Pantothenic Acid - Pure Encapsulations
... Nutrient Metabolism and Organ Function: Pantothenic acid is a precursor of coenzyme A (CoA), an important cofactor and acyl group carrier in cells. One of the main functions for CoA is the formation of acetyl-CoA, vital for cellular respiration and the metabolism of carbohydrates and fatty acids thr ...
... Nutrient Metabolism and Organ Function: Pantothenic acid is a precursor of coenzyme A (CoA), an important cofactor and acyl group carrier in cells. One of the main functions for CoA is the formation of acetyl-CoA, vital for cellular respiration and the metabolism of carbohydrates and fatty acids thr ...
Biology I What is pH?
... pH 7 is neutral; neither acid nor base Pure water is pH 7 Low pH (0-6.9) = acid High pH (7.1-14) = base The closer to the ends of the scale, the stronger the solution is ...
... pH 7 is neutral; neither acid nor base Pure water is pH 7 Low pH (0-6.9) = acid High pH (7.1-14) = base The closer to the ends of the scale, the stronger the solution is ...
Part 1 - ISpatula
... • Are assembled from (pieces of) primary metabolites • May be more prevalent or unique to certain genus, species, and similar compounds occur within genuses and families • Not necessarily involved in the essential metabolism of the cell, but exert physiologic activity for the plant, its environment ...
... • Are assembled from (pieces of) primary metabolites • May be more prevalent or unique to certain genus, species, and similar compounds occur within genuses and families • Not necessarily involved in the essential metabolism of the cell, but exert physiologic activity for the plant, its environment ...
Carbohydrate PPT Notes
... 1) How many electrons does Carbon have in the 1st energy level? 2nd energy level? 2) Which type of organic molecule is most commonly used as energy for cells? 3) If a carbohydrate has 8 carbon atoms, how many oxygen and hydrogen atoms will it most likely contain? 4) What are the monomers of carbohyd ...
... 1) How many electrons does Carbon have in the 1st energy level? 2nd energy level? 2) Which type of organic molecule is most commonly used as energy for cells? 3) If a carbohydrate has 8 carbon atoms, how many oxygen and hydrogen atoms will it most likely contain? 4) What are the monomers of carbohyd ...
Functional and structural relationship of Cst-II sialyltransferases to synthesize mono- and di-sialylated lipo-oligosaccharides derivatives
... jejuni (Cst-II) is capable of transferring sialic acid moiety from cytidine-5monophospho-N-acetyl-neuraminic acid (CMP-NeuAc) to the terminal position of lipo-oligosaccharides (LOS), thus mimicking the human ganglioside. There are two Cst-II isoforms that has either mono functional (α2,3-sialyltrans ...
... jejuni (Cst-II) is capable of transferring sialic acid moiety from cytidine-5monophospho-N-acetyl-neuraminic acid (CMP-NeuAc) to the terminal position of lipo-oligosaccharides (LOS), thus mimicking the human ganglioside. There are two Cst-II isoforms that has either mono functional (α2,3-sialyltrans ...
Acid-Base Principles to Organic Acids
... ID Nu- and E+ use curved arrows to show bonds breaking and forming show delocalized electrons with resonance structures. Key ideas: Organic acids are weak, e.g., acetic acid pKa = 5 The charge on an acid depends on pH and pK (see Chem 1B and biochem) ...
... ID Nu- and E+ use curved arrows to show bonds breaking and forming show delocalized electrons with resonance structures. Key ideas: Organic acids are weak, e.g., acetic acid pKa = 5 The charge on an acid depends on pH and pK (see Chem 1B and biochem) ...
Differential effects of n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids on tendon
... are responsible for cartilage destruction. In these studies, supplementation of cartilage explant cultures with n-3 PUFAs resulted in the dose-dependent reduction in aggrecanase and collagenase proteolytic activity. In addition, the expression of m R N A for the inflammatory mediators cyclooxygenase ...
