What is an Op-Amp? - benchmark
... the manufacturer’s specifications. Note that the military grade version (741) has a wider temperature range than the commercial, or hobbyist, grade version (741C). Output Short-Circuit Duration This is the amount of time that the op-amp’s output can be short-circuited to ground or either supply volt ...
... the manufacturer’s specifications. Note that the military grade version (741) has a wider temperature range than the commercial, or hobbyist, grade version (741C). Output Short-Circuit Duration This is the amount of time that the op-amp’s output can be short-circuited to ground or either supply volt ...
Kuliah 3(a)
... Introduction Memory Element Latch SR latch D latch Flip-flop SR flip-flop D flip-flop JK flip-flop T flip-flop ...
... Introduction Memory Element Latch SR latch D latch Flip-flop SR flip-flop D flip-flop JK flip-flop T flip-flop ...
Squishy Circuits as a Tangible Interface
... Circuits as a teaching tool in early childhood (preschool and kindergarten) in the future. ...
... Circuits as a teaching tool in early childhood (preschool and kindergarten) in the future. ...
AD9851 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... Indicates the minimum signal levels required to reliably clock the device at the indicated supply voltages. This specifies the p-p signal level and dc offset needed when the clocking signal is not of CMOS/TTL origin, i.e., a sine wave with 0 V dc offset. ...
... Indicates the minimum signal levels required to reliably clock the device at the indicated supply voltages. This specifies the p-p signal level and dc offset needed when the clocking signal is not of CMOS/TTL origin, i.e., a sine wave with 0 V dc offset. ...
Design of High-Speed Op-Amps for Signal Processing
... CMOS op-amps for signal processing (e.g. analog-to-digital converters, filters, input receivers, etc.) in nanometer size CMOS. Techniques for biasing, device size selection, topologies, and compensation are discussed. Design examples are presented and used in system level building blocks. The emphas ...
... CMOS op-amps for signal processing (e.g. analog-to-digital converters, filters, input receivers, etc.) in nanometer size CMOS. Techniques for biasing, device size selection, topologies, and compensation are discussed. Design examples are presented and used in system level building blocks. The emphas ...
OPA454
... is fully specified to perform over a wide power-supply range of ±5V to ±50V or on a single supply of 10V to 100V. The status flag is an open-drain output that allows it to be easily referenced to standard low-voltage logic circuitry. This high-voltage op amp provides excellent accuracy, wide output ...
... is fully specified to perform over a wide power-supply range of ±5V to ±50V or on a single supply of 10V to 100V. The status flag is an open-drain output that allows it to be easily referenced to standard low-voltage logic circuitry. This high-voltage op amp provides excellent accuracy, wide output ...
12 13 Examples of applying 43 + 10 log (P) to calculate
... using a reference bandwidth of 4 kHz. With a measured total mean power of 20 W: Attenuation relative to total mean power 43 10 log (20) 56 dBc. The 56 dBc value is less stringent than the 60 dBc limit, so the 56 dBc value is used. Therefore: Spurious domain emissions must not exceed 56 dBc in ...
... using a reference bandwidth of 4 kHz. With a measured total mean power of 20 W: Attenuation relative to total mean power 43 10 log (20) 56 dBc. The 56 dBc value is less stringent than the 60 dBc limit, so the 56 dBc value is used. Therefore: Spurious domain emissions must not exceed 56 dBc in ...
CMOS 180 MHz DDS/DAC Synthesizer AD9851
... Indicates the minimum signal levels required to reliably clock the device at the indicated supply voltages. This specifies the p-p signal level and dc offset needed when the clocking signal is not of CMOS/TTL origin, i.e., a sine wave with 0 V dc offset. ...
... Indicates the minimum signal levels required to reliably clock the device at the indicated supply voltages. This specifies the p-p signal level and dc offset needed when the clocking signal is not of CMOS/TTL origin, i.e., a sine wave with 0 V dc offset. ...
The LM3900 A New Current-Differencing Quad of Plus or Minus
... This basic stage can provide an adequate open-loop voltage gain (70 dB) and has the desired large output voltage swing capability. A disadvantage of this circuit is that the DC input current, IIN, is large; as it is essentially equal to the maximum output current, IOUT, divided by b2. For example, f ...
... This basic stage can provide an adequate open-loop voltage gain (70 dB) and has the desired large output voltage swing capability. A disadvantage of this circuit is that the DC input current, IIN, is large; as it is essentially equal to the maximum output current, IOUT, divided by b2. For example, f ...
Basic BJT Amplifiers Circuits
... Basic BJT Amplifiers Circuits Single-Stage BJT Amplifiers Common-Collector Amplifier The last basic configuration is to tie the collector to a fixed voltage, drive an input signal into the base and observe the output at the emitter. ...
... Basic BJT Amplifiers Circuits Single-Stage BJT Amplifiers Common-Collector Amplifier The last basic configuration is to tie the collector to a fixed voltage, drive an input signal into the base and observe the output at the emitter. ...
