Aspects of Lipid Metabolism in Crustaceans Department of
... synthesis of lipid or possibly an increased lipid during the 'molting' cycle. These ear- rate of lipid catabolism. These data sugly observations were extended by Renaud g-est that a factor (s) in the eyestalks influ(1949) who demonstrated a rise in hepa- ences lipid metabolism. To test this hypothes ...
... synthesis of lipid or possibly an increased lipid during the 'molting' cycle. These ear- rate of lipid catabolism. These data sugly observations were extended by Renaud g-est that a factor (s) in the eyestalks influ(1949) who demonstrated a rise in hepa- ences lipid metabolism. To test this hypothes ...
Lipid and fatty acid metabolism in Ralstonia eutropha: relevance for
... from acetyl-CoA (Fig. 2B) (Fujita et al. 2007). Fatty acid biosynthesis in R. eutropha has not been investigated thoroughly, if at all. The presence of fatty acid biosynthesis (fab) genes in the genome of R. eutropha H16 suggests that it synthesizes fatty acids for cell membrane similar to the E. c ...
... from acetyl-CoA (Fig. 2B) (Fujita et al. 2007). Fatty acid biosynthesis in R. eutropha has not been investigated thoroughly, if at all. The presence of fatty acid biosynthesis (fab) genes in the genome of R. eutropha H16 suggests that it synthesizes fatty acids for cell membrane similar to the E. c ...
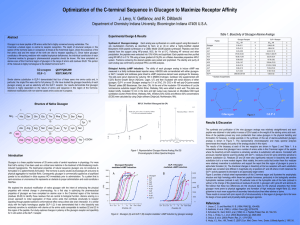
Levy APS - Indiana University Bloomington
... structure and high homology within these two peptide hormones, particularly in the biologically sensitive hydrophobic residues (colored in red). Of particular note on the hydrophilic side of this helix (colored in yellow) is the change of the glutamines at residues 20 and 24 in glucagon with lysine- ...
... structure and high homology within these two peptide hormones, particularly in the biologically sensitive hydrophobic residues (colored in red). Of particular note on the hydrophilic side of this helix (colored in yellow) is the change of the glutamines at residues 20 and 24 in glucagon with lysine- ...
Brock_Naimi_Madina_2014
... List of Figures Figure 1: Role of Insulin in Glucose Homeostasis ............................................................... 8 Figure 2: Insulin stimulates the PI3K-Akt signaling cascade in skeletal muscle leading to increased glucose uptake....................................................... ...
... List of Figures Figure 1: Role of Insulin in Glucose Homeostasis ............................................................... 8 Figure 2: Insulin stimulates the PI3K-Akt signaling cascade in skeletal muscle leading to increased glucose uptake....................................................... ...
LIP Lactate inflection point
... over 8 to 12 weeks of training, but small changes may accrue beyond this period. ...
... over 8 to 12 weeks of training, but small changes may accrue beyond this period. ...
The Incorporation of Glycerol and Lysine into the Lipid Fraction of
... of incorporation is increased by the presence of glucose and amino acids. The presence ofamino acids increases incorporation into the fraction containing 0-amino acid esters of phosphatidylglycerol. 2. Glycerol, incorporated into washed cells by incubation with glycerol, glucose and amino acids, is ...
... of incorporation is increased by the presence of glucose and amino acids. The presence ofamino acids increases incorporation into the fraction containing 0-amino acid esters of phosphatidylglycerol. 2. Glycerol, incorporated into washed cells by incubation with glycerol, glucose and amino acids, is ...
Characterization of the Plasmodium falciparum and P. berghei
... synthesize phospholipids and the lipid moieties of GPI anchors from a precursor known as phosphatidic acid (Déchamps et al., 2010). Phosphatidic acid is produced via a two-step pathway involving a glycerol 3-phosphate acyltransferase (G3PAT) and lysophosphatidic acid acyltransferase (LPAAT), which r ...
... synthesize phospholipids and the lipid moieties of GPI anchors from a precursor known as phosphatidic acid (Déchamps et al., 2010). Phosphatidic acid is produced via a two-step pathway involving a glycerol 3-phosphate acyltransferase (G3PAT) and lysophosphatidic acid acyltransferase (LPAAT), which r ...
