BSNL JTO Previous Question Paper 2008
... 83. Amplitude modulation is used for broadcasting because a. it is move noise immune than other modulation systems b. compared with other systems it requires less transmitting power c. its use avoids receiver complexity d. no other modulation system can provide the necessary bandwidth for high fidel ...
... 83. Amplitude modulation is used for broadcasting because a. it is move noise immune than other modulation systems b. compared with other systems it requires less transmitting power c. its use avoids receiver complexity d. no other modulation system can provide the necessary bandwidth for high fidel ...
Advance Matlab - Ascent Softech
... Signal Processing Operation Create sin wave, add Gain to it and plot it.Plots sign of input signal. Sine wave signal and Integrator block to create cosine wave signal. Formatting, Change the appearance of the figure. Add annotation, Add line label.Rotate, Flip blockFont and coloring Misc User define ...
... Signal Processing Operation Create sin wave, add Gain to it and plot it.Plots sign of input signal. Sine wave signal and Integrator block to create cosine wave signal. Formatting, Change the appearance of the figure. Add annotation, Add line label.Rotate, Flip blockFont and coloring Misc User define ...
ECE 3235 Electronics II
... 2. Automatic Gain Control (AGC) After performing part one of this experiment, you should be convinced that the output waveform of the Wien Bridge oscillator is somewhat distorted. This is because the circuit poles must be placed just a bit to the right of the imaginary axis for oscillation to build ...
... 2. Automatic Gain Control (AGC) After performing part one of this experiment, you should be convinced that the output waveform of the Wien Bridge oscillator is somewhat distorted. This is because the circuit poles must be placed just a bit to the right of the imaginary axis for oscillation to build ...
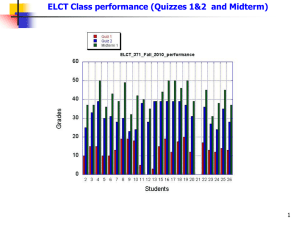
ELCT Class performance (Quizzes 1&2 and Midterm)
... load from the ac power line, and provide out of phase input voltages. ...
... load from the ac power line, and provide out of phase input voltages. ...
Combinations of Capacitors
... transformer consists of two separate circuits, the primary and the secondary. The AC in one circuit induces a magnetic field, and that magnetic field in turn induces a current (also alternating) in the second circuit. To enhance the magnetic field produced, the circuits surround an iron core. This i ...
... transformer consists of two separate circuits, the primary and the secondary. The AC in one circuit induces a magnetic field, and that magnetic field in turn induces a current (also alternating) in the second circuit. To enhance the magnetic field produced, the circuits surround an iron core. This i ...
Lab 6 - La Salle University
... transformer consists of two separate circuits, the primary and the secondary. The AC in one circuit induces a magnetic field, and that magnetic field in turn induces a current (also alternating) in the second circuit. To enhance the magnetic field produced, the circuits surround an iron core. This i ...
... transformer consists of two separate circuits, the primary and the secondary. The AC in one circuit induces a magnetic field, and that magnetic field in turn induces a current (also alternating) in the second circuit. To enhance the magnetic field produced, the circuits surround an iron core. This i ...
to print
... JG Audio went even further in the limited, Special Edition of the top model, the JG S60. The SE shares with the normal version the "single - ended structure, class A, only two amplification stages, no global feedback and regulated independent supplies for each channel. However, the Special Edition v ...
... JG Audio went even further in the limited, Special Edition of the top model, the JG S60. The SE shares with the normal version the "single - ended structure, class A, only two amplification stages, no global feedback and regulated independent supplies for each channel. However, the Special Edition v ...
Here we have some circuits with voltage sources.
... Here we have some circuits with voltage sources. We will determine whether these are valid circuits. The first circuit is 1 V applied across a resistor, which is valid. The second circuit is two series voltage sources, and the voltage simply add together to produce a net voltage of -1 V across the r ...
... Here we have some circuits with voltage sources. We will determine whether these are valid circuits. The first circuit is 1 V applied across a resistor, which is valid. The second circuit is two series voltage sources, and the voltage simply add together to produce a net voltage of -1 V across the r ...
DT3: RF On/Off Remote Control Technology
... general power measurement and control applications pulsed RF signals ...
