Stockholm University August 17–21 2015 Programme
... The importance of considering individual behavioural phenotypes, personality, in ecology and conservation requires both theoretical knowledge and ingenuity. Behaviours are by nature plastic. Discovering the non-plastic component and reveal personality, can be a challenge, but have been shown to be i ...
... The importance of considering individual behavioural phenotypes, personality, in ecology and conservation requires both theoretical knowledge and ingenuity. Behaviours are by nature plastic. Discovering the non-plastic component and reveal personality, can be a challenge, but have been shown to be i ...
How Cichlids Diversify - Evolutionary Biology | Universität Basel
... at older ages can be accounted for by appropriate allocation models (10). In such models, the force of selection declines with age, but though important, this decline is not decisive in molding fertility and mortality patterns. What is decisive is the “option set” of a species, which can be summariz ...
... at older ages can be accounted for by appropriate allocation models (10). In such models, the force of selection declines with age, but though important, this decline is not decisive in molding fertility and mortality patterns. What is decisive is the “option set” of a species, which can be summariz ...
ppt
... "It is interesting to contemplate an entangled bank, clothed with many plants of many kinds, with birds singing on the bushes, with various insects flitting about, and with worms crawling through the damp earth, and to reflect that these elaborately constructed forms, so different from each other, a ...
... "It is interesting to contemplate an entangled bank, clothed with many plants of many kinds, with birds singing on the bushes, with various insects flitting about, and with worms crawling through the damp earth, and to reflect that these elaborately constructed forms, so different from each other, a ...
Chapter 24 The Origin of Species Part C
... • In sympatric speciation, a reproductive barrier isolates a subset of a population without geographic separation from the parent species • Sympatric speciation can result from polyploidy, natural selection, or sexual selection ...
... • In sympatric speciation, a reproductive barrier isolates a subset of a population without geographic separation from the parent species • Sympatric speciation can result from polyploidy, natural selection, or sexual selection ...
LIFE HISTORY EVOLUTION: Why do we get old and die?
... • If selection can produce longer life spans, why don’t organisms evolve them? • Hypothesis 2: Accumulation of deleterious mutations ...
... • If selection can produce longer life spans, why don’t organisms evolve them? • Hypothesis 2: Accumulation of deleterious mutations ...
Misconceptions - Brookings School District
... population happens to have the genetic variation that allows some individuals to survive a particular challenge better than others, then those individuals will have more offspring in the next generation, and the population will evolve. If that genetic variation is not in the population, the populati ...
... population happens to have the genetic variation that allows some individuals to survive a particular challenge better than others, then those individuals will have more offspring in the next generation, and the population will evolve. If that genetic variation is not in the population, the populati ...
Document
... were more likely to survive to reproduce. Airborne pollution in industrial areas blackened the birch tree bark with soot. This meant that the mutant black moths were now camouflaged, while the white variety became more vulnerable to predators. This gave the black variety an advantage, and they were ...
... were more likely to survive to reproduce. Airborne pollution in industrial areas blackened the birch tree bark with soot. This meant that the mutant black moths were now camouflaged, while the white variety became more vulnerable to predators. This gave the black variety an advantage, and they were ...
Evolution Challenges – Integrating Research and Practice in
... Evans, Karl S Rosengren, Jonathan D Lane, and Kristin LS Price, such constraints can both help and hinder learning. For example, by the time students encounter the idea of evolution, they already have some ideas about biological categories: children tend to think of species as fixed and discrete cat ...
... Evans, Karl S Rosengren, Jonathan D Lane, and Kristin LS Price, such constraints can both help and hinder learning. For example, by the time students encounter the idea of evolution, they already have some ideas about biological categories: children tend to think of species as fixed and discrete cat ...
Origin
... simple and imperfect eye to one complex and perfect can be shown to exist, each grade being useful to its possessor, as is certainly the case; if further, the eye ever varies and the variations be inherited, as is likewise certainly the case; and if such variations should be useful to any animal und ...
... simple and imperfect eye to one complex and perfect can be shown to exist, each grade being useful to its possessor, as is certainly the case; if further, the eye ever varies and the variations be inherited, as is likewise certainly the case; and if such variations should be useful to any animal und ...
AP Biology Unit 4
... 7. STS. School districts in several states have been criticized by groups demanding that science classes give “equal time” to alternative, usually fundamentalist Christian, interpretations of the origin and history of life. They argue that it is only fair to let students evaluate both evolution and ...
... 7. STS. School districts in several states have been criticized by groups demanding that science classes give “equal time” to alternative, usually fundamentalist Christian, interpretations of the origin and history of life. They argue that it is only fair to let students evaluate both evolution and ...
