Chapter 13 - Angelfire
... 18. According to Darwin, any inherited characteristic that increases an organism’s fitness for survival is a(n) adaptation 19. Scientists who specialize in study of rocks and changes in the earth are called geologists 20. Scientists would be very surprised if they found a complete Skeleton 21. Scien ...
... 18. According to Darwin, any inherited characteristic that increases an organism’s fitness for survival is a(n) adaptation 19. Scientists who specialize in study of rocks and changes in the earth are called geologists 20. Scientists would be very surprised if they found a complete Skeleton 21. Scien ...
Raven (7th) Guided Notes Chapter 4
... 4. How does our present atmosphere differ? ________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ 5. Outline some valid arguments countering the reducing atmosphere hypothesis. _____________________________________________________________ ...
... 4. How does our present atmosphere differ? ________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ 5. Outline some valid arguments countering the reducing atmosphere hypothesis. _____________________________________________________________ ...
CH 32 Foldable Mammals Internal content
... mammal has to eat 10 times as much food as a reptile of the same size to maintain homeostasis. All mammals, even those living in water, use lungs to breath. The mammalian circulatory system is divided into two completely separate loops with a 4-chambered heart. One loop from the lungs…the other from ...
... mammal has to eat 10 times as much food as a reptile of the same size to maintain homeostasis. All mammals, even those living in water, use lungs to breath. The mammalian circulatory system is divided into two completely separate loops with a 4-chambered heart. One loop from the lungs…the other from ...
homologous structures
... Because bats and whales are mammals! Bat In one of the most extensive studies comparing human and chimp DNA, the researchers compared 19.8 million bases. While this sounds like a lot, it still represents slightly less than 1% of the genome. They calculated a mean similarity of 98.77% or 1.23% differ ...
... Because bats and whales are mammals! Bat In one of the most extensive studies comparing human and chimp DNA, the researchers compared 19.8 million bases. While this sounds like a lot, it still represents slightly less than 1% of the genome. They calculated a mean similarity of 98.77% or 1.23% differ ...
Chapter 18: The Chordates
... The origin of jaws opened up new feeding opportunities. The evolution of lungs, or lung-like structures gave the possibility of life on land. Tetrapods (Greek for four feet) – jawed vertebrates with two pairs of limbs were the first vertebrates on land, and could support their weight on land. Th ...
... The origin of jaws opened up new feeding opportunities. The evolution of lungs, or lung-like structures gave the possibility of life on land. Tetrapods (Greek for four feet) – jawed vertebrates with two pairs of limbs were the first vertebrates on land, and could support their weight on land. Th ...
Human Biotechnology
... The Human Organism • human consists of cells, tissue, organs, organ systems • humans are primates (180 species of animals are primates), but still quite different • organ systems do a lot of work (e.g. the heart - at age of 70 it has ...
... The Human Organism • human consists of cells, tissue, organs, organ systems • humans are primates (180 species of animals are primates), but still quite different • organ systems do a lot of work (e.g. the heart - at age of 70 it has ...
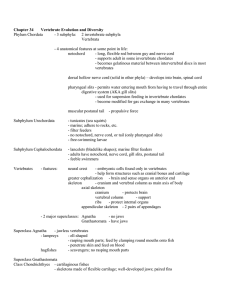
Chapter 34 Vertebrate Evolution and Diversity Phylum Chordata
... - many metamorphosize - larval stage called tadpole (gills, lateral line, etc.) ...
... - many metamorphosize - larval stage called tadpole (gills, lateral line, etc.) ...
What is Biology? - Winona State University
... Is it right to protect an endangered species at the expense of jobs? Is it ethical to use fetal tissue in biomedical research? Are there dangers in cloning humans? Are irradiated foods safe to eat? ...
... Is it right to protect an endangered species at the expense of jobs? Is it ethical to use fetal tissue in biomedical research? Are there dangers in cloning humans? Are irradiated foods safe to eat? ...
Animal Taxonomy
... The nerve cord develops into the central nervous system: the brain and the spinal cord Pharyngeal Slits or Clefts In most chordates, grooves in the pharynx called pharyngeal clefts develop into slits that open to the outside of the body Functions of pharyngeal slits: Suspension-feeding structure ...
... The nerve cord develops into the central nervous system: the brain and the spinal cord Pharyngeal Slits or Clefts In most chordates, grooves in the pharynx called pharyngeal clefts develop into slits that open to the outside of the body Functions of pharyngeal slits: Suspension-feeding structure ...
Anthropology Common Assessment
... This final assessment is designed to have students reflect back on the semester and give us insight on what they have taken from this course. This assessment will be a group presentation lasting between 4-6 minutes that focuses on one of the three essential questions of anthropology: who are we as h ...
... This final assessment is designed to have students reflect back on the semester and give us insight on what they have taken from this course. This assessment will be a group presentation lasting between 4-6 minutes that focuses on one of the three essential questions of anthropology: who are we as h ...
Chapter 9: Introduction to Genetics
... The group of annelids that protect themselves by tufts of poisonous bristles that break off and penetrate the skin of the attacker include the _____. In mollusks, ammonia is removed from the blood and released from the body through ______. In the South Pacific, many annelids that swarm at the surfac ...
