Molecular Testing and Clinical Diagnosis
... • Determines if target is present & its distribution within cells • Requires tissue sections, probe and visualization system • If fluorescent tag used = fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH ) ...
... • Determines if target is present & its distribution within cells • Requires tissue sections, probe and visualization system • If fluorescent tag used = fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH ) ...
1. Introduction Organisms are made up of the sum of their genes and
... contains a short U-rich sequence and / or a GU-rich motif (Gil and Proudfoot, 1984; Hart et al., 1985a; McLauchlan et al., 1985; Conway and Wickens, 1985; McDevitt et al., 1986; Zarkower and Wickens, 1988). Salisbury and colleagues (2006) described that the DSE element consists of two parts. The UG- ...
... contains a short U-rich sequence and / or a GU-rich motif (Gil and Proudfoot, 1984; Hart et al., 1985a; McLauchlan et al., 1985; Conway and Wickens, 1985; McDevitt et al., 1986; Zarkower and Wickens, 1988). Salisbury and colleagues (2006) described that the DSE element consists of two parts. The UG- ...
... incorporated into the conidio, or o prabct is incorporated which is detrimental to germination. These mutants can also be classified as either phase-specific or phase-critical. “Phase specific” mutations me those that affect gene prcducts that are used only in one phase of the life cycle. “Phase cri ...
1 Transcription in eukaryotes Eukaryotic RNA polymerases
... But: It was not yet possible to reconstitute RNA polymerase from separate subunits •Another option: find genes for all putative subunits, mutate them and look for the function. All the genes were discovered, cloned and sequenced. They clone for 12 putative subunits of yeast polymerase II. Each of po ...
... But: It was not yet possible to reconstitute RNA polymerase from separate subunits •Another option: find genes for all putative subunits, mutate them and look for the function. All the genes were discovered, cloned and sequenced. They clone for 12 putative subunits of yeast polymerase II. Each of po ...
File - Integrated Science
... Targeted deletion by homologous recombination (KNOCKOUT MICE) - We’ll discuss next time Specific mutational changes can be made Time consuming and limited to certain organisms Antisense RNA Variable effects and mechanism not understood ...
... Targeted deletion by homologous recombination (KNOCKOUT MICE) - We’ll discuss next time Specific mutational changes can be made Time consuming and limited to certain organisms Antisense RNA Variable effects and mechanism not understood ...
Qβ replicase discriminates between legitimate and illegitimate
... thermodynamically more stable than are the intrastand secondary structures: If a mixture of complementary is annealed (melted and then slow cooled), they are completely converted into double helix. • Within the replicative complex, the template and the nascent strands are close to one another, which ...
... thermodynamically more stable than are the intrastand secondary structures: If a mixture of complementary is annealed (melted and then slow cooled), they are completely converted into double helix. • Within the replicative complex, the template and the nascent strands are close to one another, which ...
Promega Notes: T4 RNA Ligase: A Molecular Tool for RNA and DNA
... to proceed was n=8 and that the reaction peaked at n=10-16 (8). The reaction then decreased as the chain length increased up to n=100 (8). One unit is defined as the amount of enzyme that catalyzes transformation of one nanomole of 5´-[32 P]poly(A) 14-20 into a phosphatase-resistant form in 30 minut ...
... to proceed was n=8 and that the reaction peaked at n=10-16 (8). The reaction then decreased as the chain length increased up to n=100 (8). One unit is defined as the amount of enzyme that catalyzes transformation of one nanomole of 5´-[32 P]poly(A) 14-20 into a phosphatase-resistant form in 30 minut ...
Applications of RNA minimum free energy computations
... ncRNA genes. (Coventry et al., 2004) developed the algorithm MSARI which assigns appropriate weights for local shifts of a ClustalW multiple sequence alignment of many (e.g. 11) homologous ncRNAs, in order to detect a conserved pattern of secondary structure. The authors suggest that a gene finder ...
... ncRNA genes. (Coventry et al., 2004) developed the algorithm MSARI which assigns appropriate weights for local shifts of a ClustalW multiple sequence alignment of many (e.g. 11) homologous ncRNAs, in order to detect a conserved pattern of secondary structure. The authors suggest that a gene finder ...
Model for transcriptional activation
... • Five of the seven 7 aa’s of heptad have ‘-OH’ groups that can be phosphorylated ...
... • Five of the seven 7 aa’s of heptad have ‘-OH’ groups that can be phosphorylated ...
A new heavy lanthanide-dependent DNAzyme
... only moderate cleavage was observed with Tb3+ . Efficient cleavage occurred from Dy3+ to Tm3+ , and then the cleaved product decreased rapidly with Yb3+ and Lu3+ . This is a general trend for all the six tested DNAzymes and their activities are quantified in Figure 2D. Based on this study, we reason ...
... only moderate cleavage was observed with Tb3+ . Efficient cleavage occurred from Dy3+ to Tm3+ , and then the cleaved product decreased rapidly with Yb3+ and Lu3+ . This is a general trend for all the six tested DNAzymes and their activities are quantified in Figure 2D. Based on this study, we reason ...
The search for small regulatory RNA
... Other stable RNA • Fundamental processes of life (left over from RNA world?) • Nearly universal, highly conserved • Not many ...
... Other stable RNA • Fundamental processes of life (left over from RNA world?) • Nearly universal, highly conserved • Not many ...
Bench Guide
... for synthesis of proteins. Protein synthesis is carried out by ribosomes, which consist of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and proteins. Amino acids for protein synthesis are delivered to the ribosome on transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules. RNAs are also part of riboproteins involved in RNA processing. In addition, ...
