Chapter 5
... Orbitals can hold only 2 electrons Each electron in the orbital has an opposite spin ...
... Orbitals can hold only 2 electrons Each electron in the orbital has an opposite spin ...
The Mystery of Matter: The Course
... The mass of a body or particle at rest contains energy E = mc2 This “rest mass” increases with v as the particle speeds up to the speed of light. ...
... The mass of a body or particle at rest contains energy E = mc2 This “rest mass” increases with v as the particle speeds up to the speed of light. ...
Set 9 - STEMwomen.org
... (d) Calculate the average z component of the electron’s orbital angular momentum for this ground state. (e) Does Lz commute with the hamiltonian for a hydrogen-like atom ? Show whether the z component of the electron’s orbital angular momentum in this hydrogen-like atom is a constant of the motion. ...
... (d) Calculate the average z component of the electron’s orbital angular momentum for this ground state. (e) Does Lz commute with the hamiltonian for a hydrogen-like atom ? Show whether the z component of the electron’s orbital angular momentum in this hydrogen-like atom is a constant of the motion. ...
Spin-Separation in Cyclotron Motion.
... magnetic field. Rokhinson et al. have been able to achieve such separation, in a hole-doped GaAs structure, by using the technique of magnetic focusing. The experiment exploits the fact that for holes traveling in a given direction, particles at the Fermi energy have different momenta, associated wi ...
... magnetic field. Rokhinson et al. have been able to achieve such separation, in a hole-doped GaAs structure, by using the technique of magnetic focusing. The experiment exploits the fact that for holes traveling in a given direction, particles at the Fermi energy have different momenta, associated wi ...
Solid State Physics
... along the plane containing the atoms, the bond is known as sigma () bond. Sigma bonds are strong and the electron sharing is maximum. Methane CH4 is a good example for sigma bond and it has four of them. ...
... along the plane containing the atoms, the bond is known as sigma () bond. Sigma bonds are strong and the electron sharing is maximum. Methane CH4 is a good example for sigma bond and it has four of them. ...
Atom 2 - UF Physics
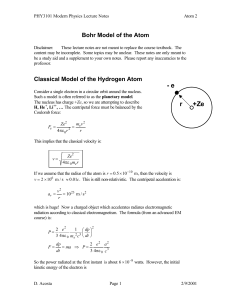
... Thus, new laws of physics must be derived for atomic physics. The Bohr Model of the atom is the first step towards the new Quantum Mechanics ...
... Thus, new laws of physics must be derived for atomic physics. The Bohr Model of the atom is the first step towards the new Quantum Mechanics ...
• Quantum physics explains the energy levels of atoms with
... These can be measured without uncertainty. • The quantum number n labels the energy level En . • The lowest energy level with n = 1 is sharp (E= 0), because an atom is stable. One can take an infinite time (t = ) to determine its energy and thereby satisfy the uncertainty relation Et ≥ h/4 . ...
... These can be measured without uncertainty. • The quantum number n labels the energy level En . • The lowest energy level with n = 1 is sharp (E= 0), because an atom is stable. One can take an infinite time (t = ) to determine its energy and thereby satisfy the uncertainty relation Et ≥ h/4 . ...
Document
... These can be measured without uncertainty. • The quantum number n labels the energy level En . • The lowest energy level with n = 1 is sharp (E= 0), because an atom is stable. One can take an infinite time (t = ) to determine its energy and thereby satisfy the uncertainty relation Et ≥ h/4 . ...
... These can be measured without uncertainty. • The quantum number n labels the energy level En . • The lowest energy level with n = 1 is sharp (E= 0), because an atom is stable. One can take an infinite time (t = ) to determine its energy and thereby satisfy the uncertainty relation Et ≥ h/4 . ...
The_Bevatron - Indico
... • In 1928, Dirac formulated a theory describing the behavior of relativistic electrons in electric and magnetic fields. – Dirac’s equation has negative energy solutions, implying the existence of antimatter. ...
... • In 1928, Dirac formulated a theory describing the behavior of relativistic electrons in electric and magnetic fields. – Dirac’s equation has negative energy solutions, implying the existence of antimatter. ...
G0MDK - FRARS
... • The proton is found in the nucleus of all atoms • The electron is found rotating about the nucleus of all atoms • Proton charge is Pos. 1.6 × 10-19 Coulombs ...
