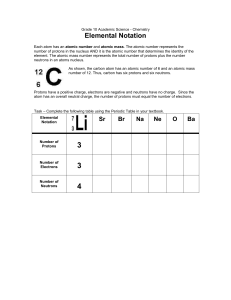
Chapter 7:The Quantum-Mechanical Model of
... Quantized energy can explain the emission of light from hot bodies, the emission of electrons from metal surfaces on which light shines (the photoelectric effect). Photoelectric Effect: Many metals emit electrons when light (photons) shines on their surface. It was observed that a minimum frequency ...
... Quantized energy can explain the emission of light from hot bodies, the emission of electrons from metal surfaces on which light shines (the photoelectric effect). Photoelectric Effect: Many metals emit electrons when light (photons) shines on their surface. It was observed that a minimum frequency ...
Chapter 1: The Basics - Bonding and Molecular Structure and
... in fully condensed formulas all of the atoms that are attached to the carbon are written immediately after the carbon, listing hydrogens rst - A bond-line formula have no carbons or hydrogens written (on occasion hydrogens may be added to indicate the geometry). Lines represent bonds, and carbon at ...
... in fully condensed formulas all of the atoms that are attached to the carbon are written immediately after the carbon, listing hydrogens rst - A bond-line formula have no carbons or hydrogens written (on occasion hydrogens may be added to indicate the geometry). Lines represent bonds, and carbon at ...
Set 9 - STEMwomen.org
... (a) Determine the values of the quantum numbers n, l, m for Ψ by inspection. Give the reason for your answers. n= l= m= (b) Determine the most probable value of r for an electron in the state specified by the Ψ(r,θ,φ) given above, when Z = 1. (c) Generate from Ψ(r,θ,φ) given above, another eigenfunc ...
... (a) Determine the values of the quantum numbers n, l, m for Ψ by inspection. Give the reason for your answers. n= l= m= (b) Determine the most probable value of r for an electron in the state specified by the Ψ(r,θ,φ) given above, when Z = 1. (c) Generate from Ψ(r,θ,φ) given above, another eigenfunc ...
Bohr vs. Correct Model of Atom
... Electrons do not circle the nucleus in little planetlike orbits. The assumptions injected into the Bohr model have no basis in physical reality. BUT the model does get some of the numbers right for SIMPLE atoms… ...
... Electrons do not circle the nucleus in little planetlike orbits. The assumptions injected into the Bohr model have no basis in physical reality. BUT the model does get some of the numbers right for SIMPLE atoms… ...
Unit 1B1 - Uddingston Grammar School
... Atoms P and Q have the same number of protons Atoms Q and R have the same number of electrons Atoms P and S have the same number of neutrons Atoms R and S are isotopes of each other Atoms S and T have different chemical properties. ...
... Atoms P and Q have the same number of protons Atoms Q and R have the same number of electrons Atoms P and S have the same number of neutrons Atoms R and S are isotopes of each other Atoms S and T have different chemical properties. ...
Chem Review
... a. Ionic b. Covalent c. Both Ionic and Covalent d. Neither Ionic or Covalent 30. Choose an orbital that is not the s orbital and state what the letter stands for. 31. Draw the 3 P orbitals and label their axis. The three p orbitals are the Px, Py and Pz. 32. Write out the electron configuration for ...
... a. Ionic b. Covalent c. Both Ionic and Covalent d. Neither Ionic or Covalent 30. Choose an orbital that is not the s orbital and state what the letter stands for. 31. Draw the 3 P orbitals and label their axis. The three p orbitals are the Px, Py and Pz. 32. Write out the electron configuration for ...
Advanced Chemical Physics
... different (HCl for example) the MO method can be applied but than because of the difference in energies between the coupled AOs, the parameter b will usually be very small and therefore the mixing between the AOs will be small. The measure for the energy is the ionization potential from each AO. For ...
... different (HCl for example) the MO method can be applied but than because of the difference in energies between the coupled AOs, the parameter b will usually be very small and therefore the mixing between the AOs will be small. The measure for the energy is the ionization potential from each AO. For ...
Shell model I - Evidence
... does not get it quite right. There are ripples and bumps which occur at the ...
... does not get it quite right. There are ripples and bumps which occur at the ...
Unit 2
... A. 17 protons, 17 electrons, and 18 neutrons. B. 17 protons, 17 electrons, and 52 neutrons. C. 35 protons, 35 electrons, and 17 neutrons. D. 18 protons, 18 electrons, and 17 neutrons. 26. The nucleus of an atom has all of the following characteristics EXCEPT that it _____ A. contains nearly all of t ...
... A. 17 protons, 17 electrons, and 18 neutrons. B. 17 protons, 17 electrons, and 52 neutrons. C. 35 protons, 35 electrons, and 17 neutrons. D. 18 protons, 18 electrons, and 17 neutrons. 26. The nucleus of an atom has all of the following characteristics EXCEPT that it _____ A. contains nearly all of t ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Duality of Matter
... the spaces between atoms in a crystal. An interference pattern is clearly ...