... for synthesis of proteins. Protein synthesis is carried out by ribosomes, which consist of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and proteins. Amino acids for protein synthesis are delivered to the ribosome on transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules. RNAs are also part of riboproteins involved in RNA processing. In addition, ...
RNA PROCESSING AND RNPs
... RNase P enzymes are found in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes, being located in the nucleus of the latter where they are therefore small nuclear RNPs (snRNPs) ...
... RNase P enzymes are found in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes, being located in the nucleus of the latter where they are therefore small nuclear RNPs (snRNPs) ...
The importance ofRNA
... that compose it, while deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) does not. This seemingly minor difference makes RNA much more flexible than DNA, resulting in a molecule that can adopt many different structures and acquire an array of functions. At the same time, RNA can in some cases use these hydroxyl groups to ...
... that compose it, while deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) does not. This seemingly minor difference makes RNA much more flexible than DNA, resulting in a molecule that can adopt many different structures and acquire an array of functions. At the same time, RNA can in some cases use these hydroxyl groups to ...
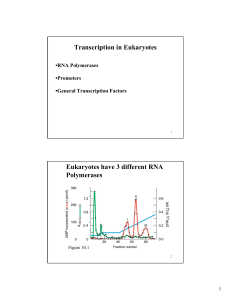
Transcription in Eukaryotes Eukaryotes have 3 different RNA
... First concensus sequence from lining up several eukaryotic promoters: TATA box ...
... First concensus sequence from lining up several eukaryotic promoters: TATA box ...
RNA AND TYPES
... mRNA is synthesized on DNA and contains the information needed to build a protein. mRNA travels from the nucleus of a cell to ribosome, the place where protein synthesis occurs, and is read by the ribosome. The result is a protein. Hence the name, messenger RNA. The information that mRNA carries ...
... mRNA is synthesized on DNA and contains the information needed to build a protein. mRNA travels from the nucleus of a cell to ribosome, the place where protein synthesis occurs, and is read by the ribosome. The result is a protein. Hence the name, messenger RNA. The information that mRNA carries ...
Enzyme and DNA Practice MULTIPLE CHOICE
... A) alternating nitrogen bases and phosphate groups linked by amide bonds B) alternating sugar and nitrogen bases liked by peptide bonds C) alternating sugar and phosphate groups linked by phosphate ester bonds D) complimentary bases held together by hydrogen bonds ...
... A) alternating nitrogen bases and phosphate groups linked by amide bonds B) alternating sugar and nitrogen bases liked by peptide bonds C) alternating sugar and phosphate groups linked by phosphate ester bonds D) complimentary bases held together by hydrogen bonds ...
Chapter 17: Transcription, RNA Processing, and Translation
... Polymerases interact with during transcription initiation? 3.) What are the components that make up the bacterial RNA Polymerase Holoenzyme? What is the function of each component? 4.) What is the significance of the -35 box, -10 box, and +1 box? In bacteria, what component of the RNA Polymerase hol ...
... Polymerases interact with during transcription initiation? 3.) What are the components that make up the bacterial RNA Polymerase Holoenzyme? What is the function of each component? 4.) What is the significance of the -35 box, -10 box, and +1 box? In bacteria, what component of the RNA Polymerase hol ...
(A) + RNA
... two or more samples and require uniform sampling conditions for this comparison to be valid. Many factors can contribute to variability in the analysis of samples, making the results difficult to reproduce between experiments: Sample degradation, extraction efficiency, contamination → RNA isolation ...
... two or more samples and require uniform sampling conditions for this comparison to be valid. Many factors can contribute to variability in the analysis of samples, making the results difficult to reproduce between experiments: Sample degradation, extraction efficiency, contamination → RNA isolation ...
Chapter 17: Transcription, RNA Processing, and Translation
... Polymerases interact with during transcription initiation? 3.) What are the components that make up the bacterial RNA Polymerase Holoenzyme? What is the function of each component? 4.) What is the significance of the -35 box, -10 box, and +1 box? In bacteria, what component of the RNA Polymerase hol ...
... Polymerases interact with during transcription initiation? 3.) What are the components that make up the bacterial RNA Polymerase Holoenzyme? What is the function of each component? 4.) What is the significance of the -35 box, -10 box, and +1 box? In bacteria, what component of the RNA Polymerase hol ...
Tutorial_9_NEW
... Minimum free energy structures and base pair probabilities from single RNA or DNA sequences. RNAalifold server Consensus secondary structures from an alignment of several related RNA or DNA sequences. You need to upload an alignment. ...
... Minimum free energy structures and base pair probabilities from single RNA or DNA sequences. RNAalifold server Consensus secondary structures from an alignment of several related RNA or DNA sequences. You need to upload an alignment. ...
RNA Tertiary Structure
... know n chromosomal translocation (exchange of DNA between chromosomes). ...
... know n chromosomal translocation (exchange of DNA between chromosomes). ...
Hammerhead ribozyme

The hammerhead ribozyme is a RNA molecule motif that catalyzes reversible cleavage and joining reactions at a specific site within an RNA molecule. It serves as a model system for research on the structure and properties of RNA, and is used for targeted RNA cleavage experiments, some with proposed therapeutic applications. Named for the resemblance of early secondary structure diagrams to a hammerhead shark, hammerhead ribozymes RNAs were originally discovered in two classes of plant virus-like RNAs: satellite RNAs and viroids. They have subsequently been found to be widely dispersed within many forms of life.The self-cleavage reactions, first reported in 1986, are part of a rolling circle replication mechanism. The hammerhead sequence is sufficient for self-cleavage and acts by forming a conserved three-dimensional tertiary structure.