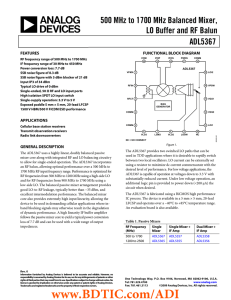
ADL5367 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... device to be used in demanding cellular applications where inband blocking signals may otherwise result in the degradation of dynamic performance. A high linearity IF buffer amplifier follows the passive mixer core to yield a typical power conversion loss of 7.7 dB and can be used with a wide range ...
... device to be used in demanding cellular applications where inband blocking signals may otherwise result in the degradation of dynamic performance. A high linearity IF buffer amplifier follows the passive mixer core to yield a typical power conversion loss of 7.7 dB and can be used with a wide range ...
Contents 1 How to Read this Design Guide IVS 102 Design Guide
... All machines with critical moving parts are covered by the machinery directive of January 1, 1995. Since a frequency converter is largely electrical, it does not fall under the machinery directive. However, if a frequency converter is supplied for use in a machine, we provide information on safety a ...
... All machines with critical moving parts are covered by the machinery directive of January 1, 1995. Since a frequency converter is largely electrical, it does not fall under the machinery directive. However, if a frequency converter is supplied for use in a machine, we provide information on safety a ...
PowerPoint
... Let’s now calculate the small-signal behavior, neglecting the bulk effect for simplicity. The circuit is NOT symmetric, and therefore we can not use the halfcircuit principle here. As a first approximation, we can consider the common sources of the input transistors as a virtual ground. The small-si ...
... Let’s now calculate the small-signal behavior, neglecting the bulk effect for simplicity. The circuit is NOT symmetric, and therefore we can not use the halfcircuit principle here. As a first approximation, we can consider the common sources of the input transistors as a virtual ground. The small-si ...
Measuring Electrical Quantities
... • Circuit Symbols (p 46) • Circuit Diagrams • Parts of a Circuit (p 45) • Measuring Electrical Quantities (p 53) • Calculating Electrical Quantities (p 47) ...
... • Circuit Symbols (p 46) • Circuit Diagrams • Parts of a Circuit (p 45) • Measuring Electrical Quantities (p 53) • Calculating Electrical Quantities (p 47) ...
29_128_manual_01_10 - John A. Goree
... A benchtop power supply typically has two knobs: voltage and current. The way it works is that only one knob will have an effect, depending on two things: the setting of the other knob and the load resistance. For example, if you turn the current knob up to its maximum value and if you use a large r ...
... A benchtop power supply typically has two knobs: voltage and current. The way it works is that only one knob will have an effect, depending on two things: the setting of the other knob and the load resistance. For example, if you turn the current knob up to its maximum value and if you use a large r ...
power electronics lab manual - Sri Siddhartha Institute of
... TRIAC Characteristics Aim: To study the v-1 characteristics of a TRIAC in both directions and also in different (1, 2, 3 & 4) modes op operation and determine break over voltages, holding current, latching current and comment on sensitivities. Apparatus required: TRIAC – BT 136, power supplies, watt ...
... TRIAC Characteristics Aim: To study the v-1 characteristics of a TRIAC in both directions and also in different (1, 2, 3 & 4) modes op operation and determine break over voltages, holding current, latching current and comment on sensitivities. Apparatus required: TRIAC – BT 136, power supplies, watt ...
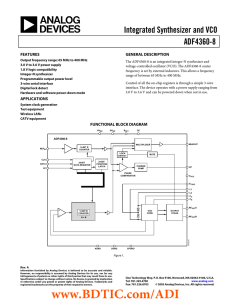
ADF4360-8 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... Analog Power Supply. This ranges from 3.0 V to 3.6 V. Decoupling capacitors to the analog ground plane should be placed as close as possible to this pin. AVDD must have the same value as DVDD. Analog Ground. This is the ground return path of the prescaler and VCO. VCO Output. The output level is pro ...
... Analog Power Supply. This ranges from 3.0 V to 3.6 V. Decoupling capacitors to the analog ground plane should be placed as close as possible to this pin. AVDD must have the same value as DVDD. Analog Ground. This is the ground return path of the prescaler and VCO. VCO Output. The output level is pro ...
Regenerative circuit
The regenerative circuit (or regen) allows an electronic signal to be amplified many times by the same active device. It consists of an amplifying vacuum tube or transistor with its output connected to its input through a feedback loop, providing positive feedback. This circuit was widely used in radio receivers, called regenerative receivers, between 1915 and World War II. The regenerative receiver was invented in 1912 and patented in 1914 by American electrical engineer Edwin Armstrong when he was an undergraduate at Columbia University. Due partly to its tendency to radiate interference, by the 1930s the regenerative receiver was superseded by other receiver designs, the TRF and superheterodyne receivers and became obsolete, but regeneration (now called positive feedback) is widely used in other areas of electronics, such as in oscillators and active filters. A receiver circuit that used regeneration in a more complicated way to achieve even higher amplification, the superregenerative receiver, was invented by Armstrong in 1922. It was never widely used in general receivers, but due to its small parts count is used in a few specialized low data rate applications, such as garage door openers, wireless networking devices, walkie-talkies and toys.