ppt
... occupy any given orbital. When two electrons occupy an orbital their spins must be paired. No two electrons in an atom can have the same set of quantum numbers. ...
... occupy any given orbital. When two electrons occupy an orbital their spins must be paired. No two electrons in an atom can have the same set of quantum numbers. ...
Chapter 9 - Fayetteville State University
... 3) Mixtures: Are composed of elements of compounds, where the elements or compounds in the mixture retain their unique properties. 4) Solutions: are homogenous mixtures of elements of compounds 5) Atoms: are the ultimate particles of elements 6) Molecules: are made of atoms and form the ultimate par ...
... 3) Mixtures: Are composed of elements of compounds, where the elements or compounds in the mixture retain their unique properties. 4) Solutions: are homogenous mixtures of elements of compounds 5) Atoms: are the ultimate particles of elements 6) Molecules: are made of atoms and form the ultimate par ...
Name - TeacherWeb
... VSEPR Theory The VSEPR theory explains the shape of molecules in three-dimensional space. The acronym VSEPR stands for valence-shell electron-pair repulsion theory. This model assumes that electron pairs repel each other as far as possible. Unshared pairs of electrons also affect the shape of the mo ...
... VSEPR Theory The VSEPR theory explains the shape of molecules in three-dimensional space. The acronym VSEPR stands for valence-shell electron-pair repulsion theory. This model assumes that electron pairs repel each other as far as possible. Unshared pairs of electrons also affect the shape of the mo ...
Review 3rd Qtr KEY
... 0.0010 has __2__ significant figures & rounded to 3 significant figures is 0.00100 or 1.00 x 10-3 3.5 x 1023 has __2___ significant figures & rounded to 4 significant figures is 3.500 x 1023 ...
... 0.0010 has __2__ significant figures & rounded to 3 significant figures is 0.00100 or 1.00 x 10-3 3.5 x 1023 has __2___ significant figures & rounded to 4 significant figures is 3.500 x 1023 ...
ATOMS
... symbol that tells how many atoms of an element there are in the compound. It means “written below”. • For example: H20 (2 is the subscript) There are 2 atoms of hydrogen (H) and 1 atom of oxygen (O). This makes up 1 molecule of water. ...
... symbol that tells how many atoms of an element there are in the compound. It means “written below”. • For example: H20 (2 is the subscript) There are 2 atoms of hydrogen (H) and 1 atom of oxygen (O). This makes up 1 molecule of water. ...
Honors Chemistry Midterm Review 2008
... b. Volume Space taken up; graduated cylinder (ml); LxWxH (cm3) c. Density Ratio of Mass to volume; Mass/Volume g/ml or g/cm3 d. Time seconds stopwatch e. Temperature Average Kinetic Energy of molecules; thermometer °C or K thermometer. Absolute zero is 0K or -273°C K= °C + 273 f. Heat Form of Energy ...
... b. Volume Space taken up; graduated cylinder (ml); LxWxH (cm3) c. Density Ratio of Mass to volume; Mass/Volume g/ml or g/cm3 d. Time seconds stopwatch e. Temperature Average Kinetic Energy of molecules; thermometer °C or K thermometer. Absolute zero is 0K or -273°C K= °C + 273 f. Heat Form of Energy ...
Energy levels of various orbitals MEMORIZE ! 1s < 2s < 2p < 3s < 3p
... Energy levels of various orbitals For hydrogen, energy level depend only on n For multielectron atoms (all others) - energy levels depend on both n and l A diagram which shows the orbital energy levels for both is shown below. ...
... Energy levels of various orbitals For hydrogen, energy level depend only on n For multielectron atoms (all others) - energy levels depend on both n and l A diagram which shows the orbital energy levels for both is shown below. ...
Semester Exam Practice Questions
... The modern periodic law states that the properties of the elements are a periodic function of their __________. a. atomic radius c. atomic mass b. atomic number d. atomic charge In the modern periodic table, the elements within a column have __________. a. similar electron configurations c. the same ...
... The modern periodic law states that the properties of the elements are a periodic function of their __________. a. atomic radius c. atomic mass b. atomic number d. atomic charge In the modern periodic table, the elements within a column have __________. a. similar electron configurations c. the same ...
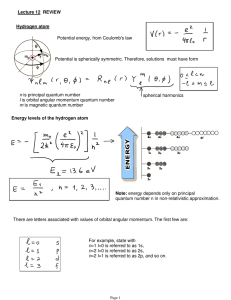
Lecture 12: Review.
... Hund's first rule: for every atomic ground state, the total electron spin has maximum value tolerated by the Pauli principle. Hund's second rule: for a given spin, the term with the largest value of the total orbital angular momentum quantum number L, consistent with overall antisymmetrization, has ...
... Hund's first rule: for every atomic ground state, the total electron spin has maximum value tolerated by the Pauli principle. Hund's second rule: for a given spin, the term with the largest value of the total orbital angular momentum quantum number L, consistent with overall antisymmetrization, has ...
Chapter 7 Many-Electron Atoms
... ("extra" and "missing" splittings of spectral lines in the presence of magnetic fields). Electron spin is also important in magnetism. Spectral lines are due to photons emitted when electrons change their energy state. Changes in the principal quantum number n cause the most noticeable changes. Howe ...
... ("extra" and "missing" splittings of spectral lines in the presence of magnetic fields). Electron spin is also important in magnetism. Spectral lines are due to photons emitted when electrons change their energy state. Changes in the principal quantum number n cause the most noticeable changes. Howe ...
