Experiment 2 - Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute
... up coil), and any extra load we add to the beam to observe how its performance depends on load conditions. Since real beams have finite mass concentrated at the center of mass of the beam, it is necessary to use the equivalent mass at the end that would produce the same frequency response. This is g ...
... up coil), and any extra load we add to the beam to observe how its performance depends on load conditions. Since real beams have finite mass concentrated at the center of mass of the beam, it is necessary to use the equivalent mass at the end that would produce the same frequency response. This is g ...
Practical Feedback Loop Design Considerations for
... phase lag at the crossover frequency is less than 180 degrees. At other frequencies, the phase lag may exceed 180 degrees and the system can be stable. The phase margin is the amount by which the phase lag at the crossover frequency is less than 180 degrees. The gain margin is the factor by which th ...
... phase lag at the crossover frequency is less than 180 degrees. At other frequencies, the phase lag may exceed 180 degrees and the system can be stable. The phase margin is the amount by which the phase lag at the crossover frequency is less than 180 degrees. The gain margin is the factor by which th ...
File - The Physics Doctor
... There are no EMFs here in this loop so the total p.ds must = 0! Starting a point A and going clockwise, the p.d through the bulb is 0.85V (V3). Continuing back to A, the p.d. through the resistor is going against the flow of current so is considered negative, so -0.85V (V3) ...
... There are no EMFs here in this loop so the total p.ds must = 0! Starting a point A and going clockwise, the p.d through the bulb is 0.85V (V3). Continuing back to A, the p.d. through the resistor is going against the flow of current so is considered negative, so -0.85V (V3) ...
- Status Instruments
... Monitoring/control equipment inputs Internally powered (Active) input: Equipment that is supplying the power to drive the loop it is monitoring from its input pins. This type of loop input cannot be connected to an external power supply. Externally or loop powered (Passive) input: Equipment where th ...
... Monitoring/control equipment inputs Internally powered (Active) input: Equipment that is supplying the power to drive the loop it is monitoring from its input pins. This type of loop input cannot be connected to an external power supply. Externally or loop powered (Passive) input: Equipment where th ...
Lab 2 - Rose
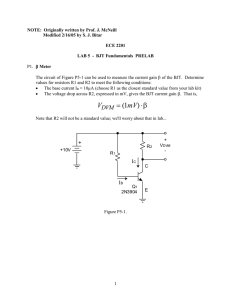
... 2.5 Now vary the frequency in appropriate steps until you have enough data to plot the gain of the op-amp versus frequency from 10 Hz to 10 kHz. Check the input waveform each time to make sure it is staying at 0.5 V peak. Since you are using a logarithmic scale for frequency, linearly spaced steps m ...
... 2.5 Now vary the frequency in appropriate steps until you have enough data to plot the gain of the op-amp versus frequency from 10 Hz to 10 kHz. Check the input waveform each time to make sure it is staying at 0.5 V peak. Since you are using a logarithmic scale for frequency, linearly spaced steps m ...
cmos differential amplifier
... Char 2: small-signal gain (slope of Vout1-Vout2 vs. Vin1-Vin2) is maximum for Vin1=Vin2 Gradually falling to zero as |Vin1-Vin2| increases • i.e. circuit becomes more nonlinear as input voltage swing increases • Circuit is in equilibrium when Vin1=Vin2 ...
... Char 2: small-signal gain (slope of Vout1-Vout2 vs. Vin1-Vin2) is maximum for Vin1=Vin2 Gradually falling to zero as |Vin1-Vin2| increases • i.e. circuit becomes more nonlinear as input voltage swing increases • Circuit is in equilibrium when Vin1=Vin2 ...
ece2201_lab5_modified
... L6. For the input signal source (a 10kHz, 0.1V peak sine wave riding on a 1.0V DC level) use the function generator with the DC offset enabled (pull out the DC OFFSET knob). Display vIN on oscilloscope channel 1; set the horizontal time scale to show a few cycles of the sine wave. To set the DC offs ...
... L6. For the input signal source (a 10kHz, 0.1V peak sine wave riding on a 1.0V DC level) use the function generator with the DC offset enabled (pull out the DC OFFSET knob). Display vIN on oscilloscope channel 1; set the horizontal time scale to show a few cycles of the sine wave. To set the DC offs ...
Sound to Light Unit
... bright flashes from LEDs. The circuit diagram in Figure 1 shows that we employ two operational amplifiers with a total gain of about 1000 times. The input of the first opamp (IC1.A) is connected to the electret microphone capsule via coupling capacitor C2. The microphone is given a certain DC bias l ...
... bright flashes from LEDs. The circuit diagram in Figure 1 shows that we employ two operational amplifiers with a total gain of about 1000 times. The input of the first opamp (IC1.A) is connected to the electret microphone capsule via coupling capacitor C2. The microphone is given a certain DC bias l ...
Pure Class A operation delivers quality power: 60 watts
... Current feedback principle assures excellent phase characteristics in high range As shown in the illustration, the A-70 uses the output signal current rather than voltage for feedback. Since the impedance at the current feedback point is very low, there is almost no phase shift. A minimal amount of ...
... Current feedback principle assures excellent phase characteristics in high range As shown in the illustration, the A-70 uses the output signal current rather than voltage for feedback. Since the impedance at the current feedback point is very low, there is almost no phase shift. A minimal amount of ...
LPF-8 manual - Warner Instruments
... attenuating higher-frequency signals. The point at which the filter will pass or attenuate frequencies is set by a frequency control. The Frequency selected will be attenuated by 3 dB (half voltage amplitude), with frequencies below the setfrequency attenuated by less than 3 dB and frequencies above ...
... attenuating higher-frequency signals. The point at which the filter will pass or attenuate frequencies is set by a frequency control. The Frequency selected will be attenuated by 3 dB (half voltage amplitude), with frequencies below the setfrequency attenuated by less than 3 dB and frequencies above ...
AD828
... For high performance circuits, the “balancing” resistor should be used to reduce the offset errors caused by bias current flowing through the input and feedback resistors. The balancing resistor equals the parallel combination of RIN and RF and thus provides a matched impedance at each input termina ...
... For high performance circuits, the “balancing” resistor should be used to reduce the offset errors caused by bias current flowing through the input and feedback resistors. The balancing resistor equals the parallel combination of RIN and RF and thus provides a matched impedance at each input termina ...
Chapter 22 notes
... resonance: a peaking of the current amplitude at a certain frequency in a constant voltage circuit. resonance angular frequency : the angular frequency ω0 at which the resonance peak occurs. The inductive and capacitive reactance are equal at the resonance angular frequency so ...
... resonance: a peaking of the current amplitude at a certain frequency in a constant voltage circuit. resonance angular frequency : the angular frequency ω0 at which the resonance peak occurs. The inductive and capacitive reactance are equal at the resonance angular frequency so ...
hood_ss-amp.pdf
... The major advantage of amplifiers of this type is that the normal static power dissipation is very low, and the overall power-conversion efficiency is high. Unfortunately there are also some inherent disadvantages due to the intrinsic dissimilarity in the response of the two halves of the push pull ...
... The major advantage of amplifiers of this type is that the normal static power dissipation is very low, and the overall power-conversion efficiency is high. Unfortunately there are also some inherent disadvantages due to the intrinsic dissimilarity in the response of the two halves of the push pull ...