Neuro Objectives 17
... NMDA receptor (activated by glutamate): NMDA acts as an agonist, primary excitatory neurotransmitter of the CNS, increase in Na+ and Ca2+ influx for depolarization (learning and memory) c. GABA receptor (activated by GABA): primary inhibitory neurotransmitter of the CNS, increase in Cl- influx for h ...
... NMDA receptor (activated by glutamate): NMDA acts as an agonist, primary excitatory neurotransmitter of the CNS, increase in Na+ and Ca2+ influx for depolarization (learning and memory) c. GABA receptor (activated by GABA): primary inhibitory neurotransmitter of the CNS, increase in Cl- influx for h ...
Biochemical Pathways – Legends General Remarks for
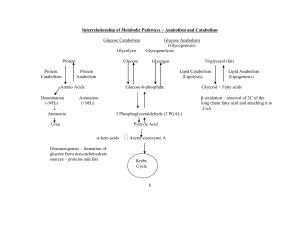
... In some microorganisms, cystathionine synthesis takes place via O-acetyl-L-homoserine. The enzyme functions for formation and degradation of fructose-2,6-bisphosphate are located on the same peptide chain. Their relative activities are regulated by phosphorylation and dephosphorylation. In muscle, t ...
... In some microorganisms, cystathionine synthesis takes place via O-acetyl-L-homoserine. The enzyme functions for formation and degradation of fructose-2,6-bisphosphate are located on the same peptide chain. Their relative activities are regulated by phosphorylation and dephosphorylation. In muscle, t ...
Fuel Metabolism
... responsive to multiple signals including insulin and insulin-dependent growth factor (IGF-I) that are particularly involved in longer term seasonal responses (and are mediated by protein kinase B) and noradrenaline that is responsible for acute activation of nonshivering thermogenesis ...
... responsive to multiple signals including insulin and insulin-dependent growth factor (IGF-I) that are particularly involved in longer term seasonal responses (and are mediated by protein kinase B) and noradrenaline that is responsible for acute activation of nonshivering thermogenesis ...
BIO C211 - BITS Pilani
... 1. Classification of vitamins 2. Structures and functions of some important vitamins. D. Biochemical Energetics 3 Ch. 1. The concept of free energy 2. Energy rich compounds 3. Coupling of reactions 4. Oxidation-Reduction E. Carbohydrate Metabolism 9 Ch. 1. Glycolysis 2. Reversal of Glycolytic sequen ...
... 1. Classification of vitamins 2. Structures and functions of some important vitamins. D. Biochemical Energetics 3 Ch. 1. The concept of free energy 2. Energy rich compounds 3. Coupling of reactions 4. Oxidation-Reduction E. Carbohydrate Metabolism 9 Ch. 1. Glycolysis 2. Reversal of Glycolytic sequen ...
View Full PDF - Biochemical Society Transactions
... presently applicable to the isolation of lysosomes. It is succinctly written and includes the essential details for anyone seriously considering purification of these organelles from particular biological sources. The chapter on lysosomal enzymes has been almost completely rewritten, and contains ex ...
... presently applicable to the isolation of lysosomes. It is succinctly written and includes the essential details for anyone seriously considering purification of these organelles from particular biological sources. The chapter on lysosomal enzymes has been almost completely rewritten, and contains ex ...
Updated - PeproTech Posters
... monocytes. CD30L binds specifically to CD30 (receptor), which is expressed on activated, but not resting, B and T cells, in lymphomas and various chronically inflamed tissues. CD30L/ CD30 interactions initiate a signaling cascade that can ultimately lead to the activation of NF-KappaB. CD30L/CD30 si ...
... monocytes. CD30L binds specifically to CD30 (receptor), which is expressed on activated, but not resting, B and T cells, in lymphomas and various chronically inflamed tissues. CD30L/ CD30 interactions initiate a signaling cascade that can ultimately lead to the activation of NF-KappaB. CD30L/CD30 si ...
Exam 2 for Review - philipdarrenjones.com
... one of his veins. What will be the most probable result of this transfusion? A) It will have no unfavorable effect as long as the water is free of viruses and bacteria B) The patient's red blood cells will shrivel up because the blood fluid (plasma) is hypotonic compared to the cells C) The patient' ...
... one of his veins. What will be the most probable result of this transfusion? A) It will have no unfavorable effect as long as the water is free of viruses and bacteria B) The patient's red blood cells will shrivel up because the blood fluid (plasma) is hypotonic compared to the cells C) The patient' ...
Sensory Systems* - University of Wisconsin–Eau Claire
... located in different areas • In taste buds (~150 cells w/ sensory neurons) in papillae (big knobs) ...
... located in different areas • In taste buds (~150 cells w/ sensory neurons) in papillae (big knobs) ...
Cell Signalling Pathways
... to DNA and transcription of androgen responsive targets. GH: Peptide that binds to receptors + exerts effects by activating responsive genes that change cell growth rate + increase muscle mass. EPO: Peptide involved in the development of various blood lineages from haematopoietic precursors. Cytokin ...
... to DNA and transcription of androgen responsive targets. GH: Peptide that binds to receptors + exerts effects by activating responsive genes that change cell growth rate + increase muscle mass. EPO: Peptide involved in the development of various blood lineages from haematopoietic precursors. Cytokin ...
Answers to Exam 1 multiple choice, TF and short answer questions
... 5. (15 pts) One of the themes that we will continue to explore this quarter is how specific cellular processes are controlled by modulating the activity level of specific proteins. In lecture we talked about a couple of mechanisms (see below) by which the function of a plasma membrane ion channel c ...
... 5. (15 pts) One of the themes that we will continue to explore this quarter is how specific cellular processes are controlled by modulating the activity level of specific proteins. In lecture we talked about a couple of mechanisms (see below) by which the function of a plasma membrane ion channel c ...
