Monte Carlo simulation of electron transport in alternating
... semble Monte Carlo simulation of steady-state hot electron transport in bulk ZnS, including a full band structure calculation for the density of states in the first two conduction bands and a treatment of electron-phonon scattering including collision broadening. His results have been interpreted as ...
... semble Monte Carlo simulation of steady-state hot electron transport in bulk ZnS, including a full band structure calculation for the density of states in the first two conduction bands and a treatment of electron-phonon scattering including collision broadening. His results have been interpreted as ...
1 Hot Electron Modeling I: Extended Drift–Diffusion Models
... Although considerably simplified, the equations are still fairly difficult to solve, particularly if one wants to use the method for engineering applications, involving intensive computations. Further approximations are possible if the transport properties of a particular material (e.g. Si or GaAs) ...
... Although considerably simplified, the equations are still fairly difficult to solve, particularly if one wants to use the method for engineering applications, involving intensive computations. Further approximations are possible if the transport properties of a particular material (e.g. Si or GaAs) ...
L01_5342_Sp02
... • Compton showed Dp = hkinitial - hkfinal, so an photon (wave) is particle-like • DeBroglie hypothesized a particle could be wave-like, l = h/p • Davisson and Germer demonstrated wave-like interference phenomena for electrons to complete the duality model L1 January 15 ...
... • Compton showed Dp = hkinitial - hkfinal, so an photon (wave) is particle-like • DeBroglie hypothesized a particle could be wave-like, l = h/p • Davisson and Germer demonstrated wave-like interference phenomena for electrons to complete the duality model L1 January 15 ...
Modern Physics
... Klein-Gordon describes a free, relativistic spinless particle. It requires two initial conditions [Ψ(t=0) and ∂Ψ/∂t(t=0)] because of 2nd derivative wrt time. Therefore specifying a wavefunction Ψ at t=0 is insufficient to uniquely specify the system’s behavior. ...
... Klein-Gordon describes a free, relativistic spinless particle. It requires two initial conditions [Ψ(t=0) and ∂Ψ/∂t(t=0)] because of 2nd derivative wrt time. Therefore specifying a wavefunction Ψ at t=0 is insufficient to uniquely specify the system’s behavior. ...
HOT ELECTRON TRANSPORT IN SEMICONDUCTOR SPACE
... equation for Is> eq. (8). By making suitable choice of the collision term (8) reduces to an ordinary differential equation of second order. Applying the energy balance equation (subject to low current densities and moderate electric fields) current density has been introduced into calculations. This ...
... equation for Is> eq. (8). By making suitable choice of the collision term (8) reduces to an ordinary differential equation of second order. Applying the energy balance equation (subject to low current densities and moderate electric fields) current density has been introduced into calculations. This ...
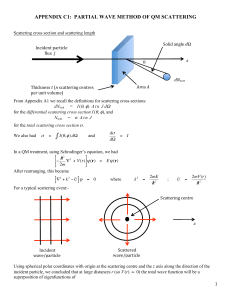
APPENDIX C1: PARTIAL WAVE METHOD OF QM SCATTERING
... because we now have identical particles, so the Pauli Exclusion Principle has to be taken into account when including the effects of spin. Also, in the case of p-p scattering there is the (repulsive) Coulomb repulsion in addition to the (attractive) potential well at small separations. At lower ener ...
... because we now have identical particles, so the Pauli Exclusion Principle has to be taken into account when including the effects of spin. Also, in the case of p-p scattering there is the (repulsive) Coulomb repulsion in addition to the (attractive) potential well at small separations. At lower ener ...
Transient like radiation quenching mechanism
... M. Kirakosyan1, A. Leonidov1 1 Lebedev Physical Institute of RAS ...
... M. Kirakosyan1, A. Leonidov1 1 Lebedev Physical Institute of RAS ...
Problems for particle physics course:
... A+B C1 + C2 + … + Cn. Calculate the threshold (i.e. minimum E) for this reaction, in terms of the various particle masses. 3. In a two-body scattering event,A+ B C + D, it is convenient to introduce the Mandelstam variables s = (pA + pB)2 t = (pA -- pC)2 u = (pA-- pD)2 a) Show that s + t + u = m ...
... A+B C1 + C2 + … + Cn. Calculate the threshold (i.e. minimum E) for this reaction, in terms of the various particle masses. 3. In a two-body scattering event,A+ B C + D, it is convenient to introduce the Mandelstam variables s = (pA + pB)2 t = (pA -- pC)2 u = (pA-- pD)2 a) Show that s + t + u = m ...