Ch19
... There are many different adaptations within organisms on this planet. Examples include ; camouflage, a human’s thumb, an Eagle’s eyesight, etc. Adaptations help an organism survive and therefore that organism will have a better chance of passing on to its offspring the particular characteristic whic ...
... There are many different adaptations within organisms on this planet. Examples include ; camouflage, a human’s thumb, an Eagle’s eyesight, etc. Adaptations help an organism survive and therefore that organism will have a better chance of passing on to its offspring the particular characteristic whic ...
1: Worksheet: Lamark versus Darwin`s Evolutionary Theory
... and Natural Selection, or ‘Survival of the Fittest’. He dedicated his life to studying plants and animals and believed that the desires of animals have nothing to do with how they evolve. He said that organisms, even of the same species, are different in some ways, and over time those creatures whic ...
... and Natural Selection, or ‘Survival of the Fittest’. He dedicated his life to studying plants and animals and believed that the desires of animals have nothing to do with how they evolve. He said that organisms, even of the same species, are different in some ways, and over time those creatures whic ...
et al
... and the Y chromosome have proven invaluable for generating a standard model for evolution of modern humans • earlier research on protein polymorphisms • Co-evolution of genes with language and some slowly evolving cultural traits, together with the genetic evolution ...
... and the Y chromosome have proven invaluable for generating a standard model for evolution of modern humans • earlier research on protein polymorphisms • Co-evolution of genes with language and some slowly evolving cultural traits, together with the genetic evolution ...
Unit #1: Evolution - Achievement First
... Speciation is the formation of a new species and results in diversity of life forms Speciation occurs when two groups of organisms become so different genetically that they can no longer interbreed successfully Speciation can occur when geographic isolation is followed by reproductive isolation, whi ...
... Speciation is the formation of a new species and results in diversity of life forms Speciation occurs when two groups of organisms become so different genetically that they can no longer interbreed successfully Speciation can occur when geographic isolation is followed by reproductive isolation, whi ...
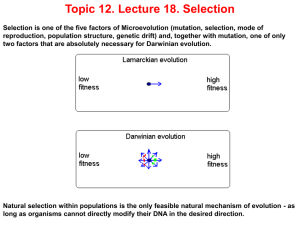
L18Selection
... lasting changes in the population only if it is, at least partially, due to variation among their genotypes. If we think in terms of populations, the impact of selection is obvious: the winner is the one who runs faster. Darwinian mechanism of evolution implies that withinpopulation variation is not ...
... lasting changes in the population only if it is, at least partially, due to variation among their genotypes. If we think in terms of populations, the impact of selection is obvious: the winner is the one who runs faster. Darwinian mechanism of evolution implies that withinpopulation variation is not ...
Population Genetics
... If the two alleles are different, and one is dominant, then the character expressed is the one of the dominant allele. If they are co-dominant, then a bit of everything is expressed. For a recessive allele to be expressed, it has to be either alone or present on both chromosomes of a homologous pair ...
... If the two alleles are different, and one is dominant, then the character expressed is the one of the dominant allele. If they are co-dominant, then a bit of everything is expressed. For a recessive allele to be expressed, it has to be either alone or present on both chromosomes of a homologous pair ...
Darwin and His Theory
... Inference 2: Survival in the struggle for existence is not random, but depends in part on the heritable characteristics of individuals. Individuals who inherit characteristics most fit for their environment are likely to leave more offspring than less fit individuals. ...
... Inference 2: Survival in the struggle for existence is not random, but depends in part on the heritable characteristics of individuals. Individuals who inherit characteristics most fit for their environment are likely to leave more offspring than less fit individuals. ...
Problems of Macroevolution (Molecular Evolution, Phenotype
... Department of Biology, Brooklyn College, C.U.N.Y., Brooklyn, New York 11210 SYNOPSIS. As seen from a hierarchical viewpoint, macroevolution is neither a functional process nor a series of events in the past. It is a record only. For this reason macroevolutionary laws are all statistical laws. Natura ...
... Department of Biology, Brooklyn College, C.U.N.Y., Brooklyn, New York 11210 SYNOPSIS. As seen from a hierarchical viewpoint, macroevolution is neither a functional process nor a series of events in the past. It is a record only. For this reason macroevolutionary laws are all statistical laws. Natura ...
understanding the times
... Kuhn points out that science is not merely a progressive, incremental discipline that studies and records facts. Scientific “facts” can be understood and interpreted in a variety of ways depending on the worldview assumptions of the scientist. Kuhn is also famous for pointing out how scientific theo ...
