
Slide 1
... rub their back and belly along the sides of trees or rocks. Then they patrol their territory, marking it with urine and a weak musk-smelling secretion from their anal gland. They search for food running along the ground or through the trees. Red pandas may alternately either use their forepaw to bri ...
... rub their back and belly along the sides of trees or rocks. Then they patrol their territory, marking it with urine and a weak musk-smelling secretion from their anal gland. They search for food running along the ground or through the trees. Red pandas may alternately either use their forepaw to bri ...
Biology Quiz 2 Review
... damaging to your view of Adam and Eve. If this account refers only to metaphoric or mythological characters, then it is hard to account for original sin and our need for Christ. 4) Fourth, the theory of evolution in general is undergoing serious challenges from within the scientific community itself ...
... damaging to your view of Adam and Eve. If this account refers only to metaphoric or mythological characters, then it is hard to account for original sin and our need for Christ. 4) Fourth, the theory of evolution in general is undergoing serious challenges from within the scientific community itself ...
DISEASES AND TREES - UC Berkeley College of Natural Resources
... for INCREASED virulence • In the short/medium term with long lived trees a pathogen is likely to increase its virulence • In long term, selection pressure should result in widespread resistance among the host ...
... for INCREASED virulence • In the short/medium term with long lived trees a pathogen is likely to increase its virulence • In long term, selection pressure should result in widespread resistance among the host ...
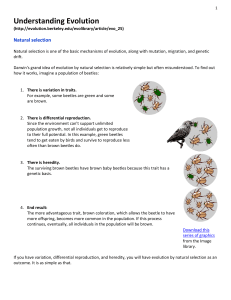
Understanding Evolution Reading Assignment
... Scientists have worked out many examples of natural selection, one of the basic mechanisms of evolution. Any coffee table book about natural history will overwhelm you with full-page glossies depicting amazing adaptations produced by natural selection, such as the examples below. ...
... Scientists have worked out many examples of natural selection, one of the basic mechanisms of evolution. Any coffee table book about natural history will overwhelm you with full-page glossies depicting amazing adaptations produced by natural selection, such as the examples below. ...
Natural Selection
... Darwin’s Ideas 1. Natural Selection – A process in which some individuals have genetically-based traits that improve survival or reproduction – Thus, they have more offspring surviving to reproductive age than other individuals. ...
... Darwin’s Ideas 1. Natural Selection – A process in which some individuals have genetically-based traits that improve survival or reproduction – Thus, they have more offspring surviving to reproductive age than other individuals. ...
ecology and evolution review
... How would Darwin explain these giraffes with longer necks? Populations naturally have individuals with different sizes of necks (natural variation) The ones with longer necks are better able to get food, survive, and pass on their longer ...
... How would Darwin explain these giraffes with longer necks? Populations naturally have individuals with different sizes of necks (natural variation) The ones with longer necks are better able to get food, survive, and pass on their longer ...
Chapter 4
... Plants are many-celled organisms that make their own food using the sun’s energy and have cell walls. Most plants live on land where they use their leaves to get sunlight, oxygen, and carbon dioxide from the air. While absorbing nutrients and water from the soil using their roots. Leaves and roots a ...
... Plants are many-celled organisms that make their own food using the sun’s energy and have cell walls. Most plants live on land where they use their leaves to get sunlight, oxygen, and carbon dioxide from the air. While absorbing nutrients and water from the soil using their roots. Leaves and roots a ...
Process of Speciation - Emerald Meadow Stables
... • How do natural selection and genetic drift create new species? – Speciation – formation of new species – Species – group of organisms that breed with one another and produce fertile offspring – share a common gene pool ...
... • How do natural selection and genetic drift create new species? – Speciation – formation of new species – Species – group of organisms that breed with one another and produce fertile offspring – share a common gene pool ...
Detection of the footprint of natural selection in the genome
... Prolonged period can increase the fixation rate of beneficial function-altering mutations • Reduction in genetic diversity The selected allele rises to fixation, bringing with it closely linked variants • High-frequency derived alleles In a selective sweep, derived alleles linked to the beneficial a ...
... Prolonged period can increase the fixation rate of beneficial function-altering mutations • Reduction in genetic diversity The selected allele rises to fixation, bringing with it closely linked variants • High-frequency derived alleles In a selective sweep, derived alleles linked to the beneficial a ...
ch16.3 & 16.4 Darwin`s Case & Evidence
... organisms which are better adapted to the environment will survive and reproduce, passing on their genes. ...
