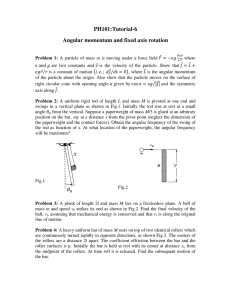
Kepler`s Laws
... Newton (1642–1727). In his treatise, Newton invented the calculus, and applied his results to solve several problems in physics. The ideas set forth by Newton in that book probably represent one of the greatest intellectual achievements of all time. Kepler’s first two laws were announced in 1609: Kep ...
... Newton (1642–1727). In his treatise, Newton invented the calculus, and applied his results to solve several problems in physics. The ideas set forth by Newton in that book probably represent one of the greatest intellectual achievements of all time. Kepler’s first two laws were announced in 1609: Kep ...
Read PDF - Physics (APS)
... In a ground-breaking work building on recent progress in invariant theory and representation theory, Klyachko exhibited an algorithm for computing all such Pauli-like constraints [4,8]. In fact, his work is part of a more general effort in quantum information theory addressing the quantum marginal p ...
... In a ground-breaking work building on recent progress in invariant theory and representation theory, Klyachko exhibited an algorithm for computing all such Pauli-like constraints [4,8]. In fact, his work is part of a more general effort in quantum information theory addressing the quantum marginal p ...
...detail
... 1. Steady Direct Current (dc): Charge-particles in motion-electric current (drift, diffusion and connection); current density and equation of continuity; potential difference and electromotive force, electric energy sources – voltage source and current source; metallic conduction and Ohm’s law, cond ...
... 1. Steady Direct Current (dc): Charge-particles in motion-electric current (drift, diffusion and connection); current density and equation of continuity; potential difference and electromotive force, electric energy sources – voltage source and current source; metallic conduction and Ohm’s law, cond ...
Production of Phonon Schr ¨odinger Cat States in Benzoid Rings
... On the other hand, Schrödinger’s paper on the current situation of quantum mechanics, published in 1935[5], proposes a Gedankenexperiment to prepare superpositions of dead and alive cats, which highlights that the vast majority of states allowed by quantum mechanics are not observed in our macrosco ...
... On the other hand, Schrödinger’s paper on the current situation of quantum mechanics, published in 1935[5], proposes a Gedankenexperiment to prepare superpositions of dead and alive cats, which highlights that the vast majority of states allowed by quantum mechanics are not observed in our macrosco ...
Algebra 3 – Chapter 10 – Matrices
... If an m n has the same number of rows as columns, that is if m = n, the matrix is referred to as a square matrix. Two m by n matrices A and B are said to be equal, written as A = B provided that each entry bij in A is equal to the corresponding entry bij in B. The Identity Matrix is a square matri ...
... If an m n has the same number of rows as columns, that is if m = n, the matrix is referred to as a square matrix. Two m by n matrices A and B are said to be equal, written as A = B provided that each entry bij in A is equal to the corresponding entry bij in B. The Identity Matrix is a square matri ...
Quantum Theory
... Quantum Theory, in physics, description of the particles that make up matter and how they interact with each other and with energy. Quantum theory explains in principle how to calculate what will happen in any experiment involving physical or biological systems, and how to understand how our world w ...
... Quantum Theory, in physics, description of the particles that make up matter and how they interact with each other and with energy. Quantum theory explains in principle how to calculate what will happen in any experiment involving physical or biological systems, and how to understand how our world w ...
Quantum Theory
... Quantum Theory, in physics, description of the particles that make up matter and how they interact with each other and with energy. Quantum theory explains in principle how to calculate what will happen in any experiment involving physical or biological systems, and how to understand how our world w ...
... Quantum Theory, in physics, description of the particles that make up matter and how they interact with each other and with energy. Quantum theory explains in principle how to calculate what will happen in any experiment involving physical or biological systems, and how to understand how our world w ...
Charge and spin quantum fluids generated by many
... are such that R̂c,−1 counts the number of electron doubly-occupied sites, R̂c,+1 counts the number of electron empty sites, R̂s,−1 counts the number of electron down-spin singlyoccupied sites, and R̂s,+1 counts the number of electron up-spin singly-occupied sites. The new physics brought about by th ...
... are such that R̂c,−1 counts the number of electron doubly-occupied sites, R̂c,+1 counts the number of electron empty sites, R̂s,−1 counts the number of electron down-spin singlyoccupied sites, and R̂s,+1 counts the number of electron up-spin singly-occupied sites. The new physics brought about by th ...
Fault-Tolerant Quantum Computation
... desirable, but it is also an unavoidable feature of any fault tolerant scheme ...
... desirable, but it is also an unavoidable feature of any fault tolerant scheme ...
Teacher text
... there has to be a continuous interaction between teacher and students to check on students’ conceptual progress (or lack thereof) and to provide constructive feedback (White & Gunstone, 1992). The importance of feedback also comes from a completely different line of studies. Black and William (1998) ...
... there has to be a continuous interaction between teacher and students to check on students’ conceptual progress (or lack thereof) and to provide constructive feedback (White & Gunstone, 1992). The importance of feedback also comes from a completely different line of studies. Black and William (1998) ...
- Philsci
... Hamiltonian. That means that the position-value of each individual particle can be linearly transformed in its own independent way, without any change in the form of the dynamics. However, if we now introduce an interaction potential V in the Hamiltonian, dependent on the differences between the par ...
... Hamiltonian. That means that the position-value of each individual particle can be linearly transformed in its own independent way, without any change in the form of the dynamics. However, if we now introduce an interaction potential V in the Hamiltonian, dependent on the differences between the par ...