... The group of annelids that protect themselves by tufts of poisonous bristles that break off and penetrate the skin of the attacker include the _____. In mollusks, ammonia is removed from the blood and released from the body through ______. In the South Pacific, many annelids that swarm at the surfac ...
Animals
... creatures on the lineage after this spilt are called “hominids”. After that time there have been a number of species of hominid, mostly living in Africa. ...
... creatures on the lineage after this spilt are called “hominids”. After that time there have been a number of species of hominid, mostly living in Africa. ...
Animals - NIU Department of Biological Sciences
... creatures on the lineage after this spilt are called “hominids”. After that time there have been a number of species of hominid, mostly living in Africa. ...
... creatures on the lineage after this spilt are called “hominids”. After that time there have been a number of species of hominid, mostly living in Africa. ...
Unit 4 Part 2 Outline Animal Diversity
... The evolutionary trend among primates is toward a larger and more complex brain. 31.4 Human Evolution All primates share one common ancestor and the other types of primates diverged from the human line of descent over time. Humans are most closely related to African apes. Evolution of Humanlike Homi ...
... The evolutionary trend among primates is toward a larger and more complex brain. 31.4 Human Evolution All primates share one common ancestor and the other types of primates diverged from the human line of descent over time. Humans are most closely related to African apes. Evolution of Humanlike Homi ...
Characteristics of Miss Ruthenberg
... • Humans eat things by using their mouths. Food is first chewed in the mouth and then it goes down the osephagus into the stomach. From there food is ground up further and is then digested in the small intestine. • Humans should have a balanced diet including lots of fresh fruit and vegetables, cere ...
... • Humans eat things by using their mouths. Food is first chewed in the mouth and then it goes down the osephagus into the stomach. From there food is ground up further and is then digested in the small intestine. • Humans should have a balanced diet including lots of fresh fruit and vegetables, cere ...
The purpose of this course in ANT-121 is to introduce the college
... content of modern biological anthropology. Attention is given to recent facts, as well as new concepts, methods, research areas, and hypotheses. This discipline offers a comprehensive, scientific, and rational understanding of and appreciation for the place of humankind within natural history. The f ...
... content of modern biological anthropology. Attention is given to recent facts, as well as new concepts, methods, research areas, and hypotheses. This discipline offers a comprehensive, scientific, and rational understanding of and appreciation for the place of humankind within natural history. The f ...
Lucy - Wesley Grove Chapel
... primates….Primates most likely evolved from small, insect-eating rodentlike mammals that lived about 60 million years ago.” ...
... primates….Primates most likely evolved from small, insect-eating rodentlike mammals that lived about 60 million years ago.” ...
“Why Do”
... of the body. Carbon dioxide passes from the blood through the thin gill tissue into the water. Gills or gill-like organs, located in different parts of the body, are found in various groups of aquatic animals, including mollusks, crustaceans, insects, fish, and amphibians. ...
... of the body. Carbon dioxide passes from the blood through the thin gill tissue into the water. Gills or gill-like organs, located in different parts of the body, are found in various groups of aquatic animals, including mollusks, crustaceans, insects, fish, and amphibians. ...
Invertebrates
... •Eating vegetables that are not washed Hookworms •Soil •Walking barefoot •anemia, malnutrition, and in children causes under-development ...
... •Eating vegetables that are not washed Hookworms •Soil •Walking barefoot •anemia, malnutrition, and in children causes under-development ...
8- Phylum Echinodermata
... Habitat: Place where an animal naturally lives. Aquatic: in water, marine or fresh water. Terrestrial: on land. Amphibious: both terrestrial and aquatic. Feeding Habits: Carnivores : feed on animals. Herbivores: feed on plants. Omnivores: feed on both plants and animals. Filter Feeders: Filter food ...
... Habitat: Place where an animal naturally lives. Aquatic: in water, marine or fresh water. Terrestrial: on land. Amphibious: both terrestrial and aquatic. Feeding Habits: Carnivores : feed on animals. Herbivores: feed on plants. Omnivores: feed on both plants and animals. Filter Feeders: Filter food ...
ECOLOGY SPRING 2009 - Florida International University
... The taxonomic group “apes” is paraphyletic Some apes are more closely related to hominids than to other apes. Living apes consist of gibbons, orangutans, gorillas and chimpanzees Hominids consist of humans and their direct ancestors Common ancestor was more like a chimpanzee than a gorilla ...
... The taxonomic group “apes” is paraphyletic Some apes are more closely related to hominids than to other apes. Living apes consist of gibbons, orangutans, gorillas and chimpanzees Hominids consist of humans and their direct ancestors Common ancestor was more like a chimpanzee than a gorilla ...
Amphibians - WordPress.com
... amphibians evolved from the lobe-finned fish 400 million years ago. The lobe-finned fish had strong fins the eventually turned into legs. Their skull is very similar to the earliest amphibians. ...
... amphibians evolved from the lobe-finned fish 400 million years ago. The lobe-finned fish had strong fins the eventually turned into legs. Their skull is very similar to the earliest amphibians. ...