... • The proton is found in the nucleus of all atoms • The electron is found rotating about the nucleus of all atoms • Proton charge is Pos. 1.6 × 10-19 Coulombs ...
Information
... element (chemical element) – a species of atoms; all atoms with the same number of protons in the atomic nucleus. A pure chemical substance composed of atoms with the same number of protons in the atomic nucleus [703]. fission – the spontaneous (or induced by particle collision) splitting of a heavy ...
... element (chemical element) – a species of atoms; all atoms with the same number of protons in the atomic nucleus. A pure chemical substance composed of atoms with the same number of protons in the atomic nucleus [703]. fission – the spontaneous (or induced by particle collision) splitting of a heavy ...
Chemistry CPA Activity Sheet Week of November 18, 2013 Unit
... Discuss the significance of the photoelectric effect and the line-emission spectrum of hydrogen to the development of the atomic model. Discuss Louis de Broglie’s role in the development of the quantum model of the atom. Explain how the Heisenberg uncertainty principle and the Schrödinger wave equat ...
... Discuss the significance of the photoelectric effect and the line-emission spectrum of hydrogen to the development of the atomic model. Discuss Louis de Broglie’s role in the development of the quantum model of the atom. Explain how the Heisenberg uncertainty principle and the Schrödinger wave equat ...
Chapter 2 Reading Guide
... Make an electron distribution diagram of water. Which element is most electronegative? Why is water considered a polar molecule? Label the regions that are more positive or more negative. (This is a very important concept. Spend some time with this one!) ...
... Make an electron distribution diagram of water. Which element is most electronegative? Why is water considered a polar molecule? Label the regions that are more positive or more negative. (This is a very important concept. Spend some time with this one!) ...
POTENTIAL GRADIENT & CATHODE RAY TUBE
... However, the electrons are released in a cloud, and must be manipulated into a beam before proceeding. The accelerating and focusing anodes serve this purpose. The accelerating anode is located in the third grid; it emits a large positive electromagnetic field which draws and accelerates the elec ...
... However, the electrons are released in a cloud, and must be manipulated into a beam before proceeding. The accelerating and focusing anodes serve this purpose. The accelerating anode is located in the third grid; it emits a large positive electromagnetic field which draws and accelerates the elec ...
ap chemistry review – multiple choice
... (a) Heisenbery uncertainty principle (b) Pauli exclusion principle (c) Hund’s rule (principle of maximum multiplicity) (d) Shielding effect (e) Wave nature of matter 15. Can be used to predict that a gaseous carbon atom in it ground state is paramagnetic 16. Explains the experimental phenomenon of e ...
... (a) Heisenbery uncertainty principle (b) Pauli exclusion principle (c) Hund’s rule (principle of maximum multiplicity) (d) Shielding effect (e) Wave nature of matter 15. Can be used to predict that a gaseous carbon atom in it ground state is paramagnetic 16. Explains the experimental phenomenon of e ...
Electromagnetic Preons as Particles of Everything
... Tachyons> as normal particles can move infinitely slow (not moving at all), a tachyon existing on the other side of the barrier would be able to move infinitely fast. As it slows and approaches the speed of light from the other side, its energy requirements become infinite. Strings> elementary ...
... Tachyons> as normal particles can move infinitely slow (not moving at all), a tachyon existing on the other side of the barrier would be able to move infinitely fast. As it slows and approaches the speed of light from the other side, its energy requirements become infinite. Strings> elementary ...
Electron scattering

Electron scattering occurs when electrons are deviated from their original trajectory. This is due to the electrostatic forces within matter interaction or, if an external magnetic field is present, the electron may be deflected by the Lorentz force. This scattering typically happens with solids such as metals, semiconductors and insulators; and is a limiting factor in integrated circuits and transistors.The application of electron scattering is such that it can be used as a high resolution microscope for hadronic systems, that allows the measurement of the distribution of charges for nucleons and nuclear structure. The scattering of electrons has allowed us to understand that protons and neutrons are made up of the smaller elementary subatomic particles called quarks.Electrons may be scattered through a solid in several ways:Not at all: no electron scattering occurs at all and the beam passes straight through.Single scattering: when an electron is scattered just once.Plural scattering: when electron(s) scatter several times.Multiple scattering: when electron(s) scatter very many times over.The likelihood of an electron scattering and the proliferance of the scattering is a probability function of the specimen thickness to the mean free path.