URIC ACID
... - Fasting (ketones inhibit renal urate excretion and there is increased purine degradation). - Exercise: Increase (lactate effect). - Pregnancy: - Levels initially fall by up to 25% in the first trimester, but then rise to values 20% higher than in the non-pregnant state. - Commonly used reference v ...
... - Fasting (ketones inhibit renal urate excretion and there is increased purine degradation). - Exercise: Increase (lactate effect). - Pregnancy: - Levels initially fall by up to 25% in the first trimester, but then rise to values 20% higher than in the non-pregnant state. - Commonly used reference v ...
Acetate formation in the photoheterotrophic bacterium Chloroflexus
... C. aurantiacus converted glucose to acetate as the major fermentation product. Up to 1.5 mol acetate per mol glucose were formed. The formation of acetate by C. aurantiacus in glucose-containing media has been reported earlier (Krasil’nikova & Kondrat’eva, 1987); however, acetate/glucose stoichiomet ...
... C. aurantiacus converted glucose to acetate as the major fermentation product. Up to 1.5 mol acetate per mol glucose were formed. The formation of acetate by C. aurantiacus in glucose-containing media has been reported earlier (Krasil’nikova & Kondrat’eva, 1987); however, acetate/glucose stoichiomet ...
Dr. V. Main Powerpoint
... • The electron transport chain is in the cristae of the mitochondrion • Most of the chain’s components are proteins, which exist in multiprotein complexes • The carriers alternate reduced and oxidized states as they accept and donate electrons • Electrons drop in free energy as they go down the chai ...
... • The electron transport chain is in the cristae of the mitochondrion • Most of the chain’s components are proteins, which exist in multiprotein complexes • The carriers alternate reduced and oxidized states as they accept and donate electrons • Electrons drop in free energy as they go down the chai ...
Heterotrophic cultures
... organic carbon, such as acetate and glucose, are added continuously in small quantities. This is done to support higher microalgal biomass and simultaneously prevent excessive bacterial growth, which would be the outcome if the organic substrates were added in large quantity. Adding organic carbon s ...
... organic carbon, such as acetate and glucose, are added continuously in small quantities. This is done to support higher microalgal biomass and simultaneously prevent excessive bacterial growth, which would be the outcome if the organic substrates were added in large quantity. Adding organic carbon s ...
Chapter 1 – Title of Chapter
... a. Inositol is made from glucose and is part of the cell membrane structure. b. Carnitine is made from lysine and transports long-chain fatty acids to be oxidized. 3. Non-vitamins are substances needed by other forms of life but not human beings. They can be potentially dangerous when used by humans ...
... a. Inositol is made from glucose and is part of the cell membrane structure. b. Carnitine is made from lysine and transports long-chain fatty acids to be oxidized. 3. Non-vitamins are substances needed by other forms of life but not human beings. They can be potentially dangerous when used by humans ...
Adjeitey_Cyril _Nii-Klu_2013_ thesis
... expenditure (EE) (223, 232). Over time this prolonged state of energy imbalance leads to the storage of excess calories as adipose tissue triglycerides. The excessive accumulation of adipose tissue as well as accumulation of intramyocellular and intrahepatic lipids is associated with several comorbi ...
... expenditure (EE) (223, 232). Over time this prolonged state of energy imbalance leads to the storage of excess calories as adipose tissue triglycerides. The excessive accumulation of adipose tissue as well as accumulation of intramyocellular and intrahepatic lipids is associated with several comorbi ...
Dr: Mohamed I Kotb El
... serum urea give useful clinical information in particular circumstance. 4. Pathophysiology of Urea: After considering the effects of high protein diet, administration of cortisol-like steroids and stressful situations, increased BUN is seen in the prerenal, renal, and post-renal ...
... serum urea give useful clinical information in particular circumstance. 4. Pathophysiology of Urea: After considering the effects of high protein diet, administration of cortisol-like steroids and stressful situations, increased BUN is seen in the prerenal, renal, and post-renal ...
