Single-Chip Li-Ion Charge and System Power-Path
... (10) To disable the fast-charge safety timer and charge termination, tie TMR to the VREF pin. Tying the TMR pin high changes the timing resistor from the external value to an internal 50 kΩ ±25%, which can add an additional tolerance to any timed specification. The TMR pin normally regulates to 2.5 ...
... (10) To disable the fast-charge safety timer and charge termination, tie TMR to the VREF pin. Tying the TMR pin high changes the timing resistor from the external value to an internal 50 kΩ ±25%, which can add an additional tolerance to any timed specification. The TMR pin normally regulates to 2.5 ...
CD4046B Phase-Locked Loop (Rev. A)
... Figure 5. Typical Waveforms for the CD4046B Employing Phase Comparator I in Locked Condition of fo Phase comparator II is an edge-controlled digital memory network. It consists of four flip-flop stages, control gating, and a 3-state output circuit comprising p and n drivers having a common output no ...
... Figure 5. Typical Waveforms for the CD4046B Employing Phase Comparator I in Locked Condition of fo Phase comparator II is an edge-controlled digital memory network. It consists of four flip-flop stages, control gating, and a 3-state output circuit comprising p and n drivers having a common output no ...
J.M. Rivas, Y. Han, O. Leitermann, A.D. Sagneri, and D.J. Perreault, “A High-Frequency Resonant Inverter Topology with Low Voltage Stress,” 2007 IEEE Power Electronics Specialists Conference, pp. 2705 – 2717
... across the semiconductor, reaching a value of almost 4.4 times the input voltage [16] for this circuit. Some radio-frequency power amplifiers, such as class F and variants, use resonant harmonic peaking of the input or output network [3], [17]– [23] to reduce the peak voltage on the switch. However, ...
... across the semiconductor, reaching a value of almost 4.4 times the input voltage [16] for this circuit. Some radio-frequency power amplifiers, such as class F and variants, use resonant harmonic peaking of the input or output network [3], [17]– [23] to reduce the peak voltage on the switch. However, ...
MAX19538 12-Bit, 95Msps, 3.3V ADC General Description Features
... The MAX19538 is a 3.3V, 12-bit, 95Msps analog-to-digital converter (ADC) featuring a fully differential wideband track-and-hold (T/H) input amplifier, driving a low-noise internal quantizer. The analog input accepts single-ended or differential signals. The MAX19538 is optimized for low power, small ...
... The MAX19538 is a 3.3V, 12-bit, 95Msps analog-to-digital converter (ADC) featuring a fully differential wideband track-and-hold (T/H) input amplifier, driving a low-noise internal quantizer. The analog input accepts single-ended or differential signals. The MAX19538 is optimized for low power, small ...
Precision Dual-Channel Difference Amplifier AD8270
... 80 dB minimum CMRR (G = 2) Two channels in small 4 mm × 4 mm LFCSP Supply current: 2.5 mA per channel Supply range: ±2.5 V to ±18 V ...
... 80 dB minimum CMRR (G = 2) Two channels in small 4 mm × 4 mm LFCSP Supply current: 2.5 mA per channel Supply range: ±2.5 V to ±18 V ...
MAX1718 Notebook CPU Step-Down Controller for Intel Mobile Voltage Positioning (IMVP-II) General Description
... The MAX1718 step-down controller is intended for core CPU DC-DC converters in notebook computers. It features a dynamically adjustable output, ultra-fast transient response, high DC accuracy, and high efficiency needed for leading-edge CPU core power supplies. Maxim’s proprietary Quick-PWM™ quick-re ...
... The MAX1718 step-down controller is intended for core CPU DC-DC converters in notebook computers. It features a dynamically adjustable output, ultra-fast transient response, high DC accuracy, and high efficiency needed for leading-edge CPU core power supplies. Maxim’s proprietary Quick-PWM™ quick-re ...
J. Santiago-Gonzalez, K.M. Elbaggari, K.K. Afridi and D.J. Perreault, “Design of Class E Resonant Rectifiers and Diode Evaluation for VHF Power Conversion,” IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, Vol.30, No. 9, pp. 4960-4972, 2015.
... systems [5,6]. In many of these applications, it is desirable for the rectifier to appear as a resistive load at its ac input port. For example, in some very-high-frequency dc-dc converters, proper operation of the inverter portion of the circuit can depend upon maintaining resistive (but possibly v ...
... systems [5,6]. In many of these applications, it is desirable for the rectifier to appear as a resistive load at its ac input port. For example, in some very-high-frequency dc-dc converters, proper operation of the inverter portion of the circuit can depend upon maintaining resistive (but possibly v ...