... organisms which are better adapted to the environment will survive and reproduce, passing on their genes. ...
Exam 4 Q3 Review Sheet Honors Biology Exam 4 will cover
... 37. How is genetic diversity measured in a population? Why do humans have such a low genetic diversity do we hypothesize? 38. Explain how different organisms generate diversity, and be sure to explain why each uses the strategy that it does. 39. Explain how alleles not favored by the current environ ...
... 37. How is genetic diversity measured in a population? Why do humans have such a low genetic diversity do we hypothesize? 38. Explain how different organisms generate diversity, and be sure to explain why each uses the strategy that it does. 39. Explain how alleles not favored by the current environ ...
National 5 Biology Life on Earth Homework
... (c) How does natural selection play a role in this process? (d) Assuming they are a population of rabbits state two possible selection pressures that could act on the isolated groups. (e) How would you know that two different species had been formed? ...
... (c) How does natural selection play a role in this process? (d) Assuming they are a population of rabbits state two possible selection pressures that could act on the isolated groups. (e) How would you know that two different species had been formed? ...
Biology Chapter 1 - revised Anderson- 8_19_2015
... • The sum of living things on the planet is called the Earth’s biodiversity • The theory of evolution operates on the hypothesis that all life originated from a common ancestor (LUCA – the Last Universal Common Ancestor) ...
... • The sum of living things on the planet is called the Earth’s biodiversity • The theory of evolution operates on the hypothesis that all life originated from a common ancestor (LUCA – the Last Universal Common Ancestor) ...
Evolutionary_Theory_03_11_14
... (cytochrome C) http://fishgenomes.blogspot.in/2011/03/workshop-on-molecularevolution-north.html ...
... (cytochrome C) http://fishgenomes.blogspot.in/2011/03/workshop-on-molecularevolution-north.html ...
Name Date ______ Period
... Darwin realized that change took time and that the Earth was constantly changing/evolving so why couldn’t this principle apply to living organisms? On the Galapagos Islands, Darwin discovered birds with differently shaped beaks. What might this tell you about the eating habits of the birds on differ ...
... Darwin realized that change took time and that the Earth was constantly changing/evolving so why couldn’t this principle apply to living organisms? On the Galapagos Islands, Darwin discovered birds with differently shaped beaks. What might this tell you about the eating habits of the birds on differ ...
File - Pomp
... • If certain beetles had to nest in or around water, the amount of water could be a selecting factor • If certain beetles had to eat only certain types of plants, the vegetation would be the selecting factor ...
... • If certain beetles had to nest in or around water, the amount of water could be a selecting factor • If certain beetles had to eat only certain types of plants, the vegetation would be the selecting factor ...
Human_Evolution_Darwin_Versus_Lamarck[1]
... Initially not much variation within a population Evolution = thousands of years ...
... Initially not much variation within a population Evolution = thousands of years ...
Species and Speciation
... Little variation in alleles present (common in inbreeding) Allele Frequency: how often a particular allele appears ...
... Little variation in alleles present (common in inbreeding) Allele Frequency: how often a particular allele appears ...
Ch. 15 notes
... This process of natural selection causes species to change over time. Species alive today are descended with modification from ancestral species that lived in the distant past. This process, by which diverse species evolved from common ancestors, unites all organisms on Earth into a single tree of l ...
... This process of natural selection causes species to change over time. Species alive today are descended with modification from ancestral species that lived in the distant past. This process, by which diverse species evolved from common ancestors, unites all organisms on Earth into a single tree of l ...
CH22: Descent With Modification
... perceived adaptation to the environment and the origin of new species as closely related processes • Adaptation: A form or structure modification to fit a changed environment • Finches • From studies made years after Darwin’s voyage, biologists have concluded that this is what happened to the Galápa ...
... perceived adaptation to the environment and the origin of new species as closely related processes • Adaptation: A form or structure modification to fit a changed environment • Finches • From studies made years after Darwin’s voyage, biologists have concluded that this is what happened to the Galápa ...
Chapter 23 Presentation-The Evolution of Populations
... In this, we have direct competition of one sex for mates of the opposite sex. A male often patrols a group of females and prevents other males from mating with her. He is often the psychological winner via a ritual that discourages competitors. This prevents harm to him and increases his own fit ...
... In this, we have direct competition of one sex for mates of the opposite sex. A male often patrols a group of females and prevents other males from mating with her. He is often the psychological winner via a ritual that discourages competitors. This prevents harm to him and increases his own fit ...
