Lecture 4 Genetics in Mendelian Populations I
... Populations contain genetic variation that arises by random mutation. Populations evolve by changes in gene frequency. Gene frequencies change through random genetic drift, gene flow, and natural selection. Most adaptive variants have small effects on the phenotype so changes are typically g ...
... Populations contain genetic variation that arises by random mutation. Populations evolve by changes in gene frequency. Gene frequencies change through random genetic drift, gene flow, and natural selection. Most adaptive variants have small effects on the phenotype so changes are typically g ...
1 The weather on Earth suddenly changes and temperatures in the
... and Group C to 0.7%. After a day, the students counted the percentage of surviving fleas in each group (Figure I.) The three groups of surviving fleas were kept separate and allowed to reproduce. The offspring in each group were then exposed to a pesticide concentration of 0.5%. The results are in f ...
... and Group C to 0.7%. After a day, the students counted the percentage of surviving fleas in each group (Figure I.) The three groups of surviving fleas were kept separate and allowed to reproduce. The offspring in each group were then exposed to a pesticide concentration of 0.5%. The results are in f ...
spatial sorting - The University of Sydney
... (3). Second, natural selection interacting with spatial sorting would lead to permanent changes. To emphasize the novelty of the concept, Shine et al. (1) focused on how spatial sorting can operate in the total absence of natural selection. However, spatial sorting, by definition, applies to traits t ...
... (3). Second, natural selection interacting with spatial sorting would lead to permanent changes. To emphasize the novelty of the concept, Shine et al. (1) focused on how spatial sorting can operate in the total absence of natural selection. However, spatial sorting, by definition, applies to traits t ...
I have put together a recommendation for teacher
... The theory of evolution explains how the immense variety of living things on Earth has developed from ancestral forms during the past three billion years. This theory is considered to be the most important unifying idea in biology. It offers an explanation, based on fossil and other scientific evide ...
... The theory of evolution explains how the immense variety of living things on Earth has developed from ancestral forms during the past three billion years. This theory is considered to be the most important unifying idea in biology. It offers an explanation, based on fossil and other scientific evide ...
Forces that change gene frequency
... to population genetics: a) Recurrent -- mutations that occur repeatedly, generally at some characteristic frequency b) Non-recurrent -- mutations that arise only once in the history of a lineage 2. Changes to gene (allele) frequencies are minimal: a) Non-recurrent mutations are of little consequence ...
... to population genetics: a) Recurrent -- mutations that occur repeatedly, generally at some characteristic frequency b) Non-recurrent -- mutations that arise only once in the history of a lineage 2. Changes to gene (allele) frequencies are minimal: a) Non-recurrent mutations are of little consequence ...
Study Questions for Test 2, Philosophy 2233
... 24. Describe some respects in which the mammal-like reptiles became more and more like mammals. 25. Explain one way in which selection could favour a balance between two alternative alleles in a population. 26. Why did Sumner conclude that natural selection, rather than climate, was the best explana ...
... 24. Describe some respects in which the mammal-like reptiles became more and more like mammals. 25. Explain one way in which selection could favour a balance between two alternative alleles in a population. 26. Why did Sumner conclude that natural selection, rather than climate, was the best explana ...
Challenges to Neo- Darwinism and Their Meaning
... a more potent force than traditional Darwinian sorting of organisms in both the spread of features within clades and the differential success of some clades over others. True species selection relies upon properties of species as entities — propensity to speciate in particular — that cannot be reduc ...
... a more potent force than traditional Darwinian sorting of organisms in both the spread of features within clades and the differential success of some clades over others. True species selection relies upon properties of species as entities — propensity to speciate in particular — that cannot be reduc ...
Evolution - Effingham County Schools
... Mimicry- a harmless species resembles a harmful one, predators learn to avoid both species Camouflage- species features blend in with the environment ...
... Mimicry- a harmless species resembles a harmful one, predators learn to avoid both species Camouflage- species features blend in with the environment ...
