Certainty and Uncertainty in Quantum Information Processing
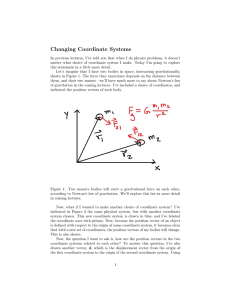
... Implications of reasoning about quantum systems to problems in classical computer science We give two surprising, elegant examples. Cryptographic protocols usually rely on the empirical hardness of a problem for their security; it is rare to be able to prove complete, information theoretic security. ...
... Implications of reasoning about quantum systems to problems in classical computer science We give two surprising, elegant examples. Cryptographic protocols usually rely on the empirical hardness of a problem for their security; it is rare to be able to prove complete, information theoretic security. ...
Introduction to loop quantum gravity
... The quantum nature of three of the four forces, electromagnetism, weak and strong interactions, suggest that gravitational force too should have quantum properties at Planck scales. Loop quantum gravity (LQG) is an attempt to quantise gravity in a non-perturbative and background independent way. Thi ...
... The quantum nature of three of the four forces, electromagnetism, weak and strong interactions, suggest that gravitational force too should have quantum properties at Planck scales. Loop quantum gravity (LQG) is an attempt to quantise gravity in a non-perturbative and background independent way. Thi ...
The harmonic oscillator in quantum mechanics: A third way F. Marsiglio
... This part is usually more abstract. Examples that are often used in this part are two state systems and matrix representations of angular momentum. Alternatively, an actual (say, 3 × 3) matrix is given, and students are asked to use matrix algebra to mimic a solution of a quantum mechanical problem. ...
... This part is usually more abstract. Examples that are often used in this part are two state systems and matrix representations of angular momentum. Alternatively, an actual (say, 3 × 3) matrix is given, and students are asked to use matrix algebra to mimic a solution of a quantum mechanical problem. ...
Numerical solution of the Dirac equation by a mapped Fourier grid
... Hamiltonian is not bounded from below and so it is not possible to use standard variational methods. The method yields a set of eigenstates which may be used, e.g., for time-dependent problems as was done in the non-relativistic case in [12]. In section 2 details are given of how to build the matrix ...
... Hamiltonian is not bounded from below and so it is not possible to use standard variational methods. The method yields a set of eigenstates which may be used, e.g., for time-dependent problems as was done in the non-relativistic case in [12]. In section 2 details are given of how to build the matrix ...
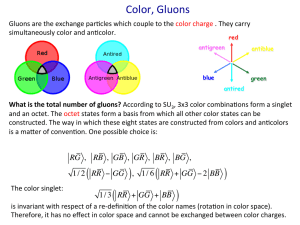
The Integer Quantum Hall Effect
... theorists started to grasp the beautiful mathematical structure behind it. In fact, the quantization has topological aspect. Its robust explanation combines functional analysis, topology (in the space of operators), and probability. In particular, it was understood that in the absence of direct cond ...
... theorists started to grasp the beautiful mathematical structure behind it. In fact, the quantization has topological aspect. Its robust explanation combines functional analysis, topology (in the space of operators), and probability. In particular, it was understood that in the absence of direct cond ...