... Kuhn points out that science is not merely a progressive, incremental discipline that studies and records facts. Scientific “facts” can be understood and interpreted in a variety of ways depending on the worldview assumptions of the scientist. Kuhn is also famous for pointing out how scientific theo ...
Evolution
... change due to the pressures of their environment, traits are acquired He proposed that by using or not using its body parts, an individual tends to develop certain characteristics, which it passes on to its offspring. ...
... change due to the pressures of their environment, traits are acquired He proposed that by using or not using its body parts, an individual tends to develop certain characteristics, which it passes on to its offspring. ...
Evolutionary naturalism: an ancient idea
... often called the father of evolutionary naturalism, argued that chance alone ‘was responsible for the entire process’ of the evolution of simple matter into modern humankind.5 Empedocles concluded that spontaneous generation fully explained the origin of life, and he also taught that all living orga ...
... often called the father of evolutionary naturalism, argued that chance alone ‘was responsible for the entire process’ of the evolution of simple matter into modern humankind.5 Empedocles concluded that spontaneous generation fully explained the origin of life, and he also taught that all living orga ...
powerpoint
... traits, will be more likely to survive and reproduce than others. There will be “differential reproductive success.” C3: Over time, adaptive traits will be passed on in a population at higher frequency than less adaptive traits. These adaptive traits will accumulate in a population. The population w ...
... traits, will be more likely to survive and reproduce than others. There will be “differential reproductive success.” C3: Over time, adaptive traits will be passed on in a population at higher frequency than less adaptive traits. These adaptive traits will accumulate in a population. The population w ...
Spring 2012 Biology Final Exam Review Guide Mrs. Hawkins What
... Evidence for Evolution? What is Speciation Vestigial Structures Homologous Structures “Are We Still Evolving”? –Why is the rate of evolution in developing countries different than the rate of evolution in the western world? What is the connection between Hemochromatosis and Alzheimers? W ...
... Evidence for Evolution? What is Speciation Vestigial Structures Homologous Structures “Are We Still Evolving”? –Why is the rate of evolution in developing countries different than the rate of evolution in the western world? What is the connection between Hemochromatosis and Alzheimers? W ...
Sample Test Questions -- Midterm 2 - People
... d. None of the above. 6. Darwin explained the differences in beak shape among Galapagos finches as being the result of a. chance events b. adaptations to eating different foods c. differences that existed in the colonizing species d. inheritance of acquired characteristics 7. Industrial melanism des ...
... d. None of the above. 6. Darwin explained the differences in beak shape among Galapagos finches as being the result of a. chance events b. adaptations to eating different foods c. differences that existed in the colonizing species d. inheritance of acquired characteristics 7. Industrial melanism des ...
Book Review On the Origin of Species by Charles Darwin. Edited by
... provides answers which were previously left unanswered or ignored. The theory of evolution by natural selection was neatly summarised by Darwin in the introduction of the Origin as follows: As many more individuals of each species are born than can possibly survive; and as, consequently, there is a ...
... provides answers which were previously left unanswered or ignored. The theory of evolution by natural selection was neatly summarised by Darwin in the introduction of the Origin as follows: As many more individuals of each species are born than can possibly survive; and as, consequently, there is a ...
K-12 Educators Workshop - Evo-Ed
... Describe in detail what might have happened at the molecular level so that these mushrooms no longer produce this toxin? Q3. The non-poisonous Toxican mushroom has become more frequent in mushroom populations and poisonous Toxican mushrooms have become rare. Define Natural Selection and use it to ex ...
... Describe in detail what might have happened at the molecular level so that these mushrooms no longer produce this toxin? Q3. The non-poisonous Toxican mushroom has become more frequent in mushroom populations and poisonous Toxican mushrooms have become rare. Define Natural Selection and use it to ex ...
Directional Selection on a discrete trait
... changes in allele frequency at each generation According to Darwin, this happens via ...
... changes in allele frequency at each generation According to Darwin, this happens via ...
Chapter 15 – Darwin`s Theory of Evolution 15
... This helped Darwin, he thought if the Earth could change over time, ________________________________________? Jean-Baptiste Lamarck recognized that living things change _____________________________ and that all species were _______________________________________________________. In 1809, Lamarck p ...
... This helped Darwin, he thought if the Earth could change over time, ________________________________________? Jean-Baptiste Lamarck recognized that living things change _____________________________ and that all species were _______________________________________________________. In 1809, Lamarck p ...
Natural Selection - Bakersfield College
... – Now believed to have arisen from single pair or pregnant female from So. American mainland • Rafted to islands by storm • Population size increased and resources decreased • Individuals capable of using other resources did so to survive • Natural selection gradually selected for those groups that ...