Cellular Respiration
... - By what process does each stage occur? - What are the total results for Aerobic Respiration? ...
... - By what process does each stage occur? - What are the total results for Aerobic Respiration? ...
Connection of Propionyl-CoA Metabolism to Polyketide
... Manuscript received February 16, 2004 Accepted for publication April 25, 2004 ABSTRACT Propionyl-CoA is an intermediate metabolite produced through a variety of pathways including thioesterification of propionate and catabolism of odd chain fatty acids and select amino acids. Previously, we found th ...
... Manuscript received February 16, 2004 Accepted for publication April 25, 2004 ABSTRACT Propionyl-CoA is an intermediate metabolite produced through a variety of pathways including thioesterification of propionate and catabolism of odd chain fatty acids and select amino acids. Previously, we found th ...
BLUEPRINT OF THE CORE TOPICS IN BIOCHEMISTRY
... Digestion of carbohydrates Mechanisms of absorption of carbohydrates Utilization of carbohydrates - Glycogenesis and Glycogenolysis - Gluconeogenesis - Glycolysis - Oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA - Oxidation of acetyl CoA in the Kreb’s citric acid cycle - ATP generation by direc ...
... Digestion of carbohydrates Mechanisms of absorption of carbohydrates Utilization of carbohydrates - Glycogenesis and Glycogenolysis - Gluconeogenesis - Glycolysis - Oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA - Oxidation of acetyl CoA in the Kreb’s citric acid cycle - ATP generation by direc ...
Cellular Respiration and Fermentation
... Proteins can also be catabolized, meaning that they can be broken down and used to produce ATP. Once they are hydrolyzed to their constituent amino acids, enzyme-catalyzed reactions remove the amino (-NH2) groups. The amino groups are excreted in urine as waste, and the remaining carbon compounds ar ...
... Proteins can also be catabolized, meaning that they can be broken down and used to produce ATP. Once they are hydrolyzed to their constituent amino acids, enzyme-catalyzed reactions remove the amino (-NH2) groups. The amino groups are excreted in urine as waste, and the remaining carbon compounds ar ...
A Review of Issues of Dietary Protein Intake in Humans
... (26). Catabolism of amino acids occurs in the liver, which contains the urea cycle (26), however the rate of conversion of amino acid derived ammonia to urea is limited. Rudman et al. (27) found that the maximal rate of urea excretion (MRUE) in healthy individuals was 55 mg urea N ∙ h-1 ∙ kg-0.75, w ...
... (26). Catabolism of amino acids occurs in the liver, which contains the urea cycle (26), however the rate of conversion of amino acid derived ammonia to urea is limited. Rudman et al. (27) found that the maximal rate of urea excretion (MRUE) in healthy individuals was 55 mg urea N ∙ h-1 ∙ kg-0.75, w ...
Ketosis

Ketosis /kɨˈtoʊsɨs/ is a metabolic state where most of the body's energy supply comes from ketone bodies in the blood, in contrast to a state of glycolysis where blood glucose provides most of the energy. It is characterised by serum concentrations of ketone bodies over 0.5 millimolar, with low and stable levels of insulin and blood glucose. It is almost always generalized with hyperketonemia, that is, an elevated level of ketone bodies in the blood throughout the body. Ketone bodies are formed by ketogenesis when liver glycogen stores are depleted (or from metabolising medium-chain triglycerides). The main ketone bodies used for energy are acetoacetate and β-hydroxybutyrate, and the levels of ketone bodies are regulated mainly by insulin and glucagon. Most cells in the body can use both glucose and ketone bodies for fuel, and during ketosis, free fatty acids and glucose synthesis (gluconeogenesis) fuel the remainder.Longer-term ketosis may result from fasting or staying on a low-carbohydrate diet, and deliberately induced ketosis serves as a medical intervention for intractable epilepsy. In glycolysis, higher levels of insulin promote storage of body fat and block release of fat from adipose tissues, while in ketosis, fat reserves are readily released and consumed. For this reason, ketosis is sometimes referred to as the body's ""fat burning"" mode.