Broad Ranges Power Measurement with One Unit
... (/G5 and /G6 options) Yokogawa’s previous model* provides two different measurement modes, called Normal and Harmonic, and each of the measurements is performed separately. The WT1800 makes it possible to simultaneously measure voltage, current fundamental wave, harmonic components, and harmonic dis ...
... (/G5 and /G6 options) Yokogawa’s previous model* provides two different measurement modes, called Normal and Harmonic, and each of the measurements is performed separately. The WT1800 makes it possible to simultaneously measure voltage, current fundamental wave, harmonic components, and harmonic dis ...
MAX3222E/MAX3232E/MAX3237E/MAX3241E ±15kV ESD
... charge pump requires only four small 0.1µF capacitors for operation from a +3.3V supply. Each device is guaranteed to run at data rates of 250kbps while maintaining RS232 output levels. The MAX3237E is guaranteed to run at data rates of 250kbps in the normal operating mode and 1Mbps in the MegaBaud™ ...
... charge pump requires only four small 0.1µF capacitors for operation from a +3.3V supply. Each device is guaranteed to run at data rates of 250kbps while maintaining RS232 output levels. The MAX3237E is guaranteed to run at data rates of 250kbps in the normal operating mode and 1Mbps in the MegaBaud™ ...
Descriptio on
... 4. Measured on “High Effective Thermal Conductivity Test Board" according to JESD51. 5. Device starts up above 5.4V and as such the minimum applied supply voltage has to be above 5.4V (plus any noise margin). The ZXLD1371 will, however, continue to function when the input voltage is reduced from ≥ 8 ...
... 4. Measured on “High Effective Thermal Conductivity Test Board" according to JESD51. 5. Device starts up above 5.4V and as such the minimum applied supply voltage has to be above 5.4V (plus any noise margin). The ZXLD1371 will, however, continue to function when the input voltage is reduced from ≥ 8 ...
Transistor Biasing
... of transistors. The major reason for these variations is that transistor is a new device and manufacturing techniques have not too much advanced. For instance, it has not been possible to control the base width and it may vary, although slightly, from one transistor to the other even of the same typ ...
... of transistors. The major reason for these variations is that transistor is a new device and manufacturing techniques have not too much advanced. For instance, it has not been possible to control the base width and it may vary, although slightly, from one transistor to the other even of the same typ ...
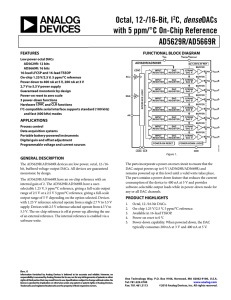
Dual, Low-Noise Variable-Gain Amplifier with Preamp (Rev. D)
... of systems and probes. The LNP gain can be programmed to one of four settings (3dB, 12dB, 18dB, 22dB), while maintaining excellent noise and signal handling characteristics. The input impedance of the LNP can be controlled by selecting one of the built-in feedback resistors. This active termination ...
... of systems and probes. The LNP gain can be programmed to one of four settings (3dB, 12dB, 18dB, 22dB), while maintaining excellent noise and signal handling characteristics. The input impedance of the LNP can be controlled by selecting one of the built-in feedback resistors. This active termination ...
Low-Power Delta-Sigma Modulators for Medical Applications Ali Fazli Yeknami
... dominant part of power in the active modulators. A careful analysis of passive filter’s non-idealities, including the noise, parasitic effect, and integrator’s loss were essential to meet the performance requirement necessary for an implantable device. The chip was tested simultaneously with its act ...
... dominant part of power in the active modulators. A careful analysis of passive filter’s non-idealities, including the noise, parasitic effect, and integrator’s loss were essential to meet the performance requirement necessary for an implantable device. The chip was tested simultaneously with its act ...
IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE)
... converter levels [4]. Each H- bridge unit generates a quasi-square waveform by phase shifting its positive and negative phase legs switching timings. Each device always conducts for 180° (or half cycle) regardless of the pulse width of the quasi-square wave. This switching method makes all of the sw ...
... converter levels [4]. Each H- bridge unit generates a quasi-square waveform by phase shifting its positive and negative phase legs switching timings. Each device always conducts for 180° (or half cycle) regardless of the pulse width of the quasi-square wave. This switching method makes all of the sw ...
NUMBER SYSTEM AND CODES INTRODUCTION:-
... ASCII CODE:The American Standard Code for Information Interchange (ASCII) pronounced as ‘ASKEE’ is widely used alphanumeric code. This is basically a 7 bit code. The number of different bit patterns that can be created with 7 bits is 27 = 128 , the ASCII can be used to encode both the uppercase and ...
... ASCII CODE:The American Standard Code for Information Interchange (ASCII) pronounced as ‘ASKEE’ is widely used alphanumeric code. This is basically a 7 bit code. The number of different bit patterns that can be created with 7 bits is 27 = 128 , the ASCII can be used to encode both the uppercase and ...
Single D-Type Flip-Flop With 3-State Output
... Texas Instruments Incorporated and its subsidiaries (TI) reserve the right to make corrections, enhancements, improvements and other changes to its semiconductor products and services per JESD46, latest issue, and to discontinue any product or service per JESD48, latest issue. Buyers should obtain t ...
... Texas Instruments Incorporated and its subsidiaries (TI) reserve the right to make corrections, enhancements, improvements and other changes to its semiconductor products and services per JESD46, latest issue, and to discontinue any product or service per JESD48, latest issue. Buyers should obtain t ...
Range and General Features ClassA HEADENDS
... b) IF filtering. A double SAW filter is used, what provides very high selectivity (>70 dB at ±5.25 MHz from the centre for 8MHz-wide channels). c) “IF o Output Channel” conversion. The output level can be adjusted between 65 and 80 dBmV. Programming of a TPC processor involves the following selections ...
