participle, or present participle) of the verb in italics, as indicated in parentheses. 1. The dancers are (perform) on stage. (present participle) 2. We (watch) a folk dance an hour ago. (past) 3. We are (learn) dances from different countries. (present participle) ...
Summary of Verb Tenses - KSU Faculty Member websites
... the same time the statement is written. This tense is formed by using am/is/are with the verb form ending in -ing. The sociologist is examining the effects that racial discrimination has on society. Past Progressive Tense Past progressive tense describes a past action which was happening when anothe ...
... the same time the statement is written. This tense is formed by using am/is/are with the verb form ending in -ing. The sociologist is examining the effects that racial discrimination has on society. Past Progressive Tense Past progressive tense describes a past action which was happening when anothe ...
Summary of Verb Tenses - KSU Faculty Member websites
... Future tense expresses an action or situation that will occur in the future. This tense is formed by using will/shall with the simple form of the verb. The speaker of the House will finish her term in May of 1998. The future tense can also be expressed by using am, is, or are with going to. The surg ...
... Future tense expresses an action or situation that will occur in the future. This tense is formed by using will/shall with the simple form of the verb. The speaker of the House will finish her term in May of 1998. The future tense can also be expressed by using am, is, or are with going to. The surg ...
1. nouns 2. determiners 3. adverbs 4. adjectives 5. verbs 6. negation
... imparfait: states of being, habitual actions imparfait: idiomatic uses (suggestions, wishes, depuis, venir de) narration: passé composé vs. imparfait plus-que-parfait passé simple (literary tense) passé antérieur (literary tense) future tenses futur proche (aller+infinitive) simple future (regular) ...
... imparfait: states of being, habitual actions imparfait: idiomatic uses (suggestions, wishes, depuis, venir de) narration: passé composé vs. imparfait plus-que-parfait passé simple (literary tense) passé antérieur (literary tense) future tenses futur proche (aller+infinitive) simple future (regular) ...