... are responsible for cartilage destruction. In these studies, supplementation of cartilage explant cultures with n-3 PUFAs resulted in the dose-dependent reduction in aggrecanase and collagenase proteolytic activity. In addition, the expression of m R N A for the inflammatory mediators cyclooxygenase ...
BIOCHEMISTRY (CHEM 360)
... Suggest an additional “metabolic function” for the reaction above (having to do with glycolysis), since the product does not serve much of a purpose and gets converted back into pyruvate in the liver. The reaction generates NAD+, which helps to maintain the rate of the only oxidation step in glycoly ...
... Suggest an additional “metabolic function” for the reaction above (having to do with glycolysis), since the product does not serve much of a purpose and gets converted back into pyruvate in the liver. The reaction generates NAD+, which helps to maintain the rate of the only oxidation step in glycoly ...
Document
... 24.5: Waxes. esters of long chain fatty acids (C16 - C36) with long chain alcohols (C24 - C36) CH3(CH2)nCO2–(CH2)nCH3 ...
... 24.5: Waxes. esters of long chain fatty acids (C16 - C36) with long chain alcohols (C24 - C36) CH3(CH2)nCO2–(CH2)nCH3 ...
2005
... amino acid _________________________. These two reactions occur in the (subcellular location) _________________________. The product of this condensation, ________________________, is transported to another subcellular location where it condenses with __________________________ to form argininosucci ...
... amino acid _________________________. These two reactions occur in the (subcellular location) _________________________. The product of this condensation, ________________________, is transported to another subcellular location where it condenses with __________________________ to form argininosucci ...
Most membrane phospholipids contain glycerol
... • sphingomyelin *** Most membrane phospholipids contain glycerol (lecithin, phosphatidylcholine phosphatidylserine and cardiolipin). Sphingomyelin contains a sphingosine backbone instead of glycerol. Phospholipids are lipids. Each molecule is made up of one glycerol molecule attached to two fatty ac ...
... • sphingomyelin *** Most membrane phospholipids contain glycerol (lecithin, phosphatidylcholine phosphatidylserine and cardiolipin). Sphingomyelin contains a sphingosine backbone instead of glycerol. Phospholipids are lipids. Each molecule is made up of one glycerol molecule attached to two fatty ac ...
Quarter 1 Review Packet
... 4. The characteristics of life suggest that all living things descended from a ________________ ancestor. 5. Describe the difference between and ecosystem and a biome. ...
... 4. The characteristics of life suggest that all living things descended from a ________________ ancestor. 5. Describe the difference between and ecosystem and a biome. ...
Ch. 3 Vocabs
... enzyme: a type of protein or RNA molecule that speeds up metabolic reactions in plant and animals without being permanently changed or destroyed substrate: a part, substance, or element that lies beneath and supports another part, substance, or element; the reactant in reactions catalyzed by enz ...
... enzyme: a type of protein or RNA molecule that speeds up metabolic reactions in plant and animals without being permanently changed or destroyed substrate: a part, substance, or element that lies beneath and supports another part, substance, or element; the reactant in reactions catalyzed by enz ...
Protein degradation in mouse brain slices
... 5.5 mM-glucose and gassed with 0 , / C 0 2 ( 1 9 1 ). ["SIMethionine (50 pCi at 1000 Ci/mmol) or [3H]leucine(10 pCi at 155 Ci/mmol were added as required. Radioactivity was incorporated into the trichloroacetic-acid-soluble fraction for up to 2 h. Because incorporation was inhibited by cyclohexiniid ...
... 5.5 mM-glucose and gassed with 0 , / C 0 2 ( 1 9 1 ). ["SIMethionine (50 pCi at 1000 Ci/mmol) or [3H]leucine(10 pCi at 155 Ci/mmol were added as required. Radioactivity was incorporated into the trichloroacetic-acid-soluble fraction for up to 2 h. Because incorporation was inhibited by cyclohexiniid ...