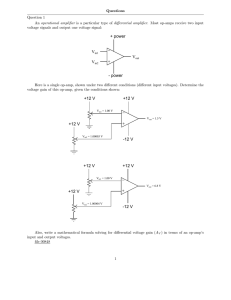
12 V +12 V +12 V
... Now this is strange. How can a simple voltage buffer output alternating current when its input is grounded and the power supply is pure DC? Perplexed, the student asks the instructor for help. ”Oh,” the instructor says, ”you need a compensation capacitor between pins 1 and 8.” What does the instruct ...
... Now this is strange. How can a simple voltage buffer output alternating current when its input is grounded and the power supply is pure DC? Perplexed, the student asks the instructor for help. ”Oh,” the instructor says, ”you need a compensation capacitor between pins 1 and 8.” What does the instruct ...
LM27341/2/1Q/2Q 2 MHz 1.5A/2A Wide Input Range Step
... that requires a minimum amount of board space. The LM27341/LM27342 is internally compensated, which reduces design time, and requires few external components. The following operating description of the LM27341/LM27342 will refer to the Block Diagram (Figure 31) and to the waveforms in Figure 32. The ...
... that requires a minimum amount of board space. The LM27341/LM27342 is internally compensated, which reduces design time, and requires few external components. The following operating description of the LM27341/LM27342 will refer to the Block Diagram (Figure 31) and to the waveforms in Figure 32. The ...
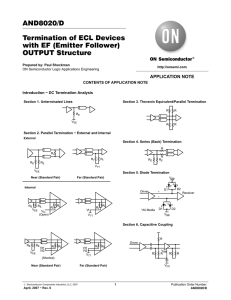
AND8020/D Termination of ECL Devices with EF (Emitter Follower) OUTPUT Structure
... Z0 = Line Characteristic Impedance The reflected signal continues to be reflected by the source and load impedances and is attenuated with each passage over the transmission line. The output response appears as a damped oscillation asymptotically approaching a steady state value. This phenomena is o ...
... Z0 = Line Characteristic Impedance The reflected signal continues to be reflected by the source and load impedances and is attenuated with each passage over the transmission line. The output response appears as a damped oscillation asymptotically approaching a steady state value. This phenomena is o ...
Design, Optimization and Integration of Doherty
... represent a favorable solution to this problem. Given the current trend of reducing devices and full integration of RF chain on a single chip, it was decided to implement this power amplifier in 65nm CMOS technology due to its performance for digital circuits, allowing the integration of a whole sys ...
... represent a favorable solution to this problem. Given the current trend of reducing devices and full integration of RF chain on a single chip, it was decided to implement this power amplifier in 65nm CMOS technology due to its performance for digital circuits, allowing the integration of a whole sys ...
AD9241 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... suited for both multiplexed systems that switch full-scale voltage levels in successive channels as well as sampling single-channel inputs at frequencies up to and beyond the Nyquist rate. Also, the AD9241 performs well in communication systems employing Direct-IF Down Conversion since the SHA in th ...
... suited for both multiplexed systems that switch full-scale voltage levels in successive channels as well as sampling single-channel inputs at frequencies up to and beyond the Nyquist rate. Also, the AD9241 performs well in communication systems employing Direct-IF Down Conversion since the SHA in th ...
Linear Current Starved Delay Element
... Loops (PWCLs) [3], etc. In VLSI ICs, the DLL is routinely employed in order to obtain correct synchronization and elimination of clock skew among different digital blocks [1], such as CPU and SDRAM interface, etc. In addition, DLL is used for on-chip clock generation [1], and vernier delay patterns ...
... Loops (PWCLs) [3], etc. In VLSI ICs, the DLL is routinely employed in order to obtain correct synchronization and elimination of clock skew among different digital blocks [1], such as CPU and SDRAM interface, etc. In addition, DLL is used for on-chip clock generation [1], and vernier delay patterns ...
BQ24314 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... Chip enable input. Active low. When CE = High, the input FET is off. Internally pulled down. ...
... Chip enable input. Active low. When CE = High, the input FET is off. Internally pulled down. ...
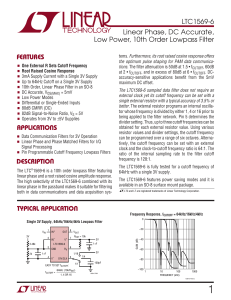
LTC1569-6 - Linear Phase, DC Accurate, Low Power, 10th Order
... IN +/IN – (Pins 1, 2): Signals can be applied to either or both input pins. The DC gain from IN + (Pin 1) to OUT (Pin␣ 8) is 1.0, and the DC gain from Pin 2 to Pin 8 is –1. The input range, input resistance and output range are described in the Applications Information section. Input voltages which ...
... IN +/IN – (Pins 1, 2): Signals can be applied to either or both input pins. The DC gain from IN + (Pin 1) to OUT (Pin␣ 8) is 1.0, and the DC gain from Pin 2 to Pin 8 is –1. The input range, input resistance and output range are described in the Applications Information section. Input voltages which ...