... – Now believed to have arisen from single pair or pregnant female from So. American mainland • Rafted to islands by storm • Population size increased and resources decreased • Individuals capable of using other resources did so to survive • Natural selection gradually selected for those groups that ...
darwin`s theory of evolution - Breakthrough Science Society
... were formerly thus connected.”1 In other words, what are known as separate species today belonging to a common genus, were earlier varieties of the same parent species. Similarly, some of those which are today varieties of a species may become new species in future. He further felt: “I look at varie ...
... were formerly thus connected.”1 In other words, what are known as separate species today belonging to a common genus, were earlier varieties of the same parent species. Similarly, some of those which are today varieties of a species may become new species in future. He further felt: “I look at varie ...
Chaptrer 23 Part 2: Intro to Hardy Weinberg
... unusual for allele with severe detrimental effects in homozygotes ...
... unusual for allele with severe detrimental effects in homozygotes ...
Chapter 19 – Introducing Evolution ()
... Natural selection is a process in which the characteristics of a population of organisms change because individuals with certain heritable traits survive specific environmental conditions and pass on their traits to their offspring. In order for natural selection to occur there must be diversity wit ...
... Natural selection is a process in which the characteristics of a population of organisms change because individuals with certain heritable traits survive specific environmental conditions and pass on their traits to their offspring. In order for natural selection to occur there must be diversity wit ...
Evolution Unit
... Essential knowledge 1.A.1: Natural selection is a major mechanism of evolution. a. According to Darwin’s theory of natural selection, competition for limited resources results in differential survival. Individuals with more favorable phenotypes are more likely to survive and produce more offspring, ...
... Essential knowledge 1.A.1: Natural selection is a major mechanism of evolution. a. According to Darwin’s theory of natural selection, competition for limited resources results in differential survival. Individuals with more favorable phenotypes are more likely to survive and produce more offspring, ...
Darwin and Feminism: Preliminary Investigations for
... bifurcation, and becoming that characterise all forms of life. His work develops an anti-humanist, ‘algorithmic’, that is, mechanical or fundamentally mindless, analysis of biological dynamics which refuses to assume that the temporal movement forward can be equated with development or progress. His ...
... bifurcation, and becoming that characterise all forms of life. His work develops an anti-humanist, ‘algorithmic’, that is, mechanical or fundamentally mindless, analysis of biological dynamics which refuses to assume that the temporal movement forward can be equated with development or progress. His ...
Natural selection

Natural selection is the differential survival and reproduction of individuals due to differences in phenotype; it is a key mechanism of evolution. The term ""natural selection"" was popularised by Charles Darwin, who intended it to be compared with artificial selection, now more commonly referred to as selective breeding.Variation exists within all populations of organisms. This occurs partly because random mutations arise in the genome of an individual organism, and these mutations can be passed to offspring. Throughout the individuals’ lives, their genomes interact with their environments to cause variations in traits. (The environment of a genome includes the molecular biology in the cell, other cells, other individuals, populations, species, as well as the abiotic environment.) Individuals with certain variants of the trait may survive and reproduce more than individuals with other, less successful, variants. Therefore, the population evolves. Factors that affect reproductive success are also important, an issue that Darwin developed in his ideas on sexual selection, which was redefined as being included in natural selection in the 1930s when biologists considered it not to be very important, and fecundity selection, for example.Natural selection acts on the phenotype, or the observable characteristics of an organism, but the genetic (heritable) basis of any phenotype that gives a reproductive advantage may become more common in a population (see allele frequency). Over time, this process can result in populations that specialise for particular ecological niches (microevolution) and may eventually result in the emergence of new species (macroevolution). In other words, natural selection is an important process (though not the only process) by which evolution takes place within a population of organisms. Natural selection can be contrasted with artificial selection, in which humans intentionally choose specific traits (although they may not always get what they want). In natural selection there is no intentional choice. In other words, artificial selection is teleological and natural selection is not teleological.Natural selection is one of the cornerstones of modern biology. The concept was published by Darwin and Alfred Russel Wallace in a joint presentation of papers in 1858, and set out in Darwin's influential 1859 book On the Origin of Species, in which natural selection was described as analogous to artificial selection, a process by which animals and plants with traits considered desirable by human breeders are systematically favoured for reproduction. The concept of natural selection was originally developed in the absence of a valid theory of heredity; at the time of Darwin's writing, nothing was known of modern genetics. The union of traditional Darwinian evolution with subsequent discoveries in classical and molecular genetics is termed the modern evolutionary synthesis. Natural selection remains the primary explanation for adaptive evolution.