... b) IF filtering. A double SAW filter is used, what provides very high selectivity (>70 dB at ±5.25 MHz from the centre for 8MHz-wide channels). c) “IF o Output Channel” conversion. The output level can be adjusted between 65 and 80 dBmV. Programming of a TPC processor involves the following selections ...
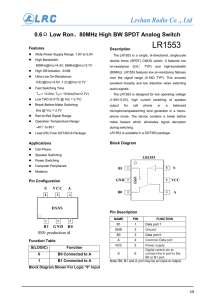
0.6 Low Ron 80MHz High BW SPDT Analog Switch Ω
... (80MHz). LR1553 features low on-resistance flatness ...
... (80MHz). LR1553 features low on-resistance flatness ...
Si9185 Micropower 500 mA CMOS LDO Regulator with Error Flag
... rejection superior to that of bipolar or BiCMOS LDO regulators, and is designed to drive lower cost ceramic, as well as tantalum, output capacitors. An external noise bypass capacitor connected to the device’s CNOISE pin will lower the LDO’s output noise for low noise applications. The Si9185 also i ...
... rejection superior to that of bipolar or BiCMOS LDO regulators, and is designed to drive lower cost ceramic, as well as tantalum, output capacitors. An external noise bypass capacitor connected to the device’s CNOISE pin will lower the LDO’s output noise for low noise applications. The Si9185 also i ...
Adjustable Battery-Backup Supervisor for RAM
... is asserted, the CE transmission gate is disabled when CEIN goes high, or 15 µs after reset asserts, whichever occurs first. This allows the current write cycle to complete during power down. When the CE transmission gate is enabled, the impedance of CEIN appears as a resistor in series with the loa ...
... is asserted, the CE transmission gate is disabled when CEIN goes high, or 15 µs after reset asserts, whichever occurs first. This allows the current write cycle to complete during power down. When the CE transmission gate is enabled, the impedance of CEIN appears as a resistor in series with the loa ...
Sample Assessment Materials
... A basic circuit diagram or a description of a suitable circuit is provided for obtaining the results required– possibly missing a method of varying the voltage / current. There is a plan to collect I – V measurements with an attempt to describe which graph to plot to show the characteristic curve. T ...
... A basic circuit diagram or a description of a suitable circuit is provided for obtaining the results required– possibly missing a method of varying the voltage / current. There is a plan to collect I – V measurements with an attempt to describe which graph to plot to show the characteristic curve. T ...
Rail-to-Rail Op Amp Design ( cont`d )
... – The square-root circuit M121-M125 keeps the sum of the square-roots of the tail currents of the input pairs and then the gm constant. – The current switch, M111, compares the common-mode input voltage with Vb3 and decides which part of the current Ib7 should be diverted to the square-root circuit. ...
... – The square-root circuit M121-M125 keeps the sum of the square-roots of the tail currents of the input pairs and then the gm constant. – The current switch, M111, compares the common-mode input voltage with Vb3 and decides which part of the current Ib7 should be diverted to the square-root circuit. ...
Exeltech User Manual - Alternative Energy, Inc.
... These inverters can supply twice their rated output power for 3 seconds, in order to start motors or supply in-rush currents to electronic loads. If output power is exceeded for greater than 3 seconds, output voltage is reduced to a level which will provide the inverter’s rated power to the load by ...
... These inverters can supply twice their rated output power for 3 seconds, in order to start motors or supply in-rush currents to electronic loads. If output power is exceeded for greater than 3 seconds, output voltage is reduced to a level which will provide the inverter’s rated power to the load by ...
- Soundtronics
... The Technobots MIDI Thru boxes or splitters as they are sometimes called address the problem of driving more than 1 MIDI device from the same MIDI source. It also resolves the problem of signal delay and signal distortion with chains of MIDI thru to MIDI in (especially where the MIDI thru is via sof ...
... The Technobots MIDI Thru boxes or splitters as they are sometimes called address the problem of driving more than 1 MIDI device from the same MIDI source. It also resolves the problem of signal delay and signal distortion with chains of MIDI thru to MIDI in (especially where the MIDI thru is via sof ...
Amplifier
An amplifier, electronic amplifier or (informally) amp is an electronic device that increases the power of a signal.It does this by taking energy from a power supply and controlling the output to match the input signal shape but with a larger amplitude. In this sense, an amplifier modulates the output of the power supply to make the output signal stronger than the input signal. An amplifier is effectively the opposite of an attenuator: while an amplifier provides gain, an attenuator provides loss.An amplifier can either be a separate piece of equipment or an electrical circuit within another device. The ability to amplify is fundamental to modern electronics, and amplifiers are extremely widely used in almost all electronic equipment. The types of amplifiers can be categorized in different ways. One is by the frequency of the electronic signal being amplified; audio amplifiers amplify signals in the audio (sound) range of less than 20 kHz, RF amplifiers amplify frequencies in the radio frequency range between 20 kHz and 300 GHz. Another is which quantity, voltage or current is being amplified; amplifiers can be divided into voltage amplifiers, current amplifiers, transconductance amplifiers, and transresistance amplifiers. A further distinction is whether the output is a linear or nonlinear representation of the input. Amplifiers can also be categorized by their physical placement in the signal chain.The first practical electronic device that amplified was the Audion (triode) vacuum tube, invented in 1906 by Lee De Forest, which led to the first amplifiers. The terms ""amplifier"" and ""amplification"" (from the Latin amplificare, 'to enlarge or expand') were first used for this new capability around 1915 when triodes became widespread. For the next 50 years, vacuum tubes were the only devices that could amplify. All amplifiers used them until the 1960s, when transistors appeared. Most amplifiers today use transistors, though tube amplifiers are still produced.