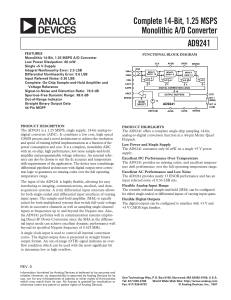
AD9241 Complete 14-Bit, 1.25 MSPS Monolithic A/D Converter
... suited for both multiplexed systems that switch full-scale voltage levels in successive channels as well as sampling single-channel inputs at frequencies up to and beyond the Nyquist rate. Also, the AD9241 performs well in communication systems employing Direct-IF Down Conversion since the SHA in th ...
... suited for both multiplexed systems that switch full-scale voltage levels in successive channels as well as sampling single-channel inputs at frequencies up to and beyond the Nyquist rate. Also, the AD9241 performs well in communication systems employing Direct-IF Down Conversion since the SHA in th ...
Figure 1. Diode circuit model
... small difference is usually ignored. However, in certain cases where the range of operating conditions is very wide the error associated with the use of the offset model may not be acceptable. Therefore, care should be taken when circuit analysis is performed with simplified models. For our scope th ...
... small difference is usually ignored. However, in certain cases where the range of operating conditions is very wide the error associated with the use of the offset model may not be acceptable. Therefore, care should be taken when circuit analysis is performed with simplified models. For our scope th ...
Eddystone Broadcast ---- XE35/75/150/300 Series 35
... the safety ‘Interlock’ relay. This relay will itself provide an over-riding mute signal if the external Interlock line is open-circuited, irrespective of any internal Exciter condition. Two sockets are provided on the Main Board for the connection of optional modules (/S Stereo Encoder etc.). The co ...
... the safety ‘Interlock’ relay. This relay will itself provide an over-riding mute signal if the external Interlock line is open-circuited, irrespective of any internal Exciter condition. Two sockets are provided on the Main Board for the connection of optional modules (/S Stereo Encoder etc.). The co ...
NCP1396A, NCP1396B High Performance Resonant Mode Controller featuring High--Voltage Drivers
... to operate (power on), the switching frequency is pushed to the programmed maximum value and slowly moves down toward the minimum frequency, until the feedback loop closes. The soft-- start sequence is activated in the following cases: a) normal startup b) back to operation from an off state: during ...
... to operate (power on), the switching frequency is pushed to the programmed maximum value and slowly moves down toward the minimum frequency, until the feedback loop closes. The soft-- start sequence is activated in the following cases: a) normal startup b) back to operation from an off state: during ...
CHAPTER 2: Diode Applications (Aplikasi Diod)
... voltage (or current) despite changes in the input, load current or temperature. Combination of a large capacitor & an IC regulator – inexpensive & produce excellent small power supply Popular IC regulators have 3 terminals: (i) input terminal (ii) output terminal (iii) reference (or adjust) term ...
... voltage (or current) despite changes in the input, load current or temperature. Combination of a large capacitor & an IC regulator – inexpensive & produce excellent small power supply Popular IC regulators have 3 terminals: (i) input terminal (ii) output terminal (iii) reference (or adjust) term ...
Amplifier
An amplifier, electronic amplifier or (informally) amp is an electronic device that increases the power of a signal.It does this by taking energy from a power supply and controlling the output to match the input signal shape but with a larger amplitude. In this sense, an amplifier modulates the output of the power supply to make the output signal stronger than the input signal. An amplifier is effectively the opposite of an attenuator: while an amplifier provides gain, an attenuator provides loss.An amplifier can either be a separate piece of equipment or an electrical circuit within another device. The ability to amplify is fundamental to modern electronics, and amplifiers are extremely widely used in almost all electronic equipment. The types of amplifiers can be categorized in different ways. One is by the frequency of the electronic signal being amplified; audio amplifiers amplify signals in the audio (sound) range of less than 20 kHz, RF amplifiers amplify frequencies in the radio frequency range between 20 kHz and 300 GHz. Another is which quantity, voltage or current is being amplified; amplifiers can be divided into voltage amplifiers, current amplifiers, transconductance amplifiers, and transresistance amplifiers. A further distinction is whether the output is a linear or nonlinear representation of the input. Amplifiers can also be categorized by their physical placement in the signal chain.The first practical electronic device that amplified was the Audion (triode) vacuum tube, invented in 1906 by Lee De Forest, which led to the first amplifiers. The terms ""amplifier"" and ""amplification"" (from the Latin amplificare, 'to enlarge or expand') were first used for this new capability around 1915 when triodes became widespread. For the next 50 years, vacuum tubes were the only devices that could amplify. All amplifiers used them until the 1960s, when transistors appeared. Most amplifiers today use transistors, though tube amplifiers are still produced.