Natural Selection and The Effects of Ecological
... (a) different species: competitors, predators, pathogens, symbionts etc. (b) same species: mates, family members, social groups etc. 4. place in which to live: other requirements, such as nest sites, shelter etc. Ecology and genetics together form the mechanisms of evolutionary change. Genetic varia ...
... (a) different species: competitors, predators, pathogens, symbionts etc. (b) same species: mates, family members, social groups etc. 4. place in which to live: other requirements, such as nest sites, shelter etc. Ecology and genetics together form the mechanisms of evolutionary change. Genetic varia ...
UNIT TITLE _VII Evolution
... 4.3.1a: The basic theory of biological evolution states that the Earth’s present-day species developed from earlier, distinctly different species 4.3.1e: Natural selection and its evolutionary consequences provide a scientific explanation for the fossil record of ancient life-forms, as well as for t ...
... 4.3.1a: The basic theory of biological evolution states that the Earth’s present-day species developed from earlier, distinctly different species 4.3.1e: Natural selection and its evolutionary consequences provide a scientific explanation for the fossil record of ancient life-forms, as well as for t ...
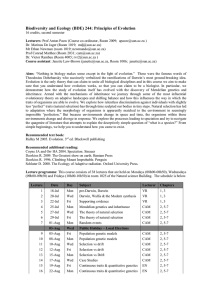
Biodiversity and Ecology (BDE) 244: Principles of Evolution
... demonstrate how the study of evolution itself has evolved with the discovery of Mendelian genetics and inheritance. Armed with the mechanisms of inheritance we journey through some of the most influential evolutionary theory on adaptive landscapes and shifting balance and how this influences the way ...
... demonstrate how the study of evolution itself has evolved with the discovery of Mendelian genetics and inheritance. Armed with the mechanisms of inheritance we journey through some of the most influential evolutionary theory on adaptive landscapes and shifting balance and how this influences the way ...
Chapter 14
... that serve similar functions to resemble one another ○ Analogous structures are structures that are outwardly similar in appearance, but differ in their ...
... that serve similar functions to resemble one another ○ Analogous structures are structures that are outwardly similar in appearance, but differ in their ...
Science of Biology - Austin Community College
... • Darwin inferred that those individuals with traits best suited to the local environment will generally leave more surviving, fertile offspring ...
... • Darwin inferred that those individuals with traits best suited to the local environment will generally leave more surviving, fertile offspring ...
formation of species
... 1. A satisfactory definition is not provided for species of extinct organisms or for organisms that do not reproduce sexually. 2. Individuals do not waste gametes by producing offspring that cannot reproduce. 3. Some species of moths on the Hawaiian Islands appear to have evolved during the past tho ...
... 1. A satisfactory definition is not provided for species of extinct organisms or for organisms that do not reproduce sexually. 2. Individuals do not waste gametes by producing offspring that cannot reproduce. 3. Some species of moths on the Hawaiian Islands appear to have evolved during the past tho ...
Charles Darwin
... After reading Lyell’s book, Darwin was convinced that Earth was old. Darwin reasoned that if geological phenomena could change the earth, then life on Earth could change as well. ...
... After reading Lyell’s book, Darwin was convinced that Earth was old. Darwin reasoned that if geological phenomena could change the earth, then life on Earth could change as well. ...
Thurs./Fri. 5/12 – 5/13 Agenda
... adapted to their environment survive and reproduce. • Other less fit organisms have a lower chance of surviving and reproducing. • Therefore, well-adapted organisms pass on more of their genes to the next generation. • As a result the gene frequency changes from one generation to the next. ...
... adapted to their environment survive and reproduce. • Other less fit organisms have a lower chance of surviving and reproducing. • Therefore, well-adapted organisms pass on more of their genes to the next generation. • As a result the gene frequency changes from one generation to the next. ...
When Hardy-Weinberg predictions about future generations are…
... 5. Natural Selection (individuals of certain genotypes leave behind more offspring than other genotypes) ...
