LMP8271 High Common Mode, Gain of 20
... High side current measurement requires a differential amplifier with gain. Here the DC voltage source represents a common mode voltage with the +IN input at the supply voltage and the −IN input very close to the supply voltage. The LMP8271 can be used with a common mode voltage, V DC in this case, o ...
... High side current measurement requires a differential amplifier with gain. Here the DC voltage source represents a common mode voltage with the +IN input at the supply voltage and the −IN input very close to the supply voltage. The LMP8271 can be used with a common mode voltage, V DC in this case, o ...
NCN5192NGEVB NCN5192NG Evaluation Board User's Manual •
... until its threshold value is reached, and will then wait an additional minimum of 35 ms until it releases the RESETB. This ensures that some time has passed after the supply voltage reaches the turn-on voltage. The RESETB en VDD pin signals during startup are shown in Figure 5. The measured start-up ...
... until its threshold value is reached, and will then wait an additional minimum of 35 ms until it releases the RESETB. This ensures that some time has passed after the supply voltage reaches the turn-on voltage. The RESETB en VDD pin signals during startup are shown in Figure 5. The measured start-up ...
Review of Resonance
... The highest frequency, though, is limited by the thickness of the material. For t ≈ 15 µm, the frequency is about 200 MHz. MEMS resonators have been demonstrated up to ∼ GHz frequencies. MEMS resonators are an active research area. Integrated MEMS resonators are fabricated from polysilicon beams (fo ...
... The highest frequency, though, is limited by the thickness of the material. For t ≈ 15 µm, the frequency is about 200 MHz. MEMS resonators have been demonstrated up to ∼ GHz frequencies. MEMS resonators are an active research area. Integrated MEMS resonators are fabricated from polysilicon beams (fo ...
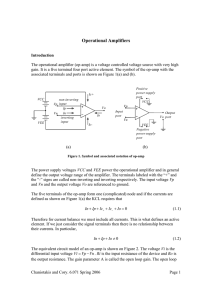
Section G9: Inverting Amplifier
... We are now going to give the inverting op-amp configuration the same treatment as the non-inverting amplifier of the previous section. Specifically, more realistic input and output impedances, as well as voltage gain, will be developed for the modified op-amp model. The schematic for a single input ...
... We are now going to give the inverting op-amp configuration the same treatment as the non-inverting amplifier of the previous section. Specifically, more realistic input and output impedances, as well as voltage gain, will be developed for the modified op-amp model. The schematic for a single input ...
AD633 Low Cost Analog Multiplier
... multiplier. It includes high impedance, differential X and Y inputs and a high impedance summing input (Z). The low impedance output voltage is a nominal 10 V full scale provided by a buried Zener. The AD633 is the first product to offer these features in modestly priced 8-lead plastic DIP and SOIC ...
... multiplier. It includes high impedance, differential X and Y inputs and a high impedance summing input (Z). The low impedance output voltage is a nominal 10 V full scale provided by a buried Zener. The AD633 is the first product to offer these features in modestly priced 8-lead plastic DIP and SOIC ...
AD8014
... high impedance current source that is shunted by a small capacitance. In this case, a high voltage pulse from a Picosecond Pulse Labs Generator that is ac-coupled through a 20 kΩ resistor is used to simulate the high impedance current source of a photodiode. This circuit will convert the input volta ...
... high impedance current source that is shunted by a small capacitance. In this case, a high voltage pulse from a Picosecond Pulse Labs Generator that is ac-coupled through a 20 kΩ resistor is used to simulate the high impedance current source of a photodiode. This circuit will convert the input volta ...
Very High Accuracy Instrumentation Amplifier
... applied to Common terminal is summed with the output. Low impedance must be maintained at this node to assure good common-mode rejection. The op amp connected as a buffer provides low impedance. THERMAL EFFECTS ON OFFSET VOLTAGE To achieve lowest offset voltage and drift, prevent air currents from c ...
... applied to Common terminal is summed with the output. Low impedance must be maintained at this node to assure good common-mode rejection. The op amp connected as a buffer provides low impedance. THERMAL EFFECTS ON OFFSET VOLTAGE To achieve lowest offset voltage and drift, prevent air currents from c ...
Kirchhoff`s Rules S2017
... Q: A galvanometer with a fullscale limit of 0.100 mA is to be used to measure a current of 60.0 mA. How much current will pass through the shunt resistance R? ...