... general power measurement and control applications pulsed RF signals ...
Circuit Note CN-0060
... video decoder are all automotive qualified which makes both products ideal for auto-vision applications. Low power, low cost, high speed, and fast settling make these amplifiers well suited for many video applications where these requirements are very important. Figure 1 shows only a single amplifie ...
... video decoder are all automotive qualified which makes both products ideal for auto-vision applications. Low power, low cost, high speed, and fast settling make these amplifiers well suited for many video applications where these requirements are very important. Figure 1 shows only a single amplifie ...
(1) You are given the circuit of Figure 1 with the indicated source
... (4) You are given the AC circuit shown in Figure 4. (a) Use nodal analysis to find the node voltages V1 and Vz as indicated in the circuit diagram. Express V1 and Vz in polar form. (b) Prepare a phasor diagram showing V1 and V2. Which voltage is leading? Explain. L ...
... (4) You are given the AC circuit shown in Figure 4. (a) Use nodal analysis to find the node voltages V1 and Vz as indicated in the circuit diagram. Express V1 and Vz in polar form. (b) Prepare a phasor diagram showing V1 and V2. Which voltage is leading? Explain. L ...
Homework Ch 4 - ECM
... 9. A change is frequency from 100 radians per second (rps) to 1000 rps causes a minus 10 db change in gain. a. True b. False ...
... 9. A change is frequency from 100 radians per second (rps) to 1000 rps causes a minus 10 db change in gain. a. True b. False ...
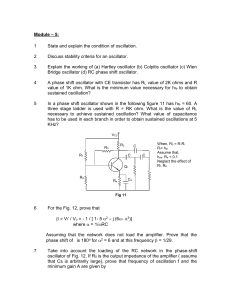
Module – 5
... Take into account the loading of the RC network in the phase-shift oscillator of Fig. 12. If R0 is the output impedance of the amplifier ( assume that Cs is arbitrarily large), prove that frequency of oscillation f and the minimum gain A are given by ...
... Take into account the loading of the RC network in the phase-shift oscillator of Fig. 12. If R0 is the output impedance of the amplifier ( assume that Cs is arbitrarily large), prove that frequency of oscillation f and the minimum gain A are given by ...
Jun 1999 LTC2400 Differential Bridge Digitizers
... as much as possible. The noise gain shown (101) allows adequate headroom for the expected signal; the attenuator reduces the overall gain to 16.8. This is approximately the point, ...
... as much as possible. The noise gain shown (101) allows adequate headroom for the expected signal; the attenuator reduces the overall gain to 16.8. This is approximately the point, ...
THEORY: AppCAD is an easy-to-use program that provides you with
... AppCAD's unique, interactive approach makes engineering calculations quick and easy for many RF, microwave, and wireless applications.AppCAD is useful for the design and analysis of many circuits, signals, and systems using products from discrete transistors and diodes to Silicon and GaAs integrated ...
... AppCAD's unique, interactive approach makes engineering calculations quick and easy for many RF, microwave, and wireless applications.AppCAD is useful for the design and analysis of many circuits, signals, and systems using products from discrete transistors and diodes to Silicon and GaAs integrated ...
Regenerative circuit
The regenerative circuit (or regen) allows an electronic signal to be amplified many times by the same active device. It consists of an amplifying vacuum tube or transistor with its output connected to its input through a feedback loop, providing positive feedback. This circuit was widely used in radio receivers, called regenerative receivers, between 1915 and World War II. The regenerative receiver was invented in 1912 and patented in 1914 by American electrical engineer Edwin Armstrong when he was an undergraduate at Columbia University. Due partly to its tendency to radiate interference, by the 1930s the regenerative receiver was superseded by other receiver designs, the TRF and superheterodyne receivers and became obsolete, but regeneration (now called positive feedback) is widely used in other areas of electronics, such as in oscillators and active filters. A receiver circuit that used regeneration in a more complicated way to achieve even higher amplification, the superregenerative receiver, was invented by Armstrong in 1922. It was never widely used in general receivers, but due to its small parts count is used in a few specialized low data rate applications, such as garage door openers, wireless networking devices, walkie-talkies and toys.