... the spaces between atoms in a crystal. An interference pattern is clearly ...
Honors Unit 5 Practice Test
... ____ 65. The strength of London dispersion forces between molecules depends on a. only the number of electrons in the molecule. b. only the number of protons in the molecule. c. both the number of electrons in the molecule and the mass of the molecule. d. both the number of electrons and the number ...
... ____ 65. The strength of London dispersion forces between molecules depends on a. only the number of electrons in the molecule. b. only the number of protons in the molecule. c. both the number of electrons in the molecule and the mass of the molecule. d. both the number of electrons and the number ...
Electrons in Atoms
... pathway for electrons. • The quantum mechanical model is concerned with the probability of finding an electron. • At this point, electrons can be explained in terms of waves, particles and beyond. ...
... pathway for electrons. • The quantum mechanical model is concerned with the probability of finding an electron. • At this point, electrons can be explained in terms of waves, particles and beyond. ...
The Periodic Table HL Page 1 of 3 G. Galvin Name: Periodic Table
... neutrons in the nucleus of an atom of that element. No. of neutrons in an atom = Mass Number (A) – Atomic Number (Z) Defn: Isotopes are atoms of the same element (i.e. they have the same atomic number) which have different mass numbers due to the different number of neutrons in the nucleus. Defn: R ...
... neutrons in the nucleus of an atom of that element. No. of neutrons in an atom = Mass Number (A) – Atomic Number (Z) Defn: Isotopes are atoms of the same element (i.e. they have the same atomic number) which have different mass numbers due to the different number of neutrons in the nucleus. Defn: R ...
Ch. 1: Atoms: The Quantum World
... 1.Principal (n = 1, 2, 3, . . .) - related to size and energy of the orbital. 2.Angular Momentum (ℓ = 0 to n 1) - relates to shape of the orbital. 3.Magnetic (mℓ = ℓ to ℓ) - relates to orientation of the orbital in space relative to other orbitals. 4.Electron Spin (ms = +1/2, 1/2) - relates to t ...
... 1.Principal (n = 1, 2, 3, . . .) - related to size and energy of the orbital. 2.Angular Momentum (ℓ = 0 to n 1) - relates to shape of the orbital. 3.Magnetic (mℓ = ℓ to ℓ) - relates to orientation of the orbital in space relative to other orbitals. 4.Electron Spin (ms = +1/2, 1/2) - relates to t ...
Fall Semester Review Packet
... 8. Describe J.J. Thomson’s and Ernest Rutherford’s contributions to the development of the atom, including the experiments they performed. 9. Describe how the current periodic table is arranged by comparing groups, periods and properties of the elements. 10. Explain the difference between a molecule ...
... 8. Describe J.J. Thomson’s and Ernest Rutherford’s contributions to the development of the atom, including the experiments they performed. 9. Describe how the current periodic table is arranged by comparing groups, periods and properties of the elements. 10. Explain the difference between a molecule ...
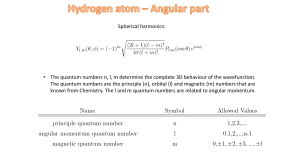
Spherical harmonics: • The quantum numbers n, l, m determine the
... The quantum numbers are the principle (n), orbital (l) and magnetic (m) numbers that are known from Chemistry. The l and m quantum numbers are related to angular momentum. ...
... The quantum numbers are the principle (n), orbital (l) and magnetic (m) numbers that are known from Chemistry. The l and m quantum numbers are related to angular momentum. ...
Adobe Acrobat file () - Wayne State University Physics and
... All states with the same principle quantum number are said to form a shell The states with given values of n and ℓ are said to form a subshell ...
... All states with the same principle quantum number are said to form a shell The states with given values of n and ℓ are said to form a subshell ...
Chapter 9: Electrons in Atoms
... Electromagnetic radiation is a form of energy transition in which electric and magnetic fields are propagated as waves through empty space (a vacuum) or through a medium such as glass. An electric field is the region around as electrically charged particle. A magnetic field is found in the region su ...
... Electromagnetic radiation is a form of energy transition in which electric and magnetic fields are propagated as waves through empty space (a vacuum) or through a medium such as glass. An electric field is the region around as electrically charged particle. A magnetic field is found in the region su ...
Electron configuration
In atomic physics and quantum chemistry, the electron configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule (or other physical structure) in atomic or molecular orbitals. For example, the electron configuration of the neon atom is 1s2 2s2 2p6.Electronic configurations describe electrons as each moving independently in an orbital, in an average field created by all other orbitals. Mathematically, configurations are described by Slater determinants or configuration state functions.According to the laws of quantum mechanics, for systems with only one electron, an energy is associated with each electron configuration and, upon certain conditions, electrons are able to move from one configuration to another by the emission or absorption of a quantum of energy, in the form of a photon.Knowledge of the electron configuration of different atoms is useful in understanding the structure of the periodic table of elements. The concept is also useful for describing the chemical bonds that hold atoms together. In bulk materials, this same idea helps explain the peculiar properties of lasers and semiconductors.