Evidence of Evolution2013
... Below is a list of the amino acids in part of a cytochrome protein molecule for 9 different animals. The more sequences that are similar the more related the organisms are at the molecular level. Directions: For each non-human animal, take a highlighter and mark any amino acids that are different th ...
... Below is a list of the amino acids in part of a cytochrome protein molecule for 9 different animals. The more sequences that are similar the more related the organisms are at the molecular level. Directions: For each non-human animal, take a highlighter and mark any amino acids that are different th ...
Ch 23 Activity List File
... AP Biology Evolution of Populations Chapter 23 How do populations evolve over time? Study Questions: 1. Explain the statement “It is the population, not the individual, that evolves.” 2. Explain how Mendel’s particulate hypothesis of inheritance provided much-needed support for Darwin’s theory of ev ...
... AP Biology Evolution of Populations Chapter 23 How do populations evolve over time? Study Questions: 1. Explain the statement “It is the population, not the individual, that evolves.” 2. Explain how Mendel’s particulate hypothesis of inheritance provided much-needed support for Darwin’s theory of ev ...
Evolution

Evolution is change in the heritable traits of biological populations over successive generations. Evolutionary processes give rise to diversity at every level of biological organisation, including the levels of species, individual organisms, and molecules.All of life on earth shares a common ancestor known as the last universal ancestor, which lived approximately 3.5–3.8 billion years ago. Repeated formation of new species (speciation), change within species (anagenesis), and loss of species (extinction) throughout the evolutionary history of life on Earth are demonstrated by shared sets of morphological and biochemical traits, including shared DNA sequences. These shared traits are more similar among species that share a more recent common ancestor, and can be used to reconstruct a biological ""tree of life"" based on evolutionary relationships (phylogenetics), using both existing species and fossils. The fossil record includes a progression from early biogenic graphite, to microbial mat fossils, to fossilized multicellular organisms. Existing patterns of biodiversity have been shaped both by speciation and by extinction. More than 99 percent of all species that ever lived on Earth are estimated to be extinct. Estimates of Earth's current species range from 10 to 14 million, of which about 1.2 million have been documented.In the mid-19th century, Charles Darwin formulated the scientific theory of evolution by natural selection, published in his book On the Origin of Species (1859). Evolution by natural selection is a process demonstrated by the observation that more offspring are produced than can possibly survive, along with three facts about populations: 1) traits vary among individuals with respect to morphology, physiology, and behaviour (phenotypic variation), 2) different traits confer different rates of survival and reproduction (differential fitness), and 3) traits can be passed from generation to generation (heritability of fitness). Thus, in successive generations members of a population are replaced by progeny of parents better adapted to survive and reproduce in the biophysical environment in which natural selection takes place. This teleonomy is the quality whereby the process of natural selection creates and preserves traits that are seemingly fitted for the functional roles they perform. Natural selection is the only known cause of adaptation but not the only known cause of evolution. Other, nonadaptive causes of microevolution include mutation and genetic drift.In the early 20th century the modern evolutionary synthesis integrated classical genetics with Darwin's theory of evolution by natural selection through the discipline of population genetics. The importance of natural selection as a cause of evolution was accepted into other branches of biology. Moreover, previously held notions about evolution, such as orthogenesis, evolutionism, and other beliefs about innate ""progress"" within the largest-scale trends in evolution, became obsolete scientific theories. Scientists continue to study various aspects of evolutionary biology by forming and testing hypotheses, constructing mathematical models of theoretical biology and biological theories, using observational data, and performing experiments in both the field and the laboratory. Evolution is a cornerstone of modern science, accepted as one of the most reliably established of all facts and theories of science, based on evidence not just from the biological sciences but also from anthropology, psychology, astrophysics, chemistry, geology, physics, mathematics, and other scientific disciplines, as well as behavioral and social sciences. Understanding of evolution has made significant contributions to humanity, including the prevention and treatment of human disease, new agricultural products, industrial innovations, a subfield of computer science, and rapid advances in life sciences. Discoveries in evolutionary biology have made a significant impact not just in the traditional branches of biology but also in other academic disciplines (e.g., biological anthropology and evolutionary psychology) and in society at large.














![Human_Evolution_Darwin_Versus_Lamarck[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/005867023_1-5184bb0b6da0eef953a784caed7af7e0-300x300.png)