Biology 1408 - Lone Star College
... D) is involved in the synthesis, storage, and export of important molecules. E) it contains its own DNA ...
... D) is involved in the synthesis, storage, and export of important molecules. E) it contains its own DNA ...
What You Need To Know about ENZYMES ???
... would not be able to dissolve protein or starch. Enzymes perform only one specific job ...
... would not be able to dissolve protein or starch. Enzymes perform only one specific job ...
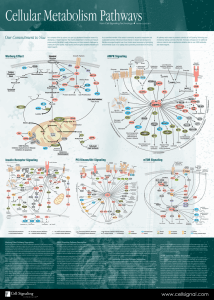
Cellular Metabolism Pathways
... Since its initial discovery as a proto-oncogene, the serine/threonine kinase Akt (also known as protein kinase B or PKB) has become a major focus of attention because of its critical regulatory role in diverse cellular processes, including cancer progression and insulin metabolism. The Akt cascade i ...
... Since its initial discovery as a proto-oncogene, the serine/threonine kinase Akt (also known as protein kinase B or PKB) has become a major focus of attention because of its critical regulatory role in diverse cellular processes, including cancer progression and insulin metabolism. The Akt cascade i ...
Receptors Functions and Signal Transduction- L4
... carrier proteins. Hormones dissociate from carrier proteins to pass through lipid component of the target plasma membrane. Receptors for the lipophilic hormones are known as nuclear hormone receptors. ...
... carrier proteins. Hormones dissociate from carrier proteins to pass through lipid component of the target plasma membrane. Receptors for the lipophilic hormones are known as nuclear hormone receptors. ...
Chapt03 Lecture 13ed Pt 4
... Enzymes are important for cellular respiration and many activities in the cell • Most enzymes are ________. • Enzymes are often named for the molecules that they work on, called ___________. • Enzymes are __________ to what substrate they work on. • Enzymes have active sites where a substrate binds. ...
... Enzymes are important for cellular respiration and many activities in the cell • Most enzymes are ________. • Enzymes are often named for the molecules that they work on, called ___________. • Enzymes are __________ to what substrate they work on. • Enzymes have active sites where a substrate binds. ...
Overview of Metaboli.. - Frozen Crocus Productions
... Hydrophobic interactions – hydrophobic amino acids will attract to each other (eg. Leucine) ...
... Hydrophobic interactions – hydrophobic amino acids will attract to each other (eg. Leucine) ...
Protein purification: the basics
... peptide bond. Higher order structure in the proteins will influence the absorption ...
... peptide bond. Higher order structure in the proteins will influence the absorption ...
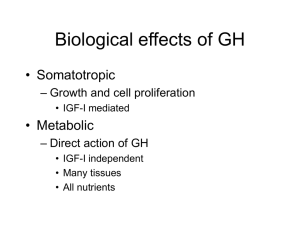
Biological effects of GH
... – Different between adipose and muscle – Growth of muscle in response to GH • Depends on availability of dietary proteins and energy • Involves IGF-I ...
... – Different between adipose and muscle – Growth of muscle in response to GH • Depends on availability of dietary proteins and energy • Involves IGF-I ...
Access Slides - Science Signaling
... Rigid Body Model: Straight jacketed receptor Rhodopsin still activates with bridges connecting the cytoplasmic ends of helices 1 & 7, and 3 & 5, and the extracellular ends of helices 3 & 4, and 5 & 6. ...
... Rigid Body Model: Straight jacketed receptor Rhodopsin still activates with bridges connecting the cytoplasmic ends of helices 1 & 7, and 3 & 5, and the extracellular ends of helices 3 & 4, and 5 & 6. ...
Recombinant Human PKA 2 beta (regulatory subunit) protein
... Regulatory subunit of the cAMP-dependent protein kinases involved in cAMP signaling in cells. Type II regulatory chains mediate membrane association by binding to anchoring proteins, including the MAP2 kinase. ...
... Regulatory subunit of the cAMP-dependent protein kinases involved in cAMP signaling in cells. Type II regulatory chains mediate membrane association by binding to anchoring proteins, including the MAP2 kinase. ...
CHEM 210(Biochemistry)
... biochemistry of pH and buffers. Structure and function of enzymes including enzyme kinetics and glycogen synthesis and degradation, and insulin and glycogenesis. DNA replication, transcription, translation, protein synthesis by RNA molecules and regulation of gene expression. Cell membrane structure ...
... biochemistry of pH and buffers. Structure and function of enzymes including enzyme kinetics and glycogen synthesis and degradation, and insulin and glycogenesis. DNA replication, transcription, translation, protein synthesis by RNA molecules and regulation of gene expression. Cell membrane structure ...
11_Lecture_picture version
... Explain why different types of cells may respond differently to the same signal molecule. For example, Epinephrine causes relaxation of smooth muscle and contraction of skeletal muscle. ...
... Explain why different types of cells may respond differently to the same signal molecule. For example, Epinephrine causes relaxation of smooth muscle and contraction of skeletal muscle. ...
Lipid signaling

Lipid signaling, broadly defined, refers to any biological signaling event involving a lipid messenger that binds a protein target, such as a receptor, kinase or phosphatase, which in turn mediate the effects of these lipids on specific cellular responses. Lipid signaling is thought to be qualitatively different from other classical signaling paradigms (such as monoamine neurotransmission) because lipids can freely diffuse through membranes (see osmosis.) One consequence of this is that lipid messengers cannot be stored in vesicles prior to release and so are often biosynthesized ""on demand"" at their intended site of action. As such, many lipid signaling molecules cannot circulate freely in solution but, rather, exist bound to special carrier proteins in serum.