C h e m g u i d e ... CARBOXYLIC ACIDS: REDUCTION
... 1. Carboxylic acids can be reduced using lithium tetrahydridoaluminate, LiAlH4, which contains the [AlH4]- ion. a) Carboxylic acids are reduced to alcohols in this way. What kind of alcohols? b) Describe the bonding between the aluminium and the four hydrogens in the [AlH4]- ion. c) Writing the redu ...
... 1. Carboxylic acids can be reduced using lithium tetrahydridoaluminate, LiAlH4, which contains the [AlH4]- ion. a) Carboxylic acids are reduced to alcohols in this way. What kind of alcohols? b) Describe the bonding between the aluminium and the four hydrogens in the [AlH4]- ion. c) Writing the redu ...
Hyaluronic Acid in Ear, Nose and Throat (ENT) Hyaluronic acid and
... in respiratory physiology, and is involved in many homeostatic mechanisms. Hyaluronic acid administered via inhaler penetrates rapidly and becomes integrated in the pulmonary interstice, preventing diffusion of macromolecules and regulating the migration of the cell populations involved in phlogisti ...
... in respiratory physiology, and is involved in many homeostatic mechanisms. Hyaluronic acid administered via inhaler penetrates rapidly and becomes integrated in the pulmonary interstice, preventing diffusion of macromolecules and regulating the migration of the cell populations involved in phlogisti ...
BDS Ist YEAR EXAMINATION 2008-09
... Define isoenzymes. Discuss the role of isoenzymes in clinical diagnosis with suitable examples. ...
... Define isoenzymes. Discuss the role of isoenzymes in clinical diagnosis with suitable examples. ...
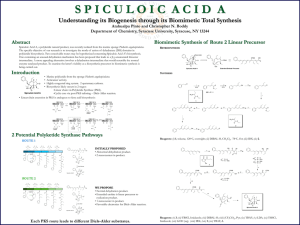
Total Synthesis of Spiculoic Acid A
... • Linear chain extension in PKS is analogous to fatty acid biosynthesis: ...
... • Linear chain extension in PKS is analogous to fatty acid biosynthesis: ...
投影片 1
... Alcohols, carbonyl compounds and carboxylic acids: REDUCTION Reduction: Addition of H2 (or H-), loss of O or O2; loss of X2 ...
... Alcohols, carbonyl compounds and carboxylic acids: REDUCTION Reduction: Addition of H2 (or H-), loss of O or O2; loss of X2 ...
Bioteknologi dalam Industri Pangan
... achieved hydrolysis using acid catalysis. The reaction was performed on starch slurry (30 – 40% dry solids) adjusted to pH 1.5 – 2.0 using hydrochloric acid. Hydrolysis was completed at 140 – 150 ° C over a 5 – 8 min period • To start with, this enzymatic liquefaction step was achieved at pH 6.0 – 6 ...
... achieved hydrolysis using acid catalysis. The reaction was performed on starch slurry (30 – 40% dry solids) adjusted to pH 1.5 – 2.0 using hydrochloric acid. Hydrolysis was completed at 140 – 150 ° C over a 5 – 8 min period • To start with, this enzymatic liquefaction step was achieved at pH 6.0 – 6 ...
Molecole per la vita
... Hydroxy acids, keto acids and amino acids are important polyfunctional compounds: ■■ hydroxy acids contain both the hydroxyl and the carboxyl functional groups; ■■ keto acids are compounds that contain both the carboxyl and the ketone groups; ■■ amino acids contain both the amino and the carboxyl gr ...
... Hydroxy acids, keto acids and amino acids are important polyfunctional compounds: ■■ hydroxy acids contain both the hydroxyl and the carboxyl functional groups; ■■ keto acids are compounds that contain both the carboxyl and the ketone groups; ■■ amino acids contain both the amino and the carboxyl gr ...
Hepoxilin

Hepoxilins (HxA3 and HxB3) are nonclassic eicosanoid hormones involved in inflammation.