DN182 - The LT1167: Single Resistor Sets the Gain of the Best Instrumentation Amplifier
... loads without a significant linearity penalty. These parametric improvements result in an overall gain error that remains unchanged over the entire input common mode range and is not degraded by supply perturbations or varying load conditions. The LT1167 can operate over a wide ±2.3V to ±18V supply ...
... loads without a significant linearity penalty. These parametric improvements result in an overall gain error that remains unchanged over the entire input common mode range and is not degraded by supply perturbations or varying load conditions. The LT1167 can operate over a wide ±2.3V to ±18V supply ...
Monobloc Power Amplifier Stealth Max Users' Manual
... the input jack and should normally be set full on (full CW). If you have higher than normal preamp gain or if your speakers are very efficient, you may find that it is desirable to adjust the level control to allow use of the preamp volume control near its mid position. The input resistance is 100 k ...
... the input jack and should normally be set full on (full CW). If you have higher than normal preamp gain or if your speakers are very efficient, you may find that it is desirable to adjust the level control to allow use of the preamp volume control near its mid position. The input resistance is 100 k ...
unit 3 class
... • Combining the high gain of BJT and infinite impedance of MOSFET will lead to BiCMOS differential amplifier design. • Rs = typical 100 KW • BICMOS cascode amplifier has overall voltage gain of C-S, but with frequency response comparable to CB Amplifier. ...
... • Combining the high gain of BJT and infinite impedance of MOSFET will lead to BiCMOS differential amplifier design. • Rs = typical 100 KW • BICMOS cascode amplifier has overall voltage gain of C-S, but with frequency response comparable to CB Amplifier. ...
CLF W-Bridge - CLF
... content to ensure that all parts are present, and have been received in good condition. Notify the shipper immediately and retain packing material for inspection if any parts appear damaged from shipping or the carton itself shows signs of mishandling. Save the carton and all packing materials. In t ...
... content to ensure that all parts are present, and have been received in good condition. Notify the shipper immediately and retain packing material for inspection if any parts appear damaged from shipping or the carton itself shows signs of mishandling. Save the carton and all packing materials. In t ...
CVX - Canvas™ : j61 Simple Circuit Wrap
... 6. a. How much energy is provided to each coulomb of charge that moves through the circuit? (Hint: consider the charge that moves and the energy that’s delivered in each second: see 4.c. and 5.c.) ...
... 6. a. How much energy is provided to each coulomb of charge that moves through the circuit? (Hint: consider the charge that moves and the energy that’s delivered in each second: see 4.c. and 5.c.) ...
Electricity
... Has only one pathway for electricity to follow. If there are more than one device in the circuit, the electricity must flow through one device and continue on to the next device. Not normally used in houses. Christmas lights are sometimes wired in series. That is why if one bulb goes out the whole l ...
... Has only one pathway for electricity to follow. If there are more than one device in the circuit, the electricity must flow through one device and continue on to the next device. Not normally used in houses. Christmas lights are sometimes wired in series. That is why if one bulb goes out the whole l ...
Electricity - Warren County Schools
... Christmas lights are sometimes wired in series. That is why if one bulb goes out the whole line goes out ...
... Christmas lights are sometimes wired in series. That is why if one bulb goes out the whole line goes out ...
Four charges, all with a charge of -6 C (-6 10
... F, 2 F, and 3 F) in series. In circuit II, you have three capacitors (with values 1 F, 2 F, and 3 F) in parallel. Both circuits are connected to separate 6 V batteries. 21) Calculate the charge stored on the 2 F capacitor in each circuit. (first Circuit I and then Circuit II) a) b) c) d) e) ...
... F, 2 F, and 3 F) in series. In circuit II, you have three capacitors (with values 1 F, 2 F, and 3 F) in parallel. Both circuits are connected to separate 6 V batteries. 21) Calculate the charge stored on the 2 F capacitor in each circuit. (first Circuit I and then Circuit II) a) b) c) d) e) ...
Analog Devices Welcomes Hittite Microwave Corporation
... The HMC439QS16G & HMC439QS16GE are digital phase-frequency detectors intended for use in low noise phase-locked loop applications for inputs from 10 to 1300 MHz. Its combination of high frequency of operation along with its ultra low phase noise floor make possible synthesizers with wide loop bandwi ...
... The HMC439QS16G & HMC439QS16GE are digital phase-frequency detectors intended for use in low noise phase-locked loop applications for inputs from 10 to 1300 MHz. Its combination of high frequency of operation along with its ultra low phase noise floor make possible synthesizers with wide loop bandwi ...
Pspice Lecture5_v1 194KB Sep 20 2011 08:28:26 AM
... Note that the voltages for node 1 and 2 are -5.882V and -12.24V also. Similar to the previous circuit with three resistors. 12. Now report the result. The results for the equivalent resistor are similar to the previous circuit. ...
... Note that the voltages for node 1 and 2 are -5.882V and -12.24V also. Similar to the previous circuit with three resistors. 12. Now report the result. The results for the equivalent resistor are similar to the previous circuit. ...
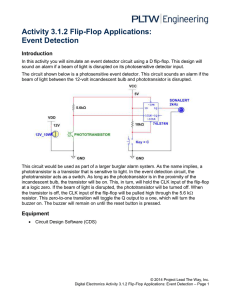
3.1.2.A Flip Flop Applications
... 1. Using the CDS, enter the simplified version of the event detector circuit. a. Close “Switch P” to simulate that the phototransistor is receiving light. b. Clear the flip-flop with “Switch C”. Make sure “Switch C” is left open as pictured above. c. Open “Switch P” to simulate the light beam being ...
... 1. Using the CDS, enter the simplified version of the event detector circuit. a. Close “Switch P” to simulate that the phototransistor is receiving light. b. Clear the flip-flop with “Switch C”. Make sure “Switch C” is left open as pictured above. c. Open “Switch P” to simulate the light beam being ...
Regenerative circuit
The regenerative circuit (or regen) allows an electronic signal to be amplified many times by the same active device. It consists of an amplifying vacuum tube or transistor with its output connected to its input through a feedback loop, providing positive feedback. This circuit was widely used in radio receivers, called regenerative receivers, between 1915 and World War II. The regenerative receiver was invented in 1912 and patented in 1914 by American electrical engineer Edwin Armstrong when he was an undergraduate at Columbia University. Due partly to its tendency to radiate interference, by the 1930s the regenerative receiver was superseded by other receiver designs, the TRF and superheterodyne receivers and became obsolete, but regeneration (now called positive feedback) is widely used in other areas of electronics, such as in oscillators and active filters. A receiver circuit that used regeneration in a more complicated way to achieve even higher amplification, the superregenerative receiver, was invented by Armstrong in 1922. It was never widely used in general receivers, but due to its small parts count is used in a few specialized low data rate applications, such as garage door openers, wireless networking devices, walkie-talkies and toys.