... 5. Natural Selection (individuals of certain genotypes leave behind more offspring than other genotypes) ...
Population Dynamics and HIV
... • Time 0 – before anti-HIV drug is taken • Time 1 – when the anti-HIV drug is started • Time 2 – 7 years later while the anti-HIV drug is still being taken. ...
... • Time 0 – before anti-HIV drug is taken • Time 1 – when the anti-HIV drug is started • Time 2 – 7 years later while the anti-HIV drug is still being taken. ...
Evolution - MrsHBraaten
... alike. These differences in traits were believed to be passed on to offspring by parents. Darwin did not understand what caused these variations among different organisms. ...
... alike. These differences in traits were believed to be passed on to offspring by parents. Darwin did not understand what caused these variations among different organisms. ...
File
... SCENARIO 7: Ostriches (birds) and giraffes (mammals) are both native to the savannahs of Africa. They share the same characteristic of a very long neck. ...
... SCENARIO 7: Ostriches (birds) and giraffes (mammals) are both native to the savannahs of Africa. They share the same characteristic of a very long neck. ...
HIGH SCHOOL SCIENCE NSPIRED - Education TI
... Students will know why natural selection acts on the phenotype rather than the genotype of an organism. ...
... Students will know why natural selection acts on the phenotype rather than the genotype of an organism. ...
Darwin and Evolutionary Theory
... many more offspring than can possibly survive on the limited resources generally available. • poverty, famine, and disease were natural outcomes that resulted from overpopulation. • However, Malthus believed that divine forces were ultimately responsible for such outcomes, which, though natural, wer ...
... many more offspring than can possibly survive on the limited resources generally available. • poverty, famine, and disease were natural outcomes that resulted from overpopulation. • However, Malthus believed that divine forces were ultimately responsible for such outcomes, which, though natural, wer ...
Natural selection

Natural selection is the differential survival and reproduction of individuals due to differences in phenotype; it is a key mechanism of evolution. The term ""natural selection"" was popularised by Charles Darwin, who intended it to be compared with artificial selection, now more commonly referred to as selective breeding.Variation exists within all populations of organisms. This occurs partly because random mutations arise in the genome of an individual organism, and these mutations can be passed to offspring. Throughout the individuals’ lives, their genomes interact with their environments to cause variations in traits. (The environment of a genome includes the molecular biology in the cell, other cells, other individuals, populations, species, as well as the abiotic environment.) Individuals with certain variants of the trait may survive and reproduce more than individuals with other, less successful, variants. Therefore, the population evolves. Factors that affect reproductive success are also important, an issue that Darwin developed in his ideas on sexual selection, which was redefined as being included in natural selection in the 1930s when biologists considered it not to be very important, and fecundity selection, for example.Natural selection acts on the phenotype, or the observable characteristics of an organism, but the genetic (heritable) basis of any phenotype that gives a reproductive advantage may become more common in a population (see allele frequency). Over time, this process can result in populations that specialise for particular ecological niches (microevolution) and may eventually result in the emergence of new species (macroevolution). In other words, natural selection is an important process (though not the only process) by which evolution takes place within a population of organisms. Natural selection can be contrasted with artificial selection, in which humans intentionally choose specific traits (although they may not always get what they want). In natural selection there is no intentional choice. In other words, artificial selection is teleological and natural selection is not teleological.Natural selection is one of the cornerstones of modern biology. The concept was published by Darwin and Alfred Russel Wallace in a joint presentation of papers in 1858, and set out in Darwin's influential 1859 book On the Origin of Species, in which natural selection was described as analogous to artificial selection, a process by which animals and plants with traits considered desirable by human breeders are systematically favoured for reproduction. The concept of natural selection was originally developed in the absence of a valid theory of heredity; at the time of Darwin's writing, nothing was known of modern genetics. The union of traditional Darwinian evolution with subsequent discoveries in classical and molecular genetics is termed the modern evolutionary synthesis. Natural selection remains the primary explanation for adaptive evolution.