... Q: A galvanometer with a fullscale limit of 0.100 mA is to be used to measure a current of 60.0 mA. How much current will pass through the shunt resistance R? ...
Experiment No
... the stage. While observing the output, bring a hot soldering iron close to, but not against the transistor. Record which peak, positive or negative, of the output wave begins to distort. 2. Now insert a 100 ohm swamping resistor in the emitter leg of circuit. Once ...again readjust the base circuit ...
... the stage. While observing the output, bring a hot soldering iron close to, but not against the transistor. Record which peak, positive or negative, of the output wave begins to distort. 2. Now insert a 100 ohm swamping resistor in the emitter leg of circuit. Once ...again readjust the base circuit ...
RF3863 数据资料DataSheet下载
... • L2/C3/C4: Placed to optimize input match and enhance out-of-band low frequency stability. • R2: Optionally placed to increase bias current and IP3. 20Ω value is found to be the best case. (See graphs.) • L1/C1: Influence output return loss. The RF3863 has internal DC-blocking capacitors at RF IN a ...
... • L2/C3/C4: Placed to optimize input match and enhance out-of-band low frequency stability. • R2: Optionally placed to increase bias current and IP3. 20Ω value is found to be the best case. (See graphs.) • L1/C1: Influence output return loss. The RF3863 has internal DC-blocking capacitors at RF IN a ...
Chapter 1 Problems
... If a receiver is underselective: a. only part of the bandwidth of the AM signal is amplified, causing some of the sideband information to be lost and distortion results. b. the tank circuits within the tuned amplifiers have too high a Q. c. when the volume control is turned up to maximum, the desire ...
... If a receiver is underselective: a. only part of the bandwidth of the AM signal is amplified, causing some of the sideband information to be lost and distortion results. b. the tank circuits within the tuned amplifiers have too high a Q. c. when the volume control is turned up to maximum, the desire ...
RF5322 3V TO 4.5V, 2.4GHz TO 2.5GHz LINEAR POWER AMPLIFIER Features
... band. The RF5322 has integrated input, interstage and output matching components thus allowing minimal bill of material (BOM) parts count in end applications. The RF5322 is designed primarily for IEEE802.11b/g/n WiFi applications where the available supply voltage and current are limited. This ampli ...
... band. The RF5322 has integrated input, interstage and output matching components thus allowing minimal bill of material (BOM) parts count in end applications. The RF5322 is designed primarily for IEEE802.11b/g/n WiFi applications where the available supply voltage and current are limited. This ampli ...
file for Lab 3
... Where A is the open-loop voltage gain of the amplifier, v+ is the non-inverting input voltage and v- is the inverting input voltage. Both v+ and v- are node voltages with respect to ground. Typically, the open-loop voltage gain A is on the order of 105 - 106. A resistor is placed between the output ...
... Where A is the open-loop voltage gain of the amplifier, v+ is the non-inverting input voltage and v- is the inverting input voltage. Both v+ and v- are node voltages with respect to ground. Typically, the open-loop voltage gain A is on the order of 105 - 106. A resistor is placed between the output ...
Lecture Notes - Resonance Circuits and Characteristics File
... The frequencies corresponding to 0.707 of the maximum current are called the band frequencies, cutoff frequencies, or half-power frequencies (ƒ1, ƒ2). Half-power frequencies are those frequencies at which the power delivered is onehalf that delivered at resonant frequency. The range of frequen ...
... The frequencies corresponding to 0.707 of the maximum current are called the band frequencies, cutoff frequencies, or half-power frequencies (ƒ1, ƒ2). Half-power frequencies are those frequencies at which the power delivered is onehalf that delivered at resonant frequency. The range of frequen ...
Resonance
... The frequencies corresponding to 0.707 of the maximum current are called the band frequencies, cutoff frequencies, or half-power frequencies (ƒ1, ƒ2). Half-power frequencies are those frequencies at which the power delivered is onehalf that delivered at resonant frequency. The range of frequen ...
... The frequencies corresponding to 0.707 of the maximum current are called the band frequencies, cutoff frequencies, or half-power frequencies (ƒ1, ƒ2). Half-power frequencies are those frequencies at which the power delivered is onehalf that delivered at resonant frequency. The range of frequen ...