Advanced electronic bonding and how these affect molecular shapes
... levels around the atom. • These energy levels are called shells. • Electrons jump to higher energy levels when provided with energy, but will automatically drop back down to the lowest energy level possible. • These energy levels are named 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 and so on. (So far the heaviest eleme ...
... levels around the atom. • These energy levels are called shells. • Electrons jump to higher energy levels when provided with energy, but will automatically drop back down to the lowest energy level possible. • These energy levels are named 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 and so on. (So far the heaviest eleme ...
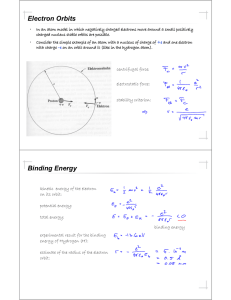
Electron Orbits
... Comment of Franck on their Experiment "It might interest you to know that when we made the experiments that we did not know Bohr's theory. We had neither read nor heard about it. We had not read it because we were negligent to read the literature well enough -- and you know how that happens. On the ...
... Comment of Franck on their Experiment "It might interest you to know that when we made the experiments that we did not know Bohr's theory. We had neither read nor heard about it. We had not read it because we were negligent to read the literature well enough -- and you know how that happens. On the ...
Quantum Theory of Atoms and Molecules
... simple harmonic oscillator and rigid rotor. Heat capacities. Comparison with classical behaviour. Deficiencies of simple models. Particle tunnelling, zero point energy. Introduction to rotational and vibrational spectroscopies. ...
... simple harmonic oscillator and rigid rotor. Heat capacities. Comparison with classical behaviour. Deficiencies of simple models. Particle tunnelling, zero point energy. Introduction to rotational and vibrational spectroscopies. ...
Exam 3 Review - Iowa State University
... d. Atomic radius, K or Cs e. Atomic radius, Se or Br 12. List three properties that distinguish nonmetals from metals. 13. Which of the following are solids at room temperature, and which are gases? a. CO2 b. BaO c. CuO d. F2 e. NO 14. Which substances are ionic and which are covalent? a. Br2 b. KO2 ...
... d. Atomic radius, K or Cs e. Atomic radius, Se or Br 12. List three properties that distinguish nonmetals from metals. 13. Which of the following are solids at room temperature, and which are gases? a. CO2 b. BaO c. CuO d. F2 e. NO 14. Which substances are ionic and which are covalent? a. Br2 b. KO2 ...
chemistry i
... decreases. The equation E = hν means that as frequency increases, energy increases. Using this information and the reference tables, which color of visible light has the least energy? A. Red b. Yellow c. Green d. Violet 38. If an electron drops from n=6 to n=2, what type of electromagnetic radiation ...
... decreases. The equation E = hν means that as frequency increases, energy increases. Using this information and the reference tables, which color of visible light has the least energy? A. Red b. Yellow c. Green d. Violet 38. If an electron drops from n=6 to n=2, what type of electromagnetic radiation ...
SEMESTER 1 EXAM Prblms/Short Ans
... appropriate units with each number used in all calculations. SF; Use the correct significant figures when expressing all answers. Use Scientific Notation for all numbers with values more than 3 decimal places from the decimal point. ANSWER AT LEAST 10 QUESTIONS! ...
... appropriate units with each number used in all calculations. SF; Use the correct significant figures when expressing all answers. Use Scientific Notation for all numbers with values more than 3 decimal places from the decimal point. ANSWER AT LEAST 10 QUESTIONS! ...
Electron-Config
... In Schrodinger’s model, there are four “quantum” numbers that tell us where an electron is likely to be located. Principal (n), 1-7, gives the energy level Subshell (l), s-p-d-f, gives the shape of region Orbital (m), gives the orientation in space of the shapes Spin (s), clockwise or coun ...
... In Schrodinger’s model, there are four “quantum” numbers that tell us where an electron is likely to be located. Principal (n), 1-7, gives the energy level Subshell (l), s-p-d-f, gives the shape of region Orbital (m), gives the orientation in space of the shapes Spin (s), clockwise or coun ...
Transcript - the Cassiopeia Project
... solving the Ultraviolet Catastrophe, Bohr said that inside the hydrogen atom, the electron was allowed to have only discrete values of angular momentum in its orbits around the nucleus. Translated, this means the electron can occupy orbits only at a certain distances from the nucleus. And Bohr simpl ...
... solving the Ultraviolet Catastrophe, Bohr said that inside the hydrogen atom, the electron was allowed to have only discrete values of angular momentum in its orbits around the nucleus. Translated, this means the electron can occupy orbits only at a certain distances from the nucleus. And Bohr simpl ...
Electron configuration
In atomic physics and quantum chemistry, the electron configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule (or other physical structure) in atomic or molecular orbitals. For example, the electron configuration of the neon atom is 1s2 2s2 2p6.Electronic configurations describe electrons as each moving independently in an orbital, in an average field created by all other orbitals. Mathematically, configurations are described by Slater determinants or configuration state functions.According to the laws of quantum mechanics, for systems with only one electron, an energy is associated with each electron configuration and, upon certain conditions, electrons are able to move from one configuration to another by the emission or absorption of a quantum of energy, in the form of a photon.Knowledge of the electron configuration of different atoms is useful in understanding the structure of the periodic table of elements. The concept is also useful for describing the chemical bonds that hold atoms together. In bulk materials, this same idea helps explain the peculiar properties of lasers and semiconductors.