You Tube Evolution
... 1. What are these fictional organisms called? __________________ 2. Because those on the east can mate with those on the west, they are part of the same gene __________. 3. What happened to isolate the two gene pools in this fictional story? ______________________________ ___________________________ ...
... 1. What are these fictional organisms called? __________________ 2. Because those on the east can mate with those on the west, they are part of the same gene __________. 3. What happened to isolate the two gene pools in this fictional story? ______________________________ ___________________________ ...
Tempo and mode in evolution
... The 16 papers that follow were presented and discussed at a colloquium sponsored by the National Academy of Sciences to celebrate the 50th anniversary of the publication of Simpson's Tempo and Mode in Evolution. These papers are in five categories: Early Life, Macroevolution, Human Evolution, Rates, ...
... The 16 papers that follow were presented and discussed at a colloquium sponsored by the National Academy of Sciences to celebrate the 50th anniversary of the publication of Simpson's Tempo and Mode in Evolution. These papers are in five categories: Early Life, Macroevolution, Human Evolution, Rates, ...
Lecture Chpt. 24 Evolutn Show 5 Origin Species
... fit together, preventing pools? not sperm transfer ...
... fit together, preventing pools? not sperm transfer ...
Notes - Dr. Bruce Owen
... − that shows that Darwin’s model actually does fit real life − there is nothing special about these finches except than that Peter and Rosemary Grant went to the trouble to document them thoroughly − and that they are historically associated with Darwin, since he observed these birds on the voyage o ...
... − that shows that Darwin’s model actually does fit real life − there is nothing special about these finches except than that Peter and Rosemary Grant went to the trouble to document them thoroughly − and that they are historically associated with Darwin, since he observed these birds on the voyage o ...
Evolution Test Bank
... 24. Scientists recently found a fossil representing a newly discovered animal species that they named Tiktaalik roseae. The fossil indicates that Tiktaalik roseae had a fish-like jaw and scale-covered fins. The front fins had bones similar to those of a shoulder, an upper arm, an elbow, a forearm, a ...
... 24. Scientists recently found a fossil representing a newly discovered animal species that they named Tiktaalik roseae. The fossil indicates that Tiktaalik roseae had a fish-like jaw and scale-covered fins. The front fins had bones similar to those of a shoulder, an upper arm, an elbow, a forearm, a ...
Chapter 8 Natural Selection Empirical studies
... for oldfield mice all 4 postulates are satisfied. There is (i) variation in coat color and it is (ii) heritable. There is (iii) differential reproductive success (or in this case differential survival which is a necessary precursor to reproduction). That differential reproductive success is (iv) ...
... for oldfield mice all 4 postulates are satisfied. There is (i) variation in coat color and it is (ii) heritable. There is (iii) differential reproductive success (or in this case differential survival which is a necessary precursor to reproduction). That differential reproductive success is (iv) ...
Midterm Review
... What types of diseases do we have in America and what causes them? By ___________ all growth plates have fused. Name some male features of the skull: Name some female features of the skull: Name some female features of the pelvis: Name some male features of the pelvis: ...
... What types of diseases do we have in America and what causes them? By ___________ all growth plates have fused. Name some male features of the skull: Name some female features of the skull: Name some female features of the pelvis: Name some male features of the pelvis: ...
speciation - changing-the
... Collected snails from a two-block area Analyzed the allele frequencies for five genes ...
... Collected snails from a two-block area Analyzed the allele frequencies for five genes ...
16.1 Darwin`s Voyage of Discovery
... Lesson Summary Darwin’s Epic Journey Darwin developed a scientific theory to explain how evolution, or change over time, occurs in living things. Darwin’s theory explains how modern organisms have evolved over long periods of time through descent from common ancestors. Observations Aboard the Beagle ...
... Lesson Summary Darwin’s Epic Journey Darwin developed a scientific theory to explain how evolution, or change over time, occurs in living things. Darwin’s theory explains how modern organisms have evolved over long periods of time through descent from common ancestors. Observations Aboard the Beagle ...
Gale Power Search
... by Charles Lyell (1797-1875). Catastrophism was the popular theory of the time about the forces driving geological change. Lyell's theory suggested that geologic change was not solely the result of random catastrophes. Rather, he proposed that geologic formations were most often the result of everyd ...
... by Charles Lyell (1797-1875). Catastrophism was the popular theory of the time about the forces driving geological change. Lyell's theory suggested that geologic change was not solely the result of random catastrophes. Rather, he proposed that geologic formations were most often the result of everyd ...
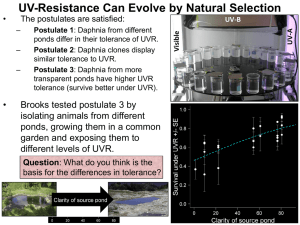
E3_Selection_2011 Part 3
... garden and exposing them to different levels of UVR. Question: What do you think is the basis for the differences in tolerance? ...
... garden and exposing them to different levels of UVR. Question: What do you think is the basis for the differences in tolerance? ...
On the claimed “circularity” of the theory of natural selection
... presented several criteria of fitness which are independent of survival in his 1859 book “On the Origin of Species” [8]. These are found in its fourth chapter, entitled “Natural selection”, and are summarized below. Evolution is a response to changing environments. Thus, certain morphological, physi ...
... presented several criteria of fitness which are independent of survival in his 1859 book “On the Origin of Species” [8]. These are found in its fourth chapter, entitled “Natural selection”, and are summarized below. Evolution is a response to changing environments. Thus, certain morphological, physi ...
Objective 4 - Shiner ISD
... Natural Selection -‐ the basic concept by Charles Darwin is that environmental conditions (or "nature") determine (or "select") how well certain traits of organisms can survive and be passed on; organisms missing these traits might die before reproducing. As ...
... Natural Selection -‐ the basic concept by Charles Darwin is that environmental conditions (or "nature") determine (or "select") how well certain traits of organisms can survive and be passed on; organisms missing these traits might die before reproducing. As ...
Evolution

Evolution is change in the heritable traits of biological populations over successive generations. Evolutionary processes give rise to diversity at every level of biological organisation, including the levels of species, individual organisms, and molecules.All of life on earth shares a common ancestor known as the last universal ancestor, which lived approximately 3.5–3.8 billion years ago. Repeated formation of new species (speciation), change within species (anagenesis), and loss of species (extinction) throughout the evolutionary history of life on Earth are demonstrated by shared sets of morphological and biochemical traits, including shared DNA sequences. These shared traits are more similar among species that share a more recent common ancestor, and can be used to reconstruct a biological ""tree of life"" based on evolutionary relationships (phylogenetics), using both existing species and fossils. The fossil record includes a progression from early biogenic graphite, to microbial mat fossils, to fossilized multicellular organisms. Existing patterns of biodiversity have been shaped both by speciation and by extinction. More than 99 percent of all species that ever lived on Earth are estimated to be extinct. Estimates of Earth's current species range from 10 to 14 million, of which about 1.2 million have been documented.In the mid-19th century, Charles Darwin formulated the scientific theory of evolution by natural selection, published in his book On the Origin of Species (1859). Evolution by natural selection is a process demonstrated by the observation that more offspring are produced than can possibly survive, along with three facts about populations: 1) traits vary among individuals with respect to morphology, physiology, and behaviour (phenotypic variation), 2) different traits confer different rates of survival and reproduction (differential fitness), and 3) traits can be passed from generation to generation (heritability of fitness). Thus, in successive generations members of a population are replaced by progeny of parents better adapted to survive and reproduce in the biophysical environment in which natural selection takes place. This teleonomy is the quality whereby the process of natural selection creates and preserves traits that are seemingly fitted for the functional roles they perform. Natural selection is the only known cause of adaptation but not the only known cause of evolution. Other, nonadaptive causes of microevolution include mutation and genetic drift.In the early 20th century the modern evolutionary synthesis integrated classical genetics with Darwin's theory of evolution by natural selection through the discipline of population genetics. The importance of natural selection as a cause of evolution was accepted into other branches of biology. Moreover, previously held notions about evolution, such as orthogenesis, evolutionism, and other beliefs about innate ""progress"" within the largest-scale trends in evolution, became obsolete scientific theories. Scientists continue to study various aspects of evolutionary biology by forming and testing hypotheses, constructing mathematical models of theoretical biology and biological theories, using observational data, and performing experiments in both the field and the laboratory. Evolution is a cornerstone of modern science, accepted as one of the most reliably established of all facts and theories of science, based on evidence not just from the biological sciences but also from anthropology, psychology, astrophysics, chemistry, geology, physics, mathematics, and other scientific disciplines, as well as behavioral and social sciences. Understanding of evolution has made significant contributions to humanity, including the prevention and treatment of human disease, new agricultural products, industrial innovations, a subfield of computer science, and rapid advances in life sciences. Discoveries in evolutionary biology have made a significant impact not just in the traditional branches of biology but also in other academic disciplines (e.g., biological anthropology